Asian Giant Tortoise

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
The Asian Giant Tortoise, the largest tortoise in mainland Asia, has been reintroduced into the Zeliang Community Reserve in Peren district, Nagaland. Local youth groups have been engaged as “tortoise guardians” to ensure protection.
About Asian Giant Tortoise
- Scientific name:Manouriaemysphayrei
- Common name: Asian Giant Tortoise / “Small elephants of the forests” (due to their role in forest ecology).
- Lineage: Among the oldest tortoise lineages in the world; display unique nesting behaviour similar to crocodilians, where they protect eggs and regulate incubation temperatures.
- Appearance: Hatchlings are greyish-brown, becoming charcoal-colored in adulthood.
- Diet: Bamboo shoots, tubers, soft vegetation, some invertebrates, and frogs.
Habitat & Distribution
- Habitat: Tropical and subtropical evergreen hill forests.
- Range in India: Northeastern states – Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Assam.
- Global distribution: Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia.
Ecological Role
- Seed Dispersal: Helps regenerate forests by dispersing seeds.
- Scavenging: Cleans forest floor by feeding on decomposed organic matter.
Threats
- Hunting and collection for consumption.
- Illegal trade (pets and exotic meat).
- Habitat destruction due to shifting cultivation, deforestation, and infrastructure projects.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
Conservation Efforts
- Captive Breeding & Assurance Colonies for population recovery.
- Reintroduction Programmes like the recent one in Nagaland.
- Community-based conservation with active participation of locals as guardians.
- Field Surveys to monitor population health and habitat conditions.
Indian Star Tortoise
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant conservation achievement under the Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP), 340 Indian Star Tortoises were successfully released into the wild at Jogapur Reserve Forest, located in Chandrapur district, Maharashtra.
Indian Star Tortoise (Geochelone elegans)
- IUCN Status:Vulnerable
- CITES Listing:Appendix I
- Protection under Indian Law:Schedule I, Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
Habitat & Range:
- Native to Northwest India, Southern India, and Sri Lanka
- Prefers arid and semi-arid ecosystems including scrublands, dry forests, grasslands, and semi-deserts
Key Characteristics:
- Recognizable by the radiating star-like patterns on its domed shell
- Faces high poaching pressure due to demand in the illegal exotic pet trade
- Exhibits crepuscular behavior (most active during dawn and dusk)
- Primarily herbivorous, consuming grasses, flowers, and leafy vegetation
Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP): A Conservation Initiative
- Launched: Late 2024; witnessed a major release event in April 2025
- Implemented By: Maharashtra Forest Department in collaboration with RESQ Charitable Trust
Objectives:
- Rescue and rehabilitate illegally trafficked tortoises and turtles
- Facilitate safe reintroduction into natural habitats through:
- Medical treatment
- Acclimatization to wild conditions
- Biometric tracking for post-release monitoring
- Raise public awareness via community engagement and school outreach
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed an innovative “self-actuating” drug delivery system that targets rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by delivering therapeutic agents only when needed. This approach offers a revolutionary alternative to conventional systemic treatments.
About Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Definition: RA is a chronic autoimmune and inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, particularly the joints, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Hands, wrists, and knees — often multiple joints simultaneously.
- Symptoms:
- Inflammation of joint lining
- Chronic pain and joint deformity
- Unsteadiness or balance issues
- May affect lungs, heart, and eyes
- Cause: The exact cause remains unknown, but it involves an immune response attacking the body’s own tissues.
- Traditional Treatment:
- Involves Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate
- Requires frequent dosing
- May lead to systemic side effects and inefficient drug retention
Breakthrough: Self-Actuating Drug Delivery System
Key Features:
- Targeted Drug Release: Releases medication only in response to biochemical signals in the inflamed synovial environment of RA-affected joints.
- Precision and Safety: Reduces side effects by limiting drug release to flare-ups, minimizing exposure to unaffected areas.
- Main Drug Used: Methotrexate, a widely used anti-rheumatic drug.
Mechanism:
- Microspheres are engineered using polymer-lipid hybrid micro-composites:
- Lipid Component (Soya Lecithin): Ensures high drug encapsulation efficiency.
- Polymer Component (Gelatin): Reacts to Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) — enzymes present during RA inflammation.
- Action:
- Enzymes like MMP-2 and MMP-9 increase during RA flare-ups.
- These enzymes cleave the gelatin, triggering controlled, pulsatile release of methotrexate.
- Outcome in Animal Studies:
- Reduced joint swelling and cartilage damage
- Promoted joint repair
- Improved drug bioavailability and retention in joints
Significance
- Improved Patient Outcomes:
- Long-lasting relief with fewer doses
- Reduced systemic toxicity
- Personalized therapy based on inflammation levels
- Enhanced joint function and slower disease progression
- Research Publication: The findings were published in the journal Biomaterial Advances.
Wider Applications
- Potential Use in:
- Other inflammatory conditions like synovitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Veterinary medicine for arthritis in animals
- Regenerative medicine and personalized drug delivery
Aircraft Turbulence

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A passenger died and many were injured when a Singapore Airlines’ Boeing 777 headed from London to Singapore “severe turbulence” en route.
What is the Aircraft Turbulence
- Turbulence means disruption of airflow over the wings of an aeroplane, which causes it to enter irregular vertical motion.
- These pockets of disturbed air can have many causes, most obviously the unstable weather patterns that trigger storms.
- It is caused by the relative movement of disturbed air through which an aircraft is flying.
There are at least seven kinds of turbulence that an aircraft can run into:
- Wind Shear: It happens when there is a sudden change in wind direction, whether vertically or horizontally.
- Typically occurs close to thunderstorms, jet streams, etc.; tricky for pilots as tailwinds suddenly change to headwinds or vice versa.
- Frontal: Created in the frontal zone when warm air is lifted by a sloping frontal surface and friction between opposing air masses.
- Most palpable when warm air is moist; intensity increases with thunderstorms. Most commonly close to thunderstorms.
- Convective: When land surface temperature rises, the air above the ground heats up and rises, creating air pockets around it.
- Convection currents cause difficulties during approach as they tend to affect the rate of descent.
- Wake: It forms behind an aircraft when it flies through air-creating wingtip vortices.
- Mechanical: This type of turbulence occurs when tall solid objects such as mountains or highrise constructions disrupt the normal airflow, causing the air for planes to fly through to become dirty.
- Clear Air: It occurs when an aircraft crosses from one air mass to another, which has a different direction.
- Clear air turbulence could also happen when an aircraft moves out of a jet stream. Clear air turbulence is mainly caused by wind or jet streams.
- Mountain View: It is one of the most severe; these are oscillations that form on the downwind side of mountains when strong winds flow towards mountains in a perpendicular fashion.
- Aircraft tracking perpendicularly across, or downwind of a mountain, may experience a sudden loss of altitude followed by a sudden reduction in airspeed.
Are turbulence incidents dangerous?
- It depends on their nature and intensity.
- Aircraft undergo some form of turbulence on a regular basis and pilots are trained to deal with these.
- However, there have been several instances when turbulence has brought down modern jetliners.
Even in these cases, while intense turbulence has been the main cause of an accident, several other factors — such as lack of proper training, and poor dissemination of weather or wind-related information — have contributed to the accident.
Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM)

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India is working with like-minded countries to promote regulated tourism in Antarctica as a steady increase in the number of tourists threatens to harm the fragile ecology in the White Continent.
About the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting:
- The Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) is the annual meeting of the Parties to the 1959 Antarctic Treaty.
- The meeting serves as a platform for the exchange of information, discussion of common interests, and promotion of the principles and purposes of the Antarctic Treaty.
- The first ATCM was held in 1961, and initially occurred every other year, though the frequency has since increased.
- During the ATCM, representatives of the member countries address various issues related to Antarctica, such as environmental protection, scientific research, and tourism regulation.
- Key agenda items include strategic planning for sustainable management of Antarctica and its resources, policy, legal, and institutional operations, and biodiversity prospecting.
- The ATCM is organized by the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and was established in 2004.
- The Secretariat is responsible for facilitating communication and information exchange among the parties involved in the Antarctic Treaty System.
- In recent years, the ATCM has been hosted by various countries, with India hosting the 46th meeting in 2024.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India, through the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) and the Secretariat of the Antarctic Treaty will jointly organise the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM 46) from 20 to 30 May 2024 at the Lulu Bolgatty International Convention Centre (LBICC) in Kochi, India.
What is the Antarctic Treaty?
- The Antarctic Treaty is an international agreement that aims to preserve and protect the Antarctic continent and its surrounding waters for scientific research and peaceful purposes.
- Signed on December 1, 1959, by 12 countries, the treaty came into effect on June 23, 1961.
- The treaty establishes Antarctica as a natural reserve devoted to scientific research, and it designates the area south of 60°S latitude as a region free of military and nuclear activities.
Key aspects of the treaty include:
-
- Freedom of scientific research and exploration, with cooperation among signatory nations
- Exchange of scientific information and personnel between treaty member nations
- Prohibition of military activities, such as the establishment of military bases or weapons testing
- Prohibition of nuclear explosions and disposal of radioactive waste
- Acknowledgement that no new territorial claims can be made on the continent
- Designation of Antarctica as a "Special Conservation Area" to protect its ecosystems and native species
- Currently, 54 countries have ratified the Antarctic Treaty, and 29 of these countries have Consultative Party status.
- Consultative Parties have the right to participate in decision-making processes related to the management and governance of the Antarctic region, while Non-Consultative Parties are encouraged to engage in scientific research and exchange information.
- On 12 September 1983, India became the fifteenth Consultative Member of the Antarctic Treaty.
- It participates in the decision-making process along with the other 28 Consultative Parties to the Antarctic Treaty.
- India’s first Antarctic research station, Dakshin Gangotri, was established in 1983.
- At present, India operates two year-round research stations: Maitri (1989) and Bharati (2012).
- The permanent research stations facilitate Indian Scientific Expeditions to Antarctica, which have been ongoing annually since 1981.
- In 2022, India enacted the Antarctic Act, reaffirming its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
Taam Ja' Blue Hole

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have uncovered a massive sinkhole off the coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
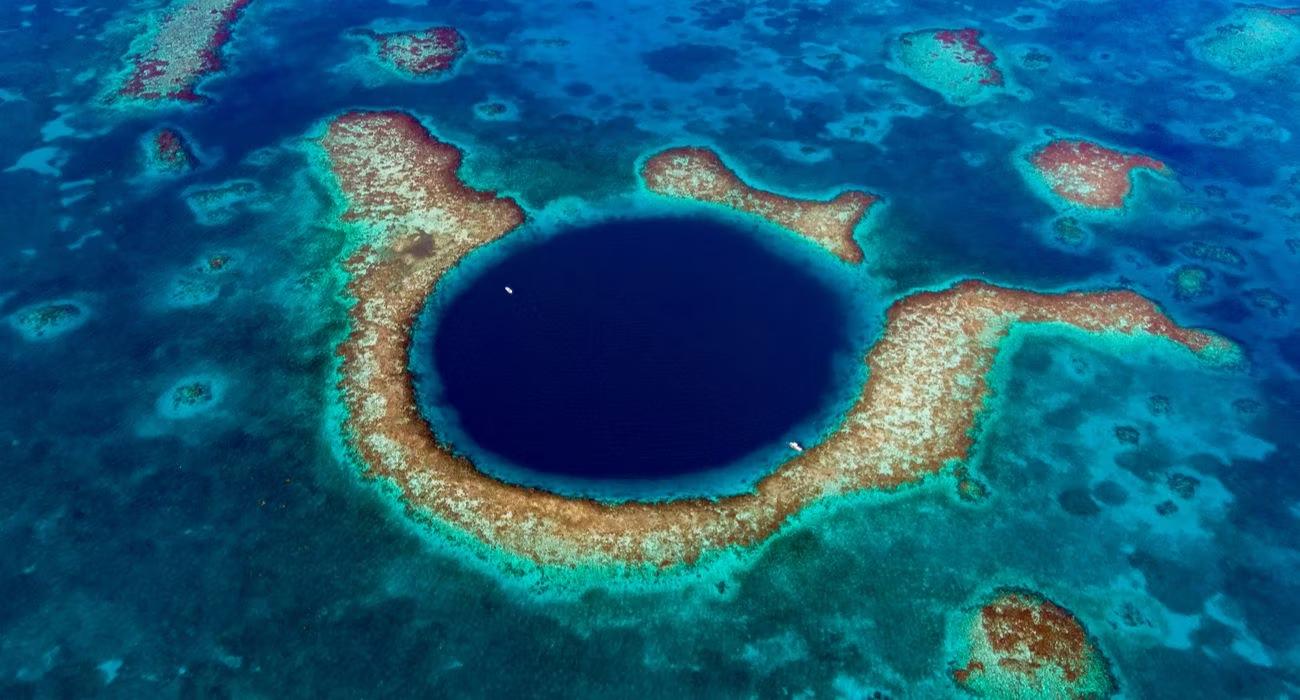
What is Taam Ja' Blue Hole?
- Taam Ja' Blue Hole is the world's deepest known underwater sinkhole, recently discovered in Chetumal Bay off Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula.
- The blue hole extends approximately 420 meters (1,380 feet) below sea level, making it significantly deeper than the previous record holder, the Dragon Hole in the South China Sea.
- The nearly circular sinkhole covers an area of around 13,660 square meters and features steep sides covered in biofilms, sediments, limestone, and gypsum ledges.
- Named "Taam Ja'," meaning "deep water" in the Mayan language, the blue hole was initially discovered by a local diver in 2003 but only recently gained scientific attention.
- Further research is ongoing to explore the unique marine life and geological features within this remarkable underwater cavern.
What is a Blue Hole?
- A blue hole is a large, underwater sinkhole or cavern with a submerged opening that appears dark blue from above due to the depth and clarity of the water.
- The name "blue hole" originates from the striking contrast between the dark blue, deep water within the hole and the lighter blue shallower water surrounding it.
- These unique geological formations are typically formed through a combination of erosion and dissolution of limestone bedrock, resulting in circular or ovular depressions in the seafloor.
- Over time, blue holes can develop distinct ecosystems hosting a variety of marine life, including unique and rare species that have adapted to the specific conditions within these habitats.
- Blue holes can be found in various parts of the world, both in oceanic and inland settings.
- Some famous examples include the Great Blue Hole in Belize, the Dean's Blue Hole in the Bahamas, and the Taam Ja' Blue Hole in Mexico.
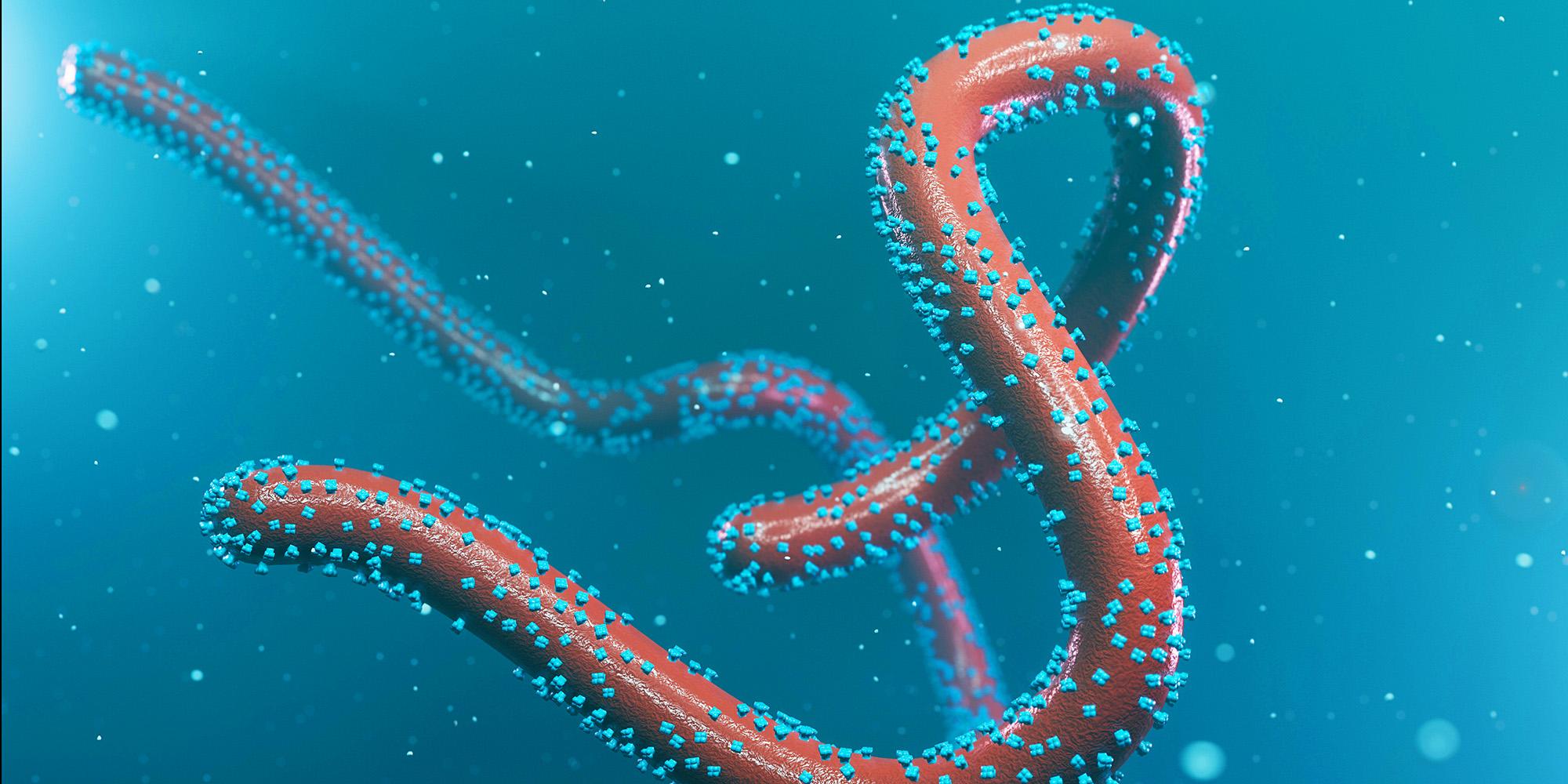
Marburg virus disease (MVD)
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kitum cave in Mount Elgon National Park, Kenya, is known as the world's deadliest cave which may have some really dangerous viruses inside, like Ebola and Marburg.
What is Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)?
- Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg hemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
- It affects both people and non-human primates.
- Marburg and Ebola viruses are both members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus).
- Though caused by different viruses, the two diseases are clinically similar.
- Both diseases are rare and can cause outbreaks with high fatality rates.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%.
- Rousettus aegyptiacus, fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family, are considered to be natural hosts of the Marburg virus.
Transmission:
- Human infection with MVD typically occurs after prolonged exposure to Rousettus bats inhabiting mines or caves.
- The virus can then spread through human-to-human transmission via direct contact with infected bodily fluids, contaminated materials, or broken skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms:
- After an incubation period of 2-21 days, symptoms arise abruptly, including fever, chills, headache, and muscle pain.
- A maculopapular rash may appear around day five, most visible on the chest, back, and stomach.
- Other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, chest pain, sore throat, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, can manifest, with severity increasing to potentially include jaundice, organ dysfunction, severe weight loss, delirium, and massive hemorrhaging.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%, varying between 24% and 88% in past outbreaks.
Treatment:
- There is currently no specific treatment for MVD, but early supportive care involving rehydration and symptom management improves survival rates.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs):
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fever (VHFs) is a group of diseases caused by several distinct families of viruses that affect multiple organ systems in the body.
- These illnesses range from mild to severe and life-threatening, with many having no known cure or vaccine.
- VHFs negatively impact the cardiovascular system and reduce overall bodily function.
Wigner Crystals

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In new peer-reviewed research, physicists from Princeton University have confirmed that electrons don’t even need atoms to party together.
What are Wigner Crystals?
- Wigner Crystals are composed entirely of electrons, unlike the common crystals which are formed by atoms or molecules.
- These negatively charged particles, which are known for their role in electricity and chemical bonding, can, under specific circumstances, arrange themselves into a lattice structure, creating a crystal made purely of electrons.
- The conditions required for the formation of Wigner Crystals are quite stringent.
- They occur at very low electron densities, where the repulsive Coulomb forces between the electrons dominate over their kinetic energy.
- This means that the electrons must be spread out enough so that their mutual repulsion causes them to settle into a fixed pattern, minimizing their potential energy.
- The discovery was made possible by cooling a two-dimensional electron system to near absolute zero and reducing the electron density to a critical level.
- Under these conditions, the electrons crystallized into a lattice, much like the atoms in a solid.
- The visualization of this electron lattice marks a monumental step in our understanding of the quantum phases of matter.
- The implications of this discovery are profound.
- Wigner Crystals could provide insights into the behavior of electrons in low-density environments, such as those found in semiconductors and other electronic materials.
- This could lead to the development of new technologies and materials with unique electronic properties.
- Moreover, the study of Wigner Crystals could shed light on other exotic states of matter and the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics.
- The confirmation of Wigner Crystals underscores the importance of theoretical physics and how ideas that once seemed purely speculative can lead to tangible discoveries.
- The realization of Wigner Crystals opens up a new chapter in the study of condensed matter physics.
- It stands as a bridge between the abstract world of quantum mechanics and the tangible reality of material science.
- As we continue to explore the quantum landscape, Wigner Crystals will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the electron and the intricate dance of particles that constitute the fabric of our universe.
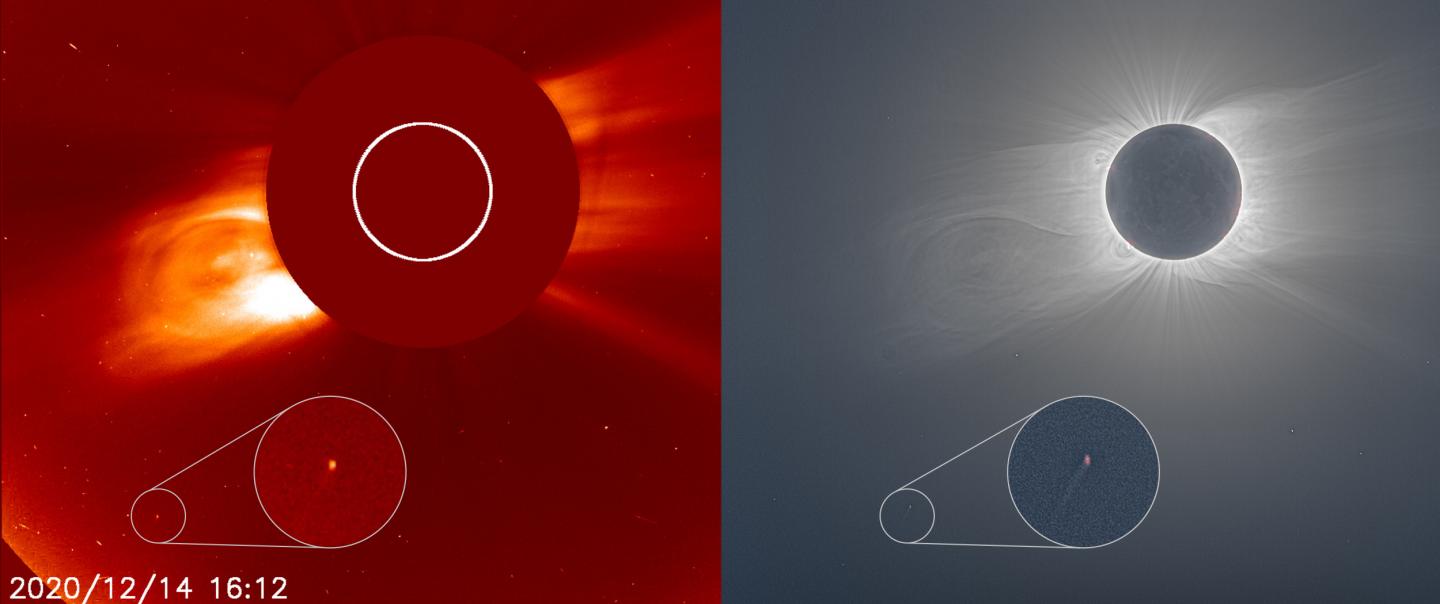
Sungrazing Comet
- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A tiny "sungrazer" comet was discovered, photographed, and destroyed during the recent total solar eclipse — all within 24 hours.
What is a Sungrazing Comet?
- Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion.
- To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion.
- Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles.
- Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons.
- They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles.
- The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also help form the tails. As they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces or gravitational stress.
- In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun.
- Although they don't crash into the solar surface, the sun can destroy them anyway.
- Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group.
- Close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway.
- Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it.
- Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011, is the best-known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer.
- And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun.
What is a Comet?
- A comet is a small celestial body made primarily of ice, dust, and rocky material that orbits the sun in an elongated path.
- When a comet approaches the sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, releasing dust and gas into a glowing coma, or halo, around the comet's nucleus.
- This glowing coma often forms a tail that stretches away from the sun due to the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- Comets are often referred to as "dirty snowballs" or "icy dirtballs" because of their composition.
- They are believed to be remnants from the early formation of the solar system and carry important information about its history.
- Comets can have highly elliptical orbits, sometimes taking thousands or even millions of years to complete a single orbit around the sun.
India initiates Anti-Dumping Probe into Solar Glass Imports from China and Vietnam (TOI)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into the import of solar glass from China and Vietnam following a complaint from domestic players.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff levied on imports from foreign countries when their prices are lower than the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- It's implemented by governments to counteract the practice of "dumping," where foreign goods are sold at unfairly low prices in the domestic market, posing a threat to local businesses.
- The primary objective of anti-dumping duty is to safeguard domestic industries from unfair competition and restore fair trade practices.
- This measure is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to address instances where dumping causes genuine harm to domestic industries.
- To impose anti-dumping duties, governments must provide evidence of dumping, quantify its extent in terms of costs, and demonstrate the resulting injury or threat to domestic markets.
- While aimed at protecting local industries, anti-dumping duties can sometimes lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
About Countervailing Duty (CVD):
- Countervailing duty (CVD) is a type of tariff imposed by a government to offset the adverse effects of import subsidies on domestic producers.
- It serves as an import tax applied by the importing country on subsidised products from abroad.
- CVD is imposed to address situations where foreign governments provide subsidies to their producers, lowering the cost of their goods and potentially disrupting fair competition.
- To prevent the influx of subsidised products into their markets, importing countries levy CVD, effectively neutralising the price advantage enjoyed by these imports.
- The imposition of CVD is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to help maintain fair trade practices among its member countries.
Difference Between Anti-dumping Duty and Countervailing Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is enacted to safeguard domestic markets from the harmful effects of low-priced foreign goods, while CVD targets products benefiting from government subsidies, resulting in artificially low prices.
- The amount of Anti-dumping duty is determined by the margin of dumping, whereas CVD is calculated based on the subsidy value granted to foreign goods.
DoT Unveils 'Sangam: Digital Twin' Initiative (TOI)

- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications has introduced the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative, which aims to transform infrastructure planning and design through innovation and the integration of advanced technologies.
What is Sangam: Digital Twin initiative?
- Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling monitoring, simulation, and analysis for adaptive outcomes.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' consists of two stages:
- The first is exploratory for creative exploration, and
- The second is for the practical demonstration of specific use cases, creating a future blueprint for collaboration in future infrastructure projects.
- The initiative aligns with advancements in communication, computation and sensing over the past decade, fostering a collaborative approach to reshape infrastructure planning and design.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin and next-gen computational technologies to break silos and promote a whole-of-nation approach.
- The new initiative aims to transform ideas into solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualisation and realisation, and fostering advancements in infrastructure.
- Sangam encourages a holistic approach to innovation, uniting stakeholders to harness unified data and collective intelligence.
- It is aimed at creating an ecosystem that maximises the value of technological advancements for development.
- Sangam aims to demonstrate the practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions, providing a model framework for collaboration and a future blueprint for scaling successful strategies in future projects.
- The platform also offers a blog for pre-registered participants to connect, share insights, and engage in discussions.
Significance of Digital Twins:
- Facilitates remote monitoring, making it applicable for use in hazardous operations.
- Enhances predictive capabilities, assisting in making informed policy decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency, thereby ensuring the maintenance of output quality.
- Assists in urban planning by generating various simulations and forecasts.
Alaskapox Claims One Life in US (TOI)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
An elderly man has died from Alaskapox, the first known fatality from the recently discovered virus.
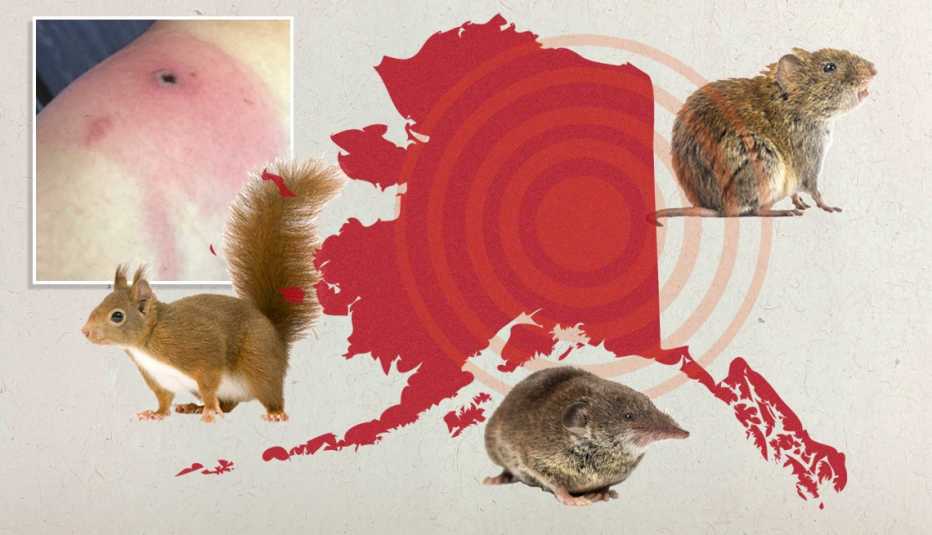
What is Alaskapox?
- Alaskapox is caused by orthopoxvirus, a family of brick-shaped viruses that can infect both animals and humans, leading to skin lesions or pox.
- The virus was first identified in a woman living near Fairbanks, Alaska, and has since been primarily detected in small mammals like red-backed voles and shrews.
- However, domestic pets such as dogs and cats may also be carriers of the virus.
What are the symptoms of Alaskapox?
- Symptoms of Alaskapox include the development of one or more bumps or pustules on the skin, accompanied by joint or muscle pain and swollen lymph nodes.
- While the majority of the seven known human cases in Alaska over the past nine years have experienced mild illnesses that were resolved without intervention, the virus poses a greater threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
How is Alaskapox Transmitted?
- Transmission of Alaskapox is believed to occur through direct contact with infected animals.
- Unlike some of its orthopoxvirus relatives, there have been no documented instances of Alaskapox spreading from person to person.
- Though it's not clear how Alaskapox is transmitted, researchers say that it may be zoonotic meaning it can jump from animals to humans.
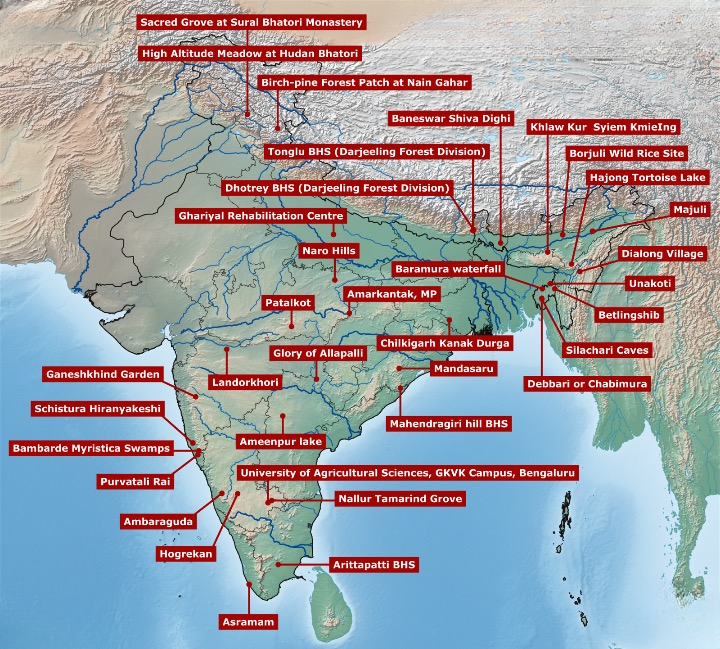
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
NAL Successfully Tested High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) at Challakere, Karnataka (TOI)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from city-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab, achieved a breakthrough by successfully testing an unmanned aerial vehicle called High-Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS) at Chitradurga's Challakere in Karnataka.
News Summary:
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has achieved a milestone with the successful testing of an unmanned aerial vehicle known as the High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) in Challakere, Karnataka.
- This innovative system, measuring 5 meters in length with an impressive 11-meter wingspan and weighing 23 kg, soared to an altitude of approximately 3 km and maintained its position for an impressive duration of eight hours.
- A comprehensive series of tests is slated, with the ultimate goal of developing a full-fledged aircraft boasting a remarkable 30-meter wingspan comparable to a Boeing 737 by the year 2027.
- This advanced craft is anticipated to ascend to an impressive altitude of 23 km and remain airborne for a remarkable period of at least 90 days.
- NAL's ambitious agenda includes the design and construction of various components essential for the HAPS, including propellers, battery management systems, carbon-composite airframes, flight-control systems, and high-powered electric motors capable of withstanding extreme temperature variations.
- Additionally, in a separate endeavour, a Bengaluru-based private company recently conducted the inaugural test flight of a solar-powered, long-endurance drone, achieving an impressive flight duration of 21 hours.
About High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS):
- Since the 1990s, numerous global initiatives have been undertaken to explore the potential applications of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites, also known as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS).
- Positioned above 20 km altitude in the stratosphere, these unmanned aircraft are designed for exceptionally long-duration flights, spanning months or even years.
- HAPS encompass various aircraft types, including airplanes, airships, and balloons.
Benefits/Advantages of HAPS:
- These solar-powered vehicles bridge the gap between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) operating in lower altitudes and traditional satellites in space.
- They offer a wide array of applications, including telecommunications, emergency/public safety communications, intelligent transportation systems, maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and land border control.
- Compared to ground-based communication networks, HAPS can cover larger areas with minimal interference and facilitate data transfer between satellites and ground-based telecom networks.
- Unlike traditional satellites, which are costly to construct and launch, HAPS are more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
- It has both military and civilian applications, including intelligence, surveillance, telecommunication, and disaster response.
- The technology offers lower latency and can connect to multiple ground stations.
Significance for India:
- In India, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced in 2022 its collaboration with a startup company to develop a "futuristic" high-altitude pseudo satellite.
- Given India's extensive land borders stretching approximately 15,000 km and a coastline spanning 7,500 km, securing these borders is paramount, necessitating diverse solutions.
- Hovering at the Earth's atmospheric edge, HAPS offer valuable services for efficient border surveillance, tracking enemy movements deep into territories or seas, and conducting round-the-clock missions.
- Equipped with advanced optical and infrared cameras, state-of-the-art sensors, and other sophisticated technology, these aerial platforms are ideal for border patrolling, target tracking, maritime surveillance, navigation, and even missile detection.
- China's Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), a state-owned aerospace and defense conglomerate, has been actively developing various HAPS platforms for surveillance purposes.
- In 2018, it successfully tested the solar-powered Morning Star drone, renowned for its prolonged airborne endurance.
Israel discovers 6-million-year-old giant underwater canyon of Messinian Event (TOI)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Israel Geological Survey announced recently that Israeli geologists discovered a huge underwater canyon on the bottom of the Eastern Mediterranean that was formed about 6 million years ago.
What is Messinian Event?
- The Messinian Event, also referred to as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC).
- It marks a significant geological occurrence during which the Mediterranean Sea experienced a cycle of partial or near-complete desiccation, making it one of the most severe ecological crises in Earth's history.
- This event unfolded approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and persisted until around 5.3 MYA.
- The process began with the severance of the connection between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This disconnection resulted from a combination of reduced sea levels globally and the collision of the European and African plates, causing the land to rise.
- Consequently, the Mediterranean experienced significant evaporation, as its evaporation rate exceeded its precipitation rate.
- Without a substantial influx of water from the Atlantic, the sea began to evaporate rapidly.
- During this period, a vast underground canyon formed, with rivers cutting deep into the basin floor, creating a canyon much larger than the Grand Canyon, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters (6562 feet).
- As the Mediterranean water evaporated, salt deposits, primarily composed of Halite and Gypsum, accumulated on the basin floor, some reaching depths of 800 meters (2,500 feet).
- Despite the rapid evaporation, salt deposition did not keep pace, resulting in an increase in water salinity.
- The heightened salinity levels made the Mediterranean inhospitable to marine life, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Eventually, the sea dried up almost entirely, culminating in the Zanclean flood when the Atlantic Ocean reclaimed the basin.
What is Deep-sea Canyon?
- Deep-sea canyons, such as those formed during the Messinian Event, are steep valleys carved into the seafloor of the continental slope, extending onto the continental shelf.
- These canyons vary in size and shape and have been sculpted by various erosional processes, including river flows during periods of low sea levels, mudslides, debris flows, and turbidity currents.
INS Sandhayak - the Indian Navy’s First Survey Vessel Large (SVL) Ship (TOI)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Defense minister Rajnath Singh commissioned survey vessel INS Sandhayak into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard recently.
About INS Sandhayak:
- INS Sandhayak stands as the first unit in a series of four Survey Vessel (Large) ships under construction at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Its primary mission is to conduct thorough coastal and deep-water Hydrographic Surveys, focusing on Port and Harbour approaches, navigational channels, and routes.
- The operational scope extends to maritime limits, encompassing the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and extended continental shelf.
Features:
-
- The vessel is equipped to gather oceanographic and geophysical data, serving the needs of both defense and civil applications.
- In a secondary role, it provides limited defense capabilities and can function as a hospital ship during wartime or emergencies.
- Cutting-Edge Technology:
-
- Equipped with advanced hydrographic tools, including a Data Acquisition and Processing System, Autonomous Underwater Vehicle, Remotely Operated Vehicle, DGPS Long-range positioning systems, and Digital side-scan sonar.
- Performance Specifications:
-
- Powered by two diesel engines, INS Sandhayak boasts a speed capability exceeding 18 knots.
- With a length of 110 meters and a displacement of 3400 tons, the vessel maintains an indigenous content exceeding 80 per cent by cost.
- Historical Continuity:
-
- This ship has been re-incarnated in its current form from the previous Sandhayak, decommissioned in 2021.
Digital Detox for Responsible Gaming (TOI)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka government recently said it would launch a 'Digital Detox' initiative in collaboration with the All India Game Developers Forum (AIGDF), with special emphasis on gaming and social media.
What is Digital Detox?
- A digital detox entails voluntarily refraining from using digital devices like smartphones, computers, and social media platforms for a defined period.
- This period can range from a few hours to as long as a week or even a month.
- Research indicates that approximately 25% of smartphone owners aged 18 to 44 cannot recall the last time they were separated from their phones.
Benefits:
- Overcoming Technology Addiction: Studies reveal that around 61% of individuals acknowledge their addiction to the internet and digital screens.
- A digital detox aids in combating this addiction.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Disconnecting from technology can alleviate stress and anxiety, thereby fostering improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Productivity and Creativity: Taking a break from continuous digital engagement bolsters focus and concentration, leading to heightened productivity and creativity.
- Improved Sleep: Excessive screen time has been linked to poor sleep quality. A digital detox helps in promoting better sleep by reducing exposure to blue light and stimulating content.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Reducing online time allows for more face-to-face interactions, nurturing better communication skills and social connections.
Challenges:
- Feelings of Disconnection: Detox participants may feel disconnected from friends and family members.
- Fear of Missing Out: Participants may experience FOMO (fear of missing out) or anxiety about missing important information.
- Boredom or Restlessness: Detoxes may lead to feelings of boredom or restlessness.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety or boredom.
Way forward:
- Start Small: Initiate the detox with shorter periods and gradually extend the duration.
- Inform Others: Notify friends and family about the detox to avoid misinterpretations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Utilize detox time for activities like reading, spending time outdoors, or exercising.
- Minimize Notifications: Turn off device notifications and store them out of sight.
- Reward Progress: Offer yourself incentives for achieving detox goals.
Conclusion
Digital dependence can contribute to mental health issues, shorter attention spans, and strained interpersonal relationships. While technology offers convenience and connectivity, excessive screen time exacts a toll. A digital detox presents an opportunity to enhance mental and physical well-being, as well as nurture healthier relationships. With proper planning and commitment, a successful and fulfilling detox experience is achievable.
5 Wetlands Added to The Global List of Wetlands of International Importance under Ramsar Convention (TOI)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day, five more wetlands in India got the tag of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, making it the fourth largest country in terms of the number of sites on the list.
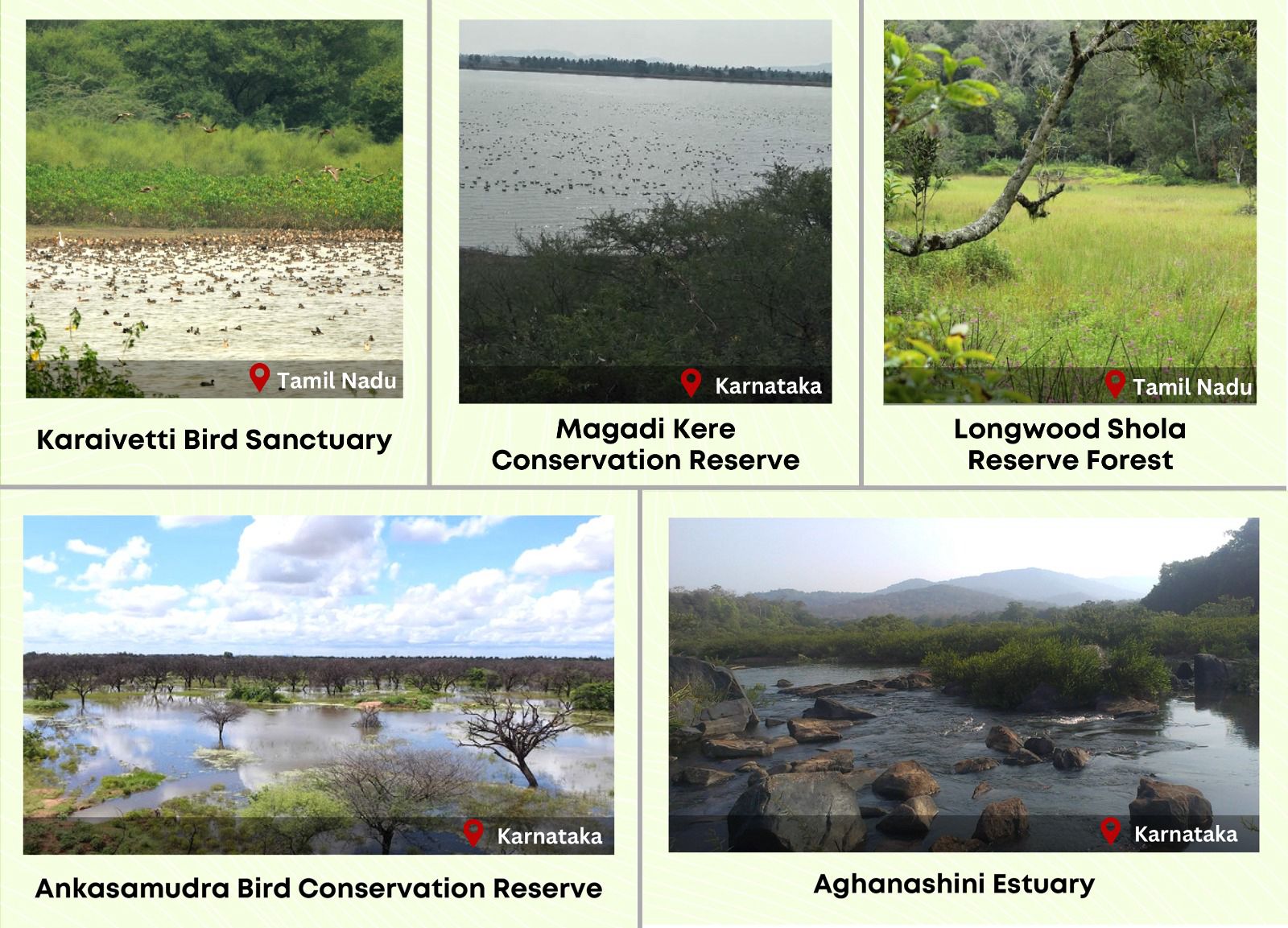
About the New Ramsar sites:
- The five newly added Indian sites in the list are Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve and Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka.
- In India, Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar sites (16) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary is one of the largest inland wetlands of Tamil Nadu and is a significant source of groundwater recharge for the area.
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- Karaivetti has one of the largest congregations of waterbirds in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest derives its name from the Tamil word, "Solai", which means ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
- As many as 14 out of 26 endemic bird species of the Western Ghats are found in these wetlands.
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve is a human made Village Irrigation Tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 98.76ha.
- It is an ecologically important wetland, rich in biodiversity, comprising over 210 species of plants, mammal species, reptiles, birds etc.
- It supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of Painted Stork and Black-headed Ibis.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Aghanashini Estuary is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods to families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (??Karnataka): Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely the Common pochard and River tern and four near-threatened species, namely the Oriental Darter Black-headed Ibis Woolly-necked Stork and Painted Stork.
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India.
- The wetland is a designated Important Bird Area (IBA) and is also listed as a priority area for conservation in India.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention was signed on 2nd February 1971 to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed in 1971, and places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The World Wetlands Day, celebrated on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for human prosperity and a healthy planet.
Delhi HC Upholds Validity of Anti-profiteering Provision of CGST Act (TOI)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court has upheld the constitutional validity of the anti-profiteering clause in the GST law, which mandates companies to pass on the benefit of lower taxes and input tax credits to consumers.
What is an ‘Anti-profiteering’ Activity?
- Any reduction in the rate of GST tax on any supply of goods or services or the benefit of input tax credit should have been passed on to the recipient by way of a commensurate reduction in prices.
- The wilful action of not changing the final price of the good or service by various means, despite the reduction in the rate of the tax for that particular good or service, amounts to “profiteering”.
How is the Anti-profiteering Mechanism Under the CGST Act?
- CGST mandate a 3-tier structure for investigation and adjudication of the complaints regarding profiteering.
- a) National Anti-profiteering
- b) Authority Directorate General of Safeguards
- c) State-level screening committees and standing committee
How Does the Screening Committee and Standing Committee Work?
- GST council may constitute a standing committee, having members from both state and central government.
- Every state shall constitute one state-level screening committee.
- It will have one member from the state government and one member from the central government as nominated by the respective appropriate authority.
- The complaints or issues of local nature will be first examined by the screening committee.
- State-level screening and standing committee will examine the complaint and determine the prime facie evidence to support the validity of the complaint.
- If any committee satisfies that the supplier has contravened section 171 of the CGST Act, the case shall be transferred to DG Safeguards for further investigation.
- The committees shall complete the investigation within a period of a month from the date of the receipt of the application.
What is the Role of DG Safeguards in the Anti-profiteering Mechanism?
- DG safeguards are the main investigation arm in the anti-profiteering mechanism.
- It can summon the interested parties make inquiries or call the relevant documents.
- It can seek help from technical experts in the due course of investigation.
- DG Safeguards shall complete the investigation within a period of three months from the date of receipt of the report from either screening or standing committee.
- The period can be extended for another three months.
Who Can File the Complaint Against Profiteering?
- Any consumer or organisation experiencing a non-reduction in the price of the goods or service despite the reduction in the rate of GST can file a complaint with proper evidence.
- Any supplier, trader, wholesaler or retailer, who could not get the benefit of input tax credit on account of a reduction in the rate of GST, can also file the complaint with proper evidence.
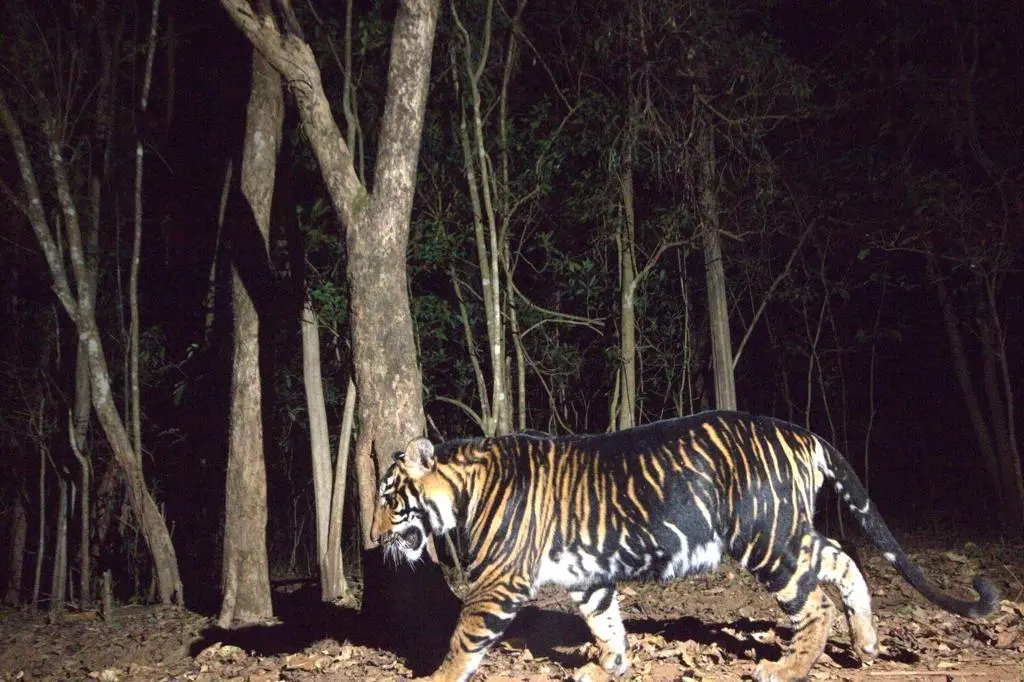
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
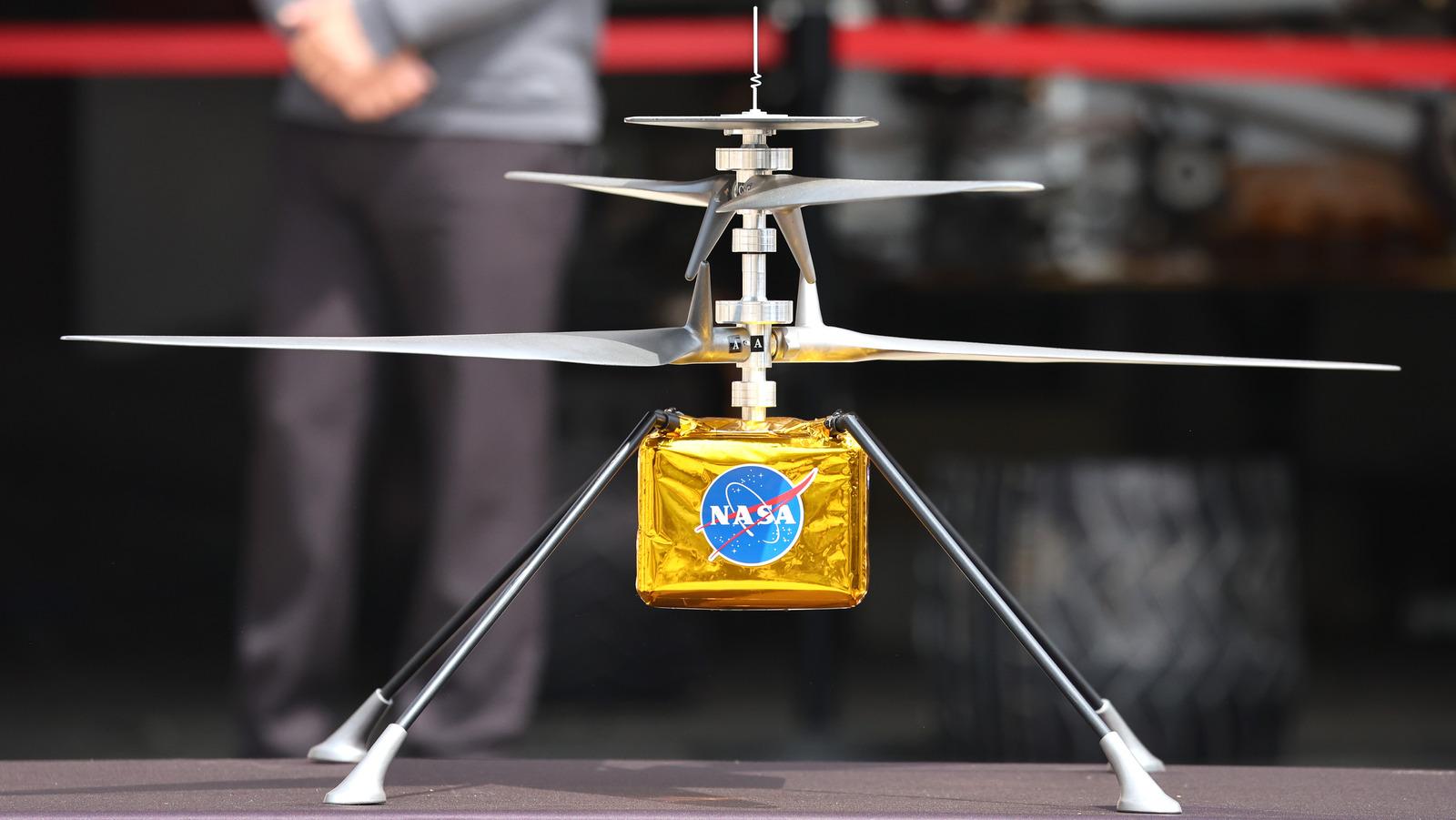
After tiny chopper Ingenuity, NASA planning to send giant fixed-wing plane Maggie to Red Planet (TOI)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In its pursuit of extensively exploring Mars to find signs of water, Nasa is considering a proposed idea to send a giant fixed-wing plane to the Red Planet.
What is Ingenuity Mars Helicopter?
- The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is a small, autonomous aircraft that is part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- It was deployed to the surface of Mars on April 3, 2021, and made its first powered, controlled flight on another planet on April 19, 2021.
- Ingenuity is a technology demonstration mission, and its main goal is to show that powered flight is possible on Mars.
- The helicopter has four carbon-fiber blades creating enough lift to overcome the thin Martian atmosphere.
- It is powered by solar cells and can fly for up to 90 seconds at a time.
- Since its first flight, Ingenuity has completed 72 flights, far exceeding its original planned five flights.
- It has flown a total of 17 km and reached an altitude of 24 m.
- The helicopter has also helped to scout ahead for the Perseverance rover, taking images and collecting data from areas that the rover cannot reach.
- Ingenuity's success has paved the way for future aerial exploration of Mars.
- Future helicopters could be used to scout for landing sites, study the Martian surface in more detail, and even carry small payloads of scientific instruments.
About Perseverance Rover:
- Perseverance is a robotic rover exploring Jezero Crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- Launched on July 30, 2020, it successfully landed on February 18, 2021, making it the most sophisticated and heaviest rover ever sent to Mars.
Mission Highlights:
- Seeking signs of ancient microbial life: Perseverance is equipped with several instruments to analyze Martian rocks and soil for potential signs of past life.
- Collecting rock samples: The rover drills and collects rock samples that will be cached on Mars for potential return to Earth by future missions.
- Testing technology for future missions: Perseverance is demonstrating new technologies that will be crucial for future human exploration of Mars, such as the MOXIE instrument that produces oxygen from the Martian atmosphere and the Ingenuity helicopter, the first powered aircraft to fly on another planet.
- Perseverance Achievements:
- Finding evidence of an ancient lake in Jezero Crater that may have been habitable for microbial life.
- Collecting the first rock samples from Mars that will be returned to Earth.
- Demonstrating the feasibility of using a helicopter on Mars (the Ingenuity helicopter hitched a ride with Perseverance).
India celebrates 76th Army Day with pride and gratitude (TOI)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Droupani Murmu conveyed their warm wishes to Indian Army personnel on the occasion of Army Day.
Why is Army Day celebrated?
- On January 15, KM Cariappa took charge of the Indian Army from General Sir Francis Roy Bucher in 1949, who was the last British-serving Army chief.
- KM Cariappa became the first-ever Indian General to command the Army in its long eventful journey.
- Later, General Cariappa also became the Field Marshal of India.
- KM Cariappa, who is popularly known as Kipper, received King's commission in 1919 and was part of the first group of Indian cadets at the Royal Military College in Sandhurst, UK.
- He was the first Indian who attended Staff College in Quetta and the first one to command a battalion.
- In 1942, Cariappa raised the 7th Rajput Machine Gun which was later known as 17 Rajput.
- He was conferred with Field Marshal Rank in 1986 and passed away in 1993 at the age of 94.
Indian Army Day 2024: Theme
- The theme of the Indian Army Day 2024 is “In Service of the Nation”.
- The theme of 2024 focuses on the main essence of the Army.
- This year’s theme also resembles the motto of the Indian Army, “Service Before Self.”
- This year marks the 76th Army Day.
- The parade will be held under the command of the Army's Central Command, which is headquartered in Lucknow.
Indian Army Day 2024: Significance
- Indian Army Day is also known as Bhartiya Sena Diwas.
- The day promises a grand celebration to honour the valour and service of the Army officers.
- It also proves to be a day dedicated to spreading awareness and enthusiasm among the youth of the nation to join the Bhartiya Sena and serve the country selflessly.
- Army Day is dedicated to appreciating and acknowledging the sacrifice and dedication of the Indian Army towards protecting the country from the illegal invasion of enemies and attacks.
Indian Army Day 2024: History
- The Indian Army was established on 1 April 1895 by the British.
- Initially, the Indian Army was known as the Royal Indian Army.
- India attained Independence on 15 August 1947.
- On 15 January 1949, the first Commander-in-Chief of India General K.M. Cariappa took over the rule of British Army Official General Sir Francis Roy Bucher. Since then, this historic moment has been celebrated as Bhartiya Sena Divas.
- India is following the tradition of celebrating this grand day with great zeal and patriotism.
- Since 15 January 1949, India has been self-reliant in the field of defence.
Article 30 Not Intended To Ghettoise Minorities, Minority Institution Can Include Others In Administration: Supreme Court In AMU Case Hearing (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent observation, the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, highlighted that the right granted to religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer their educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the constitution was not intended to "ghettoise" them.
What is Article 30 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution states the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- It says: “All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.”
When was Article 30 adopted?
- Article 30 was adopted on December 8, 1948.
Features of Article 30 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 30 of the Indian constitution consists of provisions that safeguard various rights of the minority community in the country keeping in mind the principle of equality as well.
- Article 30(1) says that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 30(1A) deals with the fixation of the amount for the acquisition of property of any educational institution established by minority groups.
- Article 30(2) states that the government should not discriminate against any educational institution on the ground that it is under the management of a minority, whether based on religion or language while giving aid.
The debate around Article 30:
- On December 8, 1948, the Constituent Assembly debated the need for imparting primary education in one's mother tongue.
- One of the members of the Assembly moved an amendment to restrict the scope of this article to linguistic minorities.
- He argued that a secular state should not recognise minorities based on religion.
- Another member of the Assembly proposed to guarantee linguistic minorities the fundamental right to receive primary education in their language and script.
- He was concerned about the status of minority languages, even in regions which had a significant minority population.
- The Constituent Assembly rejected the proposals.
What is Article 29 of the Indian Constitution?
- Both Article 29 and Article 30 guarantee certain rights to minorities.
- Article 29 protects the interests of minorities by making a provision that any citizen/section of citizens having a distinct language, script or culture has the right to conserve the same.
- Article 29 mandates that no discrimination would be done on the grounds of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
Concept of Minority in the Indian Constitution:
Religious minorities:
- While Article 30 and Article 29 of the Constitution do not specify 'minorities' in India, it is classified into religious minorities and linguistic minorities.
Religious Minorities in India:
- The basic ground for a community to be nominated as a religious minority is the numerical strength of the community.
- For example, in India, Hindus are the majority community.
- As India is a multi-religious country, it becomes important for the government to conserve and protect the religious minorities of the country.
- Section 2, clause (c) of the National Commission of Minorities Act, declares six communities as minority communities. They are:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Buddhists
- Sikhs
- Jains and
- Zoroastrians (Parsis)
Linguistic Minorities:
- A class or group of people whose mother language or mother tongue is different from that of the majority groups is known as the linguistic minority.
- The Constitution of India protects the interests of these linguistic minorities.
Isro’s futuristic fuel cell system could power space station (TOI)
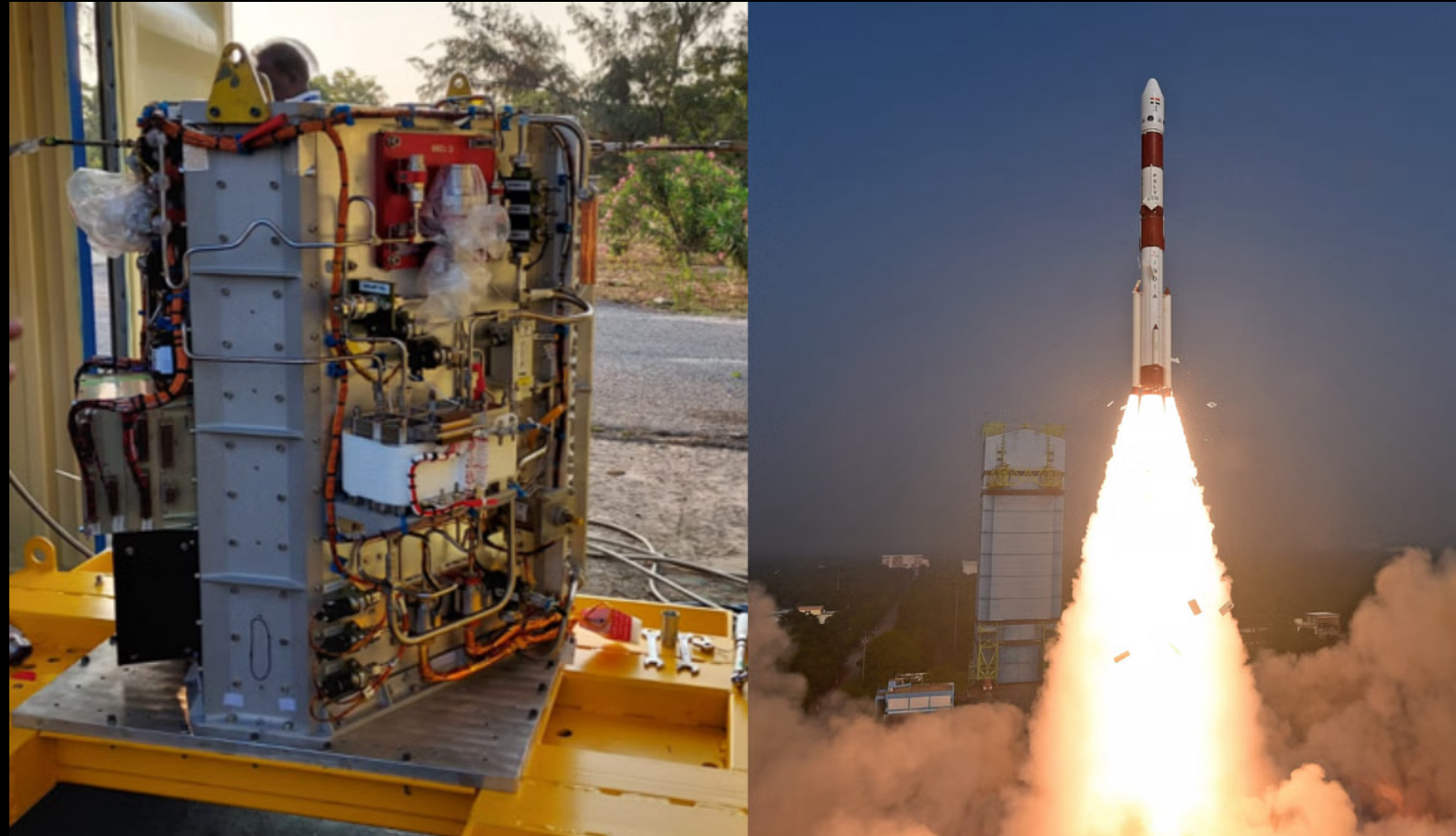

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, a futuristic fuel cell-based power system was successfully tested by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to provide a sustainable and reliable power source for space stations.
What is a Fuel Cell?
- Fuel cells, intricate devices powered by chemical reactions, have diverse applications spanning transportation, industrial sectors, commercial and residential buildings, and reversible grid energy storage systems.
- Operationally, fuel cells consist of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte.
- The anode, supplied with hydrogen fuel, undergoes oxidation to produce hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Simultaneously, the cathode, exposed to an oxidizer like oxygen, results in the production of water as hydrogen ions absorb electrons.
- The voltage per unit cell is determined by the energy level disparity at the electrodes. While a single fuel cell generates a modest amount of direct-current electricity, practical use often involves assembling stacks of these cells.
- Advantages: Advantages of fuel cells include lower or zero emissions, particularly with hydrogen fuel cells emitting only water, addressing climate concerns by avoiding carbon dioxide emissions.
- They operate quietly with few moving parts, achieve higher efficiencies compared to combustion engines, and resemble batteries but offer prolonged electrical energy due to continuous external fuel and air/oxygen sources.
- This longevity distinguishes them from batteries that rely on finite fuel material and oxidant, making fuel cells a sustainable and efficient choice for various applications.
About ISRO:
- The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the pioneer space exploration agency of the Government of India, headquartered at Bengaluru.
- ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development, while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research.
- ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, considered amongst the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
BRO Implements Indigenous Technology for Road Construction Near China Border in Arunachal Pradesh (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
In order to improve operational capacity of the defence forces in the high-altitude areas along the Indo-China border in Arunachal Pradesh, the BRO will build bituminous roads using an indigenous technology, “Rejupave” developed by India’s oldest and premier road research organisation, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI).
What is Rejupave Technology?
- CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), India's oldest road research organization, developed the Rejupave Technology.
- It is beneficial for constructing high-altitude bituminous roads in low and sub-zero temperatures.
- The technology actively reduces production and rolling temperatures of bituminous mixes by 30 to 400 degrees Celsius, ensuring minimal heat loss during transit in snowy conditions and long haulage times.
- The bio-oil-based asphalt modifier of this technology significantly lowers the heating requirements of bituminous mixes and preserves mix temperature during transit.
- In cold climatic regions, the 'Rejupave' asphalt modifier enhances long-term durability and resistance to thermal cracking under low-temperature conditions.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the eco-sensitive mountainous environment of Arunachal Pradesh.
About CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI):
- Established in 1952, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) stands as a premier national laboratory under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CRRI's major research and development programs encompass a range of projects, including the design, construction, and maintenance of roads and runways, traffic and transportation planning for large and medium cities, management of roads in diverse terrains, improvement of marginal materials, utilization of industrial waste in road construction, and landslide control.
- The institute extends its expertise by providing technical and consultancy services to various organizations both within India and internationally.
- CRRI actively contributes to capacity building in highway engineering, empowering human resources to undertake and execute road and runway projects.
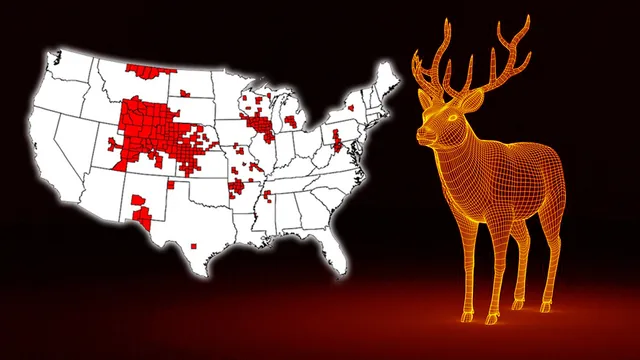
Zombie deer disease: Why are scientists concerned over its transmission to humans? (TOI)
- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers in the US have warned that Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) spreading among wildlife across North America, could also spread to humans.
What is Zombie Deer Disease??
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Zombie deer disease or chronic wasting disease is a prion disease that affects deer, elk, reindeer, sika deer and moose.
- Prion diseases affect both humans and animals and are distinguished by long incubation periods.
- In the case of chronic wasting disease or the zombie deer disease, "it may take over a year before an infected animal develops symptoms.
- History of the Disease?: The zombie deer disease was first discovered in Colorado (USA) in 1967.
- Until now, reports of humans getting affected have not come to the fore.
- However, the findings of several studies suggest that it can easily jump to human beings.
Why are health experts and scientists worried about a possible transmission??
- Experts are giving examples of the mad cow disease or the Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE).
- “The BSE outbreak in Britain provided an example of how, overnight, things can get crazy when a spillover event happens from livestock to people.
Symptoms of the Disease:
- The common signs of the disease are drastic weight loss (wasting), stumbling, and other neurologic symptoms.
- Other symptoms seen in animals infected with this disease are listlessness, drooling, excessive thirst or urination, drooping ears, and lack of fear of people.
It is difficult to eradicate this disease??
- The chronic wasting disease is extremely difficult to eradicate from the environment once the infection has started.
- It can persist for years in dirt or on surfaces, and it is resistant to disinfectants, formaldehyde, radiation, and incineration at 600C (1,100F).
- Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) is fatal to animals, and there are no treatments or vaccines.
Prevention?:
- To avoid the spread of the disease, humans should avoid shoot, handling, or eating meat from deer and elk that look sick or are acting strangely or are found dead.
- Individuals should wear latex or rubber gloves when dressing the animal or handling the meat.
Good Governance Day: Govt launches 3 new features on iGOT Mission Karmayogi platform (TOI)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi by introducing three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform that include My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs..
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi, the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), is geared towards equipping Civil Servants with enhanced creativity, constructiveness, and innovation, utilising transparency and technology to prepare them for future challenges.
- This innovative program serves as a cornerstone for the country's civil servants, emphasizing a balanced approach between 'on-site learning' and traditional 'off-site learning.'
- Approved by the Government on September 2, 2020, Mission Karmayogi encompasses six key pillars:
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- The electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS), and
- The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
- Encompassing all civil servants, including contractual employees, across various ministries, departments, organizations, and agencies of the Union Government, the program introduces three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform:
- My iGOT: Delivers targeted training courses on the home page of individual officers, directly addressing their unique capacity-building needs identified in the Capacity-Building Plan for their Ministries/Departments.
- Blended Programs: Facilitates equitable access to training methodologies across all levels by integrating traditional offline (in-person) classroom courses with online learning components.
- This approach enables officers and faculty to benefit from both the flexibility of online courses and the invaluable interactions of face-to-face classroom sessions.
- Curated Programs: Designed to cater to diverse learning needs of Ministries/Departments and Training Institutions, offering a custom approach to address the specific requirements of different segments within the civil services.
Cops lose Rs 12 crore in chit fund scheme, probe on (TOI)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Around 70 persons belonging to AP special police have lost nearly Rs 12 crore in a chit fund scheme in Mangalagiri, said the police. Mangalagiri police registered a case and launched an public sector investigation.
What are Chit Funds?
- Chit funds, also known as Kuri and Chitty, serve as versatile financial instruments encompassing both borrowing and saving components.
- In this financial arrangement, a group of individuals collectively contributes a fixed sum at regular intervals, with the understanding that one member will receive the total pooled amount during each interval.
- This process repeats until every member has received their share.
- Typically managed by a chit-fund company, this financial instrument operates by having a group of contributors make regular contributions toward the chit value for a duration equivalent to the total number of subscribers.
- The recipient of the pooled money is determined through an auction or lucky draw, employing a reverse auction system where the individual willing to accept the lowest amount is chosen.
- The sum forfeited by the winning bidder is distributed among other bidders, deducting a foreman's charges and commission.
- The share each bidder receives is termed a dividend. Interestingly, a winning bidder can continue to invest in subsequent intervals, even after claiming their sum.
Types of Chit Funds:
Chit funds can be categorized into three types:
- Chit Funds Run by State Governments:
- Managed and regulated by state governments.
- Public sector undertakings (PSUs) also fall under this category.
- These funds are considered safe, with limited chances of loss. Business processes are transparent and well-regulated.
- Private Registered Chit Funds:
- Registered under the Chit Funds Act of 1982.
- Typically initiated by well-established financial institutions or business entities.
- While participation in these funds may not be as secure as state-run or public-sector funds, the calculated risk is manageable due to their association with reputable private-sector entities.
- Unregistered Chit Funds:
- These chit-funds lack legal recognition, and participation involves a higher risk.
- Commonly found throughout India, they are often formed by a close-knit group of associates.
- Participation in unregistered chit funds is discouraged due to the potential for disputes, which rely heavily on the integrity and honesty of the members involved.
What is Saradha Chit Fund Scam?
- The Saradha scam, also known as the Saradha Group financial scandal, was a major financial scam that surfaced in 2013.
The Saradha scheme:
- The scheme, run by Saradha Group (an umbrella company with 200 private players), was launched in the early 2000s by businessman Sudipto Sen.
- Aimed at small investors, the scheme became popular in a very short time as it promised high returns.
- The money was collected through a wide network of agents, who were paid commissions of over 25 per cent.
- The Saradha Group raised about Rs 2,500 crore in a few years time.
- The company used varied marketing means to build its brand.
- Apart from popular marketing techniques like celebrity endorsements, the company used to sponsor cultural events such as Durga Puja and invest in popular football clubs to attract more investors.
- The scheme soon expanded to Odisha, Assam, and Tripura, and the number of investors reached close to 1.7 million.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
List Niemann-Pick as a rare disease, parents of young patients (TOI)
- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, parents of children with Niemann-Pick disease urged the Union government to notify the disease under the National Policy for Rare Diseases.
About Niemann-Pick Disease:
Niemann-Pick Disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the buildup of harmful substances in the body's cells and organs.
- Genetic Basis: It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that both parents must carry a mutated gene for their child to develop the disease.
- Types: There are several types of Niemann-Pick Disease, with types A and B being more common and types C and D being rarer.
- Lipid Accumulation: The disease is primarily characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lipids, specifically sphingomyelin, in various tissues and organs.
- Symptoms: Symptoms vary depending on the specific type of Niemann-Pick Disease but can include hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen), neurological problems, and lung issues.
- Type A: Niemann-Pick Disease Type A typically presents in infancy and can lead to severe neurological problems, making it a life-limiting condition.
- Type B: Niemann-Pick Disease Type B generally has a later onset and primarily affects the liver and spleen, with milder or absent neurological symptoms.
- Type C and D: Type C and D are characterized by cholesterol metabolism issues and can lead to neurological symptoms.
- Type C, in particular, can present with cognitive decline and movement problems.
- Treatment: There is currently no cure for Niemann-Pick Disease, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and may include enzyme replacement therapy, medications, and supportive care.
Niemann-Pick Disease is a complex condition with various subtypes, and the severity and specific symptoms can differ significantly among affected individuals.
AMANGARH TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The tiger population at the Amangarh Tiger Reserve has increased from 21 mature tigers and six cubs in 2021 to 28 mature tigers and four cubs now.
Facts About:
Amangarh Tiger Reserve is situated in Amangarh, Bijnor district, Uttar Pradesh, covering an area of approximately 97 square kilometres.
- It shares its boundaries with Uttarakhand's Jim Corbett National Park.
Originally a part of Jim Corbett National Park, Amangarh became a separate reserve in Uttar Pradesh when Uttarakhand was carved out of UP..
- It received the status of a tiger reserve in 2012.
The reserve features diverse ecosystems, including grasslands, wetlands, and dense forests.
Wildlife: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife.
- Among the mammals present are tigers, elephants, swamp deer, sambar, cheetal, hog deer, kakar, langur, sloth bear, porcupine, and otter.
- The bird population includes hornbills, red jungle fowl, pea fowl, Bengal floricans, fishing eagles, serpent eagles, ospreys, woodpeckers, shamas, Indian pittas, paradise flycatchers, orioles, and emerald doves.
- Additionally, the reserve is inhabited by reptiles such as monitor lizards, turtles, pythons, Gangetic dolphins, muggers, and gharial.
THE SUBSURFACE WATER ICE MAPPING (SWIM) PROJECT (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project, funded by NASA, has released its fourth map pinpointing potential subsurface water ice locations on Mars.
Facts About:
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project goal is to find the best locations to access water ice buried beneath the Mars' surface.
Recently, they released their fourth set of maps, which are the most detailed and accurate maps so far since the project began in 2017.
This project is led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
- They gather data from various NASA missions like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), the 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars Global Surveyor.
To create these maps, SWIM utilized two high-resolution cameras on the MRO.
- They used Context Camera data to make better maps of the Northern Hemisphere.
- For the first time, they used HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) data to get the closest, most detailed view of the ice's edge near the equator.
The SWIM project was done in two phases.
- The first phase, finished in 2019, focused on the northern hemisphere, and
- The second phase, completed in 2020, included the southern hemisphere.
One exciting thing about the new map is that it shows 'polygon terrain,' where the ice beneath the surface causes the ground to crack into polygonal shapes.
- This suggests there's more ice hidden below.
NASA-ISRO SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (NISAR) (TOI)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 'NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar' (NISAR) is set to enable the investigation of how changes in Earth's forest and wetland ecosystems affect the worldwide carbon cycle and exert an influence on climate change.
Facts About:
- NASA and ISRO collaborated to develop the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory known as NISAR.
It's about the size of an SUV and weighs 2,800 kilograms.
- It is a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite, having both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments.
- The first satellite mission to measure variations in the surface of our planet will be NISAR, which will use two distinct radar frequencies (L-band and S-band).
No matter the weather, SAR can gather data day or night and penetrate clouds to gather information.
- NASA has contributed GPS, an L-band radar, a payload data subsystem, and a high-capacity solid-state recorder for data storage.
ISRO on the other hand supplied the S-band radar, as well as the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Additionally, it has a sizable 39-foot stationary antenna reflector with an upward-facing feed on the instrument structure that will be used to focus "the radar signals emitted and received."
The reflector is constructed of gold-plated wire mesh.
- The mission's objectives are to measure the dynamic surfaces, ice masses, and changing ecosystems of Earth in order to gather data on groundwater, biomass, natural hazards, and sea level rise.
- NISAR is going to perform global 12-day regular observations of Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces during ascending and descending passes.
MELGHAT TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a tiger was found dead in the Susarda range within the buffer zone of Melghat Tiger Reserve's Paratwada division.
Facts About:
The name "Melghat" signifies the confluence of various 'ghats' or valleys, reflecting the landscape of the reserve.
Location: Melghat Tiger Reserve is situated in the Amaravati district of Maharashtra.
- It's positioned on the southern offshoot of the Satpura Hill Range known as Gavilgarh Hill, approximately 225 km west of Nagpur.
Establishment: It was initially designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1967 and later declared a tiger reserve in 1974.
- Melghat was one of the first nine tiger reserves established under Project Tiger in 1973-74, an initiative for the conservation of Bengal tigers in India.
- It is one of the largest tiger reserves in India in terms of its area.
Rivers: Melghat Tiger Reserve serves as the catchment area for five significant rivers: Khandu, Khapra, Sipna, Gadga, and Dolar.
Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of tropical dry deciduous trees, with teak being the dominant species.
Wildlife: Apart from Bengal tigers, the reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including Sloth Bears, Indian Gaur, Sambar deer, Leopards, Nilgais, and more.
- Notably, the endangered Forest Owlet, once believed to be extinct, has been found in various areas of Melghat.
Tribal Communities: The largest tribal community in Melghat is the Korkus.
PROJECT UDBHAV (TOI)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has launched a new project called 'Udbhav' to integrate ancient strategic knowledge with modern military practices.
Facts About:
- The Indian Army launched the Project Udbhav initiative to re-discover the rich Indian heritage of statecraft and strategic ideas drawn from ancient Indian texts on diplomacy, warcraft, and grand strategy.
It concentrates on a wide range of topics, such as indigenous military systems, historical texts, regional texts and kingdoms, thematic studies, and complex Kautilya studies.
Project Udbhav's main goal is to build a link between the past and the present.
- The project aims to create an indigenous strategic vocabulary that is deeply rooted in India's rich philosophical and cultural heritage, going beyond simply rediscovering historical narratives.
- The ultimate goal is to incorporate traditional knowledge into contemporary military education so that the Indian Army can use age-old principles in the complex strategic environment of today.
EXERCISE 'MILAN' (TOI)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Navy will host the Mid Planning Conference (MPC) of the MILAN 24 Exercise in Visakhapatnam from February 19 to February 27, 2024.
Facts About:
- ‘MILAN’ is a multilateral naval exercise held every two years.
- It was established in 1995 by the Indian Navy.
- MILAN was originally conceived in accordance with India's 'Look East Policy,' but has since grown to include participation from other Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs) in conjunction with the Government of India's 'Act East Policy' and Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative.
- The harbor phase of MILAN 24 will include a City Parade at RK Beach, an International Maritime Seminar, a Swavlamban Exhibition, a Subject Matter Expert Exchange, and a Milan of Young Officers.
Friendly foreign country ships, maritime patrol aircraft, and submarines would take part in the sea phase alongside Indian Navy units.
- The operations will include large-force maneuvers, sophisticated air defense operations, anti-submarine warfare, and anti-surface warfare.
- MILAN 22 was held in/around Visakhapatnam from February 25th to March 4th, with 39 countries taking part.
Bolson tortoises (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Biologists are working slowly and steadily to assist North America's biggest and most uncommon tortoise species.
Facts About:
- Bolson tortoises are the biggest and rarest land reptiles in North America.
They are also the rarest among the six Gopherus species that are found on this continent.
- Among Bolson tortoises, adult females are generally larger than males.
- These tortoises are land-dwellers and spend over 95% of their time in burrows they dig using their shovel-like front feet.
- They are most active from around April to October when they do everything like searching for food, nesting, and mating.
- While we don't know their exact lifespan, Bolson tortoises can live for more than a century.
- Currently, Bolson tortoises are found in a small area in north-central Mexico, specifically in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Durango.
However, they exist in separate groups within this region.
- In terms of conservation, Bolson tortoises are Critically Endangered according to the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
I2U2 Group (TOI)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The I2U2 group has just unveiled a new collaborative space project with the goal of developing a one-of-a-kind space tool designed for use by policymakers, organizations, and business innovators.
Facts About:
- The I2U2 Group comprises India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States.
- Formation:
This alliance was originally established in October 2021 with the primary objective of addressing infrastructure, transportation, and maritime security issues in the region.
Originally, it was named the "International Forum for Economic Cooperation" and was also referred to as the "West Asian Quad."
- First Virtual Summit: In July 2022, the group conducted its inaugural virtual summit.
- This unique coalition of nations identifies viable projects and initiatives aimed at addressing significant challenges.
- It places special emphasis on collaborative investments and new endeavors in areas such as water, energy, transportation, space, health, food security, and technology.
- The group's objectives encompass mobilizing private sector resources and expertise to achieve various goals, including the modernization of infrastructure, the promotion of low-carbon development pathways, and enhancements in public health.
Vanadium (TOI)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Vanadium, a critical raw material for many industrial applications, has been found in sediment samples collected from Gulf of Khambhat, which opens into the Arabian Sea off Alang in Gujarat.
Facts About:
- Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol "V" and atomic number 23.
- Vanadium is a naturally occurring element found in minerals and ores.
It was first discovered in the early 19th century.
- It is a transition metal known for its various applications in science and industry.
Applications:
- Strengthens Steel: One of its primary uses is as an alloying agent in steel production.
Vanadium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
It is commonly used in manufacturing tools, knives, and structural components in construction.
- Aerospace Alloys: Vanadium alloys are utilized in aerospace applications, such as jet engines and rocket frames, due to their high-temperature resistance and lightweight properties.
- Batteries: Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are emerging as a promising energy storage technology.
They offer scalability and long cycle life, making them suitable for grid-level energy storage.
- Catalysts: Vanadium compounds act as catalysts in chemical reactions, particularly in the production of sulfuric acid and maleic anhydride.
- Medical Applications: Vanadium has potential health benefits and is being studied for its role in managing diabetes and its antioxidant properties.
- Dye and Pigment Production: Vanadium compounds are used in the manufacture of dyes, pigments, and ceramics.
- Metallurgy: Vanadium is employed in the refining of certain metals like aluminum and titanium.
- Nuclear Applications: In nuclear reactors, vanadium serves as a structural material due to its neutron-absorbing properties.
- Research and Development: Vanadium's unique properties make it valuable for scientific research, including studies in material science and chemistry.
Vanadium's versatility and strength-enhancing properties find application in various industries, from steel manufacturing to energy storage and even potential health-related uses, making it a vital element in modern technology and innovation.
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (TOI)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India is getting ready to bring in a new group of cheetahs from South Africa and release them into the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated at the northern border of Madhya Pradesh's Mandsaur and Nimach districts, adjacent to Rajasthan.
- Area: Covers 368.62 km2 (142.32 sq mi) and is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest ecoregion.
- Establishment: Established in 1974 and officially designated as a sanctuary in 1984.
- River Chambal: Divides the sanctuary into two sections and adds to its unique landscape.
- Terrain: Features diverse topography, including hills, plateaus, and the catchment area of the Gandhi Sagar Dam on the Chambal River.
- Cultural Significance: Houses historical, archaeological, and religious sites like Chaurasigarh, Chaturbhujnath temple, Bhadkaji rock paintings, Narsinghjhar Hinglajgarh fort, and Taxakeshwar temple.
- Flora: Dominated by tree species like Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, and Palash.
- Fauna: Home to herbivores such as Chinkara, Nilgai, and Spotted Deer, as well as carnivores like the Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena, and Jackal. The sanctuary also hosts a variety of aquatic life, including crocodiles, fish, otters, and turtles.
Competition Commission of India (CCI) (TOI)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Competition Commission of India has recently unveiled preliminary rules for overseeing mergers and acquisitions involving significant India-based operations, particularly those in the technology sector, thereby extending the authority of the antitrust regulator.
Facts About:
- CCI is a government-established statutory body founded in March 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The primary objective of CCI is to foster fair competition in the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and promoting market dynamics that benefit consumers.
- The Commission's key focus areas include eradicating practices detrimental to competition, fostering and maintaining competitive environments, safeguarding consumer interests, and upholding the freedom of trade in India's markets.
Mandate: CCI enforces the provisions of The Competition Act, 2002, which:
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by enterprises.
- Regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that could potentially harm competition within India. Hence, deals exceeding certain thresholds require clearance from CCI.
- Monitors the activities of large enterprises to ensure they do not misuse their 'dominant position' by controlling supply, setting high purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that may harm emerging businesses.
Composition: CCI functions as a quasi-judicial body, consisting of one chairperson and six additional members, all appointed by the Central Government.
Headquarters: The Commission is headquartered in New Delhi.
Chitala Fish (TOI)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister for Fisheries, Livestock, and Dairying has just revealed plans to boost the population of the Uttar Pradesh state fish Chitala by introducing it into natural water sources like the Ganga through river ranching.
Facts About:
Chitala Fish is a type of predator fish that primarily hunts at night and preys on smaller fish.
Distribution:
- Although it's often reported to inhabit various parts of southern Asia, this species is mainly found in the Indian subcontinent, including Pakistan, India (particularly in states like Manipur, Uttaranchal, West Bengal, Assam, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar), Nepal, and Bangladesh.
Habitat:
- Chitala Fish is commonly found in major river channels and freshwater lakes but has also been observed in swamps.
- Its primary habitat includes the Indus, Ganges-Brahmaputra, and Mahanadi river basins in India.
Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN, Chitala Fish is classified as "Near Threatened."
Significance of Chitala’s River Ranching:
- The river ranching initiative has multiple aims, including restoring the aquatic ecosystem's balance, boosting the income of fish farmers, and providing the public with a protein-rich diet.
Additionally, Uttar Pradesh has ongoing projects worth over 1000 crore under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
Bhoramdev Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) (TOI)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chhattisgarh High Court has recently rejected a public interest litigation (PIL) seeking the designation of the Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) as a tiger reserve.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the Kawardha district of Chhattisgarh, this sanctuary takes its name from the renowned 11th-century Bhoramdeo Temple located nearby.
-
- It shares its boundary with Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, making it a significant tiger habitat in central India.
- Covering an expanse of around 325 square kilometres (125 square miles), it boasts a diverse landscape.
- The sanctuary serves as the origin of the Fen and Sankari rivers.
- Characterized by lush green forests, undulating hills, and the Maikal Range of the Satpura Hills, it presents a picturesque setting.
- Vegetation: Comprising a blend of dense forests and open grasslands, it offers a rich variety of flora.
- Flora Highlights: Notable plant species within the sanctuary include sal, saja, tinsa, kara, and haldu.
- Diverse Fauna: Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a wide range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, wild dogs, sloth bears, sambar deer, barking deer, chital (spotted deer), gaur (Indian bison), as well as numerous bird and reptile species.
