10th phase of Sagar Parikrama covering AP and Puducherry coastal districts to start from Mon (PIB)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Parshottam Rupala along with Minister of State Dr L Murugan will participate in the Sagar Parikrama (Phase X) event being organized from 1st January 2024 to 6th January 2024 at various locations of Andhra Pradesh and Puducherry
About Sagar Parikrama Phase-10:
- Sagar Parikrama Phase-X is poised to be a pivotal event in the ongoing efforts to promote sustainable fisheries, empower stakeholders, and contribute to the economic growth of coastal communities.
- It will continue and cover the remaining coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh namely Nellore, Prakasam, Bapatla, Krishna, West Godavari, Konaseema, Kakinada, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, Srikakulam and Yanam (Union Territory of Puducherry).
What is “Sagar Parikrama”?
- Sagar Parikrama is a testament to the transformative power of visionary leadership for the welfare of the fishing community and coastal development.
- It is an initiative taken by the Government, with an aim to resolve the issues of the fishers, and other stakeholders and facilitate their economic upliftment through various fisheries’ schemes and programs being implemented by the Government such as Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and Kisan Credit Card for Fisheries (KCC).
- It represents a transformative voyage along the coastal belt, symbolizing unity with fisherfolk, fish farmers, and all stakeholders in the spirit of the 75th Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The Sagar Parikrama Yatra features the interactions of ministers with fishermen, fish farmers and other relevant stakeholders.
- State fisheries officials, fishermen representatives, fish farmers, entrepreneurs, fishermen cooperative society leaders, professionals, scientists, and other stakeholders from across the nation will accompany the events.
- The journey of the first phase of “Sagar Parikrama” started from Mandvi, Gujarat on 5th March 2022.
- So far, the total 9 phases of Sagar Parikrama have been covered in the coastal States/UTs of Gujarat, Daman & Diu, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andaman & Nicobar, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and part of Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh during initiation of its tenth phase.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- Sagar Parikrama is making a notable impact on improving the quality of life and economic well-being of the fishing community.
- By providing a platform for direct interaction with Ministers and senior government officials, the initiative ensures that the concerns and issues of fishermen and fish farmers are addressed promptly.
How two choke points could turn into a perfect storm for global trade (Indian Express)
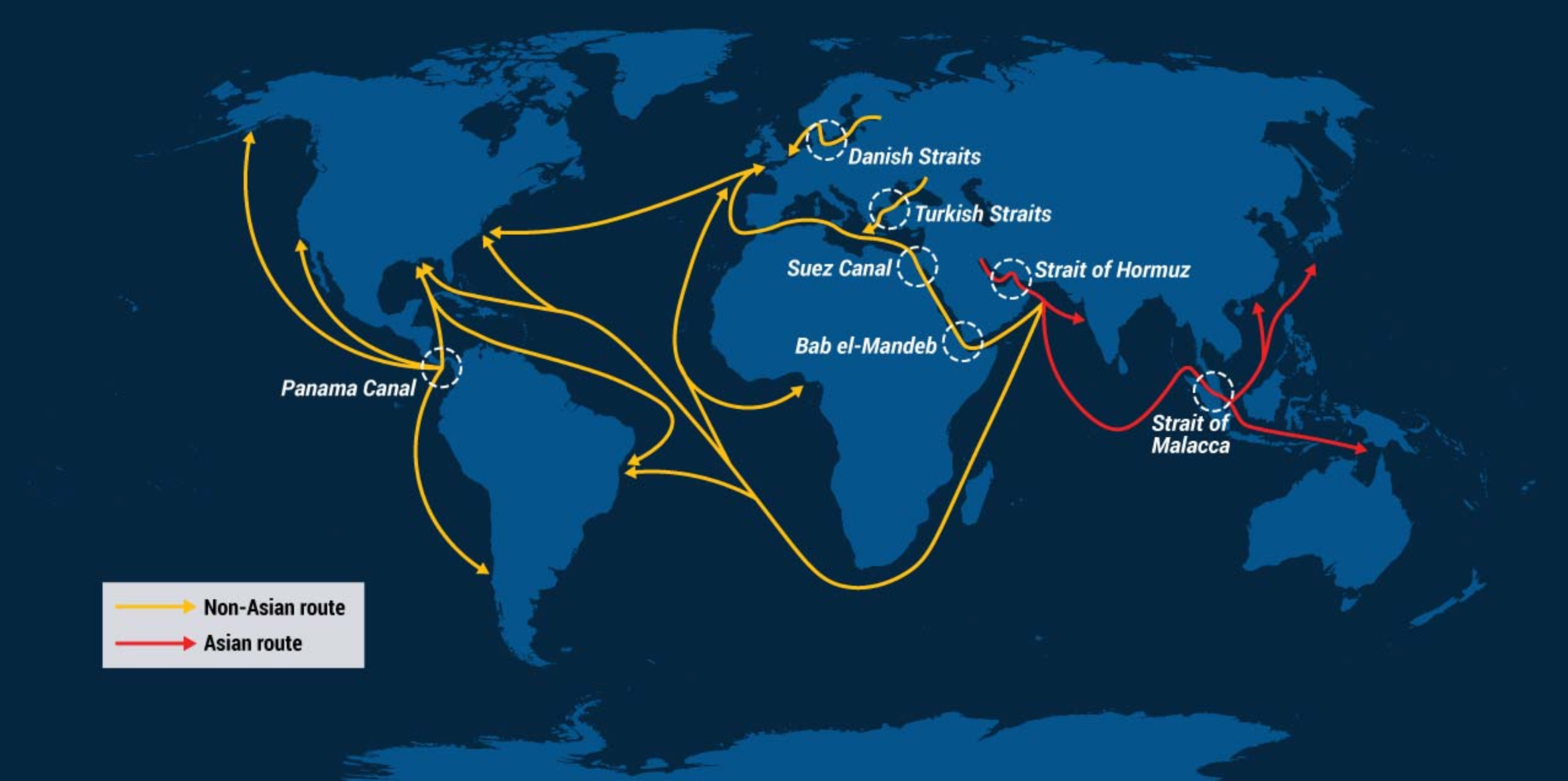
- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Shipping giant Maersk on Sunday suspended passage of its vessels through the Red Sea route for 48 hours after fresh attacks by Yemen-based Houthi rebels. This comes barely a week after the company announced plans to resume operation citing the deployment of a US-led military operation to guard the crucial sea route.
What do the ongoing Red Sea and Panama Canal crises mean for world trade?
- A disruption in maritime transport is a crucial concern for the world economy, as over 80 per cent of the global goods trade is carried by sea.
- The share of trade via sea is much higher for developing countries such as India.
- Currently, two important shipping routes are facing blockages.
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait which leads to the Suez Canal in the Red Sea region connects Asia and parts of North East and East Africa to Europe.
- The 100-year-old Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Both these routes are among the busiest in the world and a blockage results in forcing global shipping lines to take longer alternate routes, pushing up freight rates.
- The disruption at the Red Sea route, for instance, is estimated to push the prices of Indian agricultural products by 10 to 20 per cent, as shipments would be routed around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope.
- This comes at a time when much of the West is witnessing higher interest rates to curb inflation.
- Higher prices could further fuel demand concerns for global and Indian exporters.
Why is trade via the Panama Canal slowing?
- Shipping via the Panama Canal has dropped by over 50 per cent due to drought conditions at the 51-mile stretch.
- Due to the shortage of water, ships moving from Asia to the US are being forced to use the Suez Canal, which takes six more days compared to the Panama Canal.
- Moreover, Panama is facing its driest rainy season in decades, raising fears of prolonged canal bottlenecks.
How have the attacks impacted freight rates?
- Ever since the attacks along the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait began, global shipping firms have begun imposing war risk surcharges over and above the normal freight rates.
- Indian exporters said that freight rates for Indian shipments headed to Europe and Africa could surge as much as 25-30 per cent if the ongoing security concern along the Red Sea trade route continues.
- This is troubling, as the European Union is one of India’s second-largest export destinations.
- Slowing demand from the region has impacted India’s labour-intensive sectors, such as textiles, gems and jewellery exports.
Panama Canal
- It is an artificial canal that spans the Isthmus of Panama and links the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- Together with the Suez Canal, it is one of the two most strategically important man-made waterways in the world.
- It has a length of around 80 kilometres.
- The United States constructed the canal between 1904 and 1914, and on August 15, 1914, it was formally inaugurated.
- Since 1999, when control of the Canal was moved from the United States to Panama, it has been owned and operated by the Republic of Panama.
- To make it easier for ships to cross the continental divide, the Panama Canal is made up of a network of locks that raise and decrease the water level.
Over 1 lakh people availed free treatment under Delhi Arogya Kosh scheme till October (Indian Express)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
As many as 1.13 lakh people have availed of free health treatment being provided under the city Government’s ‘Delhi Arogya Kosh’ scheme, till October last year, according to government data.
What is the 'Delhi Arogya Kosh' Scheme?
- Constituted in 2011, the Delhi Arogya Kosh (DAK) has five components/schemes:
- Financial assistance to EWS patients
- Free High-End Radiological Diagnostic Test Scheme
- Cashless Specified Surgeries scheme
- RTA (Road Traffic Accident) Scheme (‘i.e. Farishtey Scheme’) and
- Cashless Dialysis Scheme.
- There are 4 schemes under the name of Delhi Arogya Kosh which include financial support from the government for medical implants, various types of surgeries, 136 types of medical tests and the Farishtey scheme for treatment of accident victims.
- Under this scheme, if any citizen of Delhi goes to Delhi government hospitals for treatment and has to face a waiting period for examination or treatment and the patient needs immediate care, then the patient can avail the above-mentioned services in a private hospital with a doctor’s reference.
- Cashless check-ups and treatment will be provided for them in all the empanelled hospitals and the cost of this will be borne by the government.
- Under this scheme, every citizen of Delhi who has Delhi's voter card can get treatment.
- Children below 19 years of age can avail this facility based on their parents' voter cards.
Schemes Under 'Delhi Arogya Kosh':
- Financial assistance up to 5 lakh for different types of medical implants: Under this scheme, the government provides financial assistance up to Rs 5 lakh to the patients.
- To avail of the benefit of this scheme, patients need to submit their application and relevant documents.
- After their screening, the government bears the cost of implants and the treatment of the patient up to Rs 5 lakh.
- It is a cashless scheme.
- 136 free medical test facilities at private labs for patients: In the case of a long waiting list at government hospitals, patients can get the tests done at private hospitals or labs.
- Under this scheme, patients can get about 136 types of medical tests done for free.
- Under this, while waiting in a government hospital, patients can get all medical tests from private hospitals and labs free of cost, including X-ray, MRI, PET scan, CT scan and ultrasound.
- Free Surgery Scheme for patients to get the surgery done in private hospitals: If a patient goes to Delhi government hospital for treatment and has to undergo surgery but the waiting time is more than 30 days, then patients can avail free surgery in private hospitals under the 'Free Surgery Scheme' under this scheme.
- The government bears all the expenses incurred in the surgery.
- Accident victims’ free treatment : The Farishtey Scheme is also covered under Delhi Arogya Kosh.
- Under this scheme, if a person meets with an accident, he or she is provided immediate treatment in a government hospital for free and if the patient gets admitted within 72 hours of an accident, he or she can also avail treatment at a private hospital for free.
-
- All the expenses of patients will be borne by the Delhi government.
SC’s translation projects raced ahead in 2023 as retd. HC judges and law clerks help AI (The Hindu)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court’s monumental project of translating all of its 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages achieved unprecedented speed in 2023, with the E-SCR portal starting with just 2,238 translated judgments in January and ending the year with over 31,000.
Background:
- In 2023, the Supreme Court of India embarked on a groundbreaking venture to translate its extensive archive of 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages.
- This innovative initiative, powered by collaboration between retired High Court judges, law clerks, and artificial intelligence, has made significant strides.
- However, concerns linger regarding the practical application of these translated judgments and the absence of a standardized legal vocabulary across diverse regional languages.
- The launch of the E-SCR portal in 2023 marked a modest beginning with 2,238 translated judgments in January, reaching a commendable milestone of over 31,000 rulings translated by the year's end.
- Recent statistics reveal that Hindi leads with the highest number of translated judgments at 22,396, followed by Punjabi (3,572), Kannada (1,899), Tamil (1,172), and Gujarati (1,112).
- While the translation speed witnessed a significant improvement in 2023, legal experts express concerns about the practical utility of translated judgments, particularly when High Courts, except in the Hindi-speaking States, cannot conduct proceedings in regional languages.
What is the Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software (SUVAS)?
- SUVAS was introduced in November 2019 by the then-Chief Justice of India (CJI) S.A. Bobde.
- It was created to encourage and ensure the use of regional languages in judicial proceedings.
- It is an artificial intelligence (AI)--trained machine translation tool.
- Constitutional Standing: While Article 348(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution mandates that proceedings in the Supreme Court and every High Court be conducted in English, Article 348(2) provides a provision.
- It allows a State Governor, with the President's consent, to authorize the use of Hindi or another state language in the High Court of that particular State.
- In this context, SUVAS is vested with authority under Article 348, serving as a pivotal tool to promote linguistic diversity within the constitutional framework.
Planning to invest in green deposits? RBI releases latest guidelines to explain key provisions (Live Mint)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent guideline, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) don’t need to raise green deposits.
What are Green Deposits?
- A green deposit is essentially a fixed-term deposit designed for individuals seeking to invest in eco-friendly projects.
- Similar to a standard Fixed Deposit scheme, the green deposit offers interest to investors and has a predetermined term.
Key Features:
- Allocation to Green Finance: The funds deposited in a green deposit are specifically earmarked for allocation to green finance initiatives, promoting environmentally conscious investments.
- Environmentally Friendly Focus: Also referred to as an environmentally friendly fixed deposit, this financial instrument encourages sustainable development by directing funds toward projects related to renewable energy, clean technology, and other environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Priority Sector Classification: Green activities or projects financed through this framework may be classified under the priority sector, provided they meet the requirements outlined in the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Overdraft Facility: Banks are permitted to offer overdraft facilities to customers against their Green Deposits, providing added flexibility.
- Currency Denomination: As per the current framework, green deposits can only be denominated in Indian Rupees.
- Insurance Coverage: Deposits raised under this framework are covered by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) in accordance with the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961, and the relevant regulations.
- Renewal or Withdrawal: Upon maturity, depositors have the option to either renew or withdraw their green deposits, providing flexibility and choice.
Advantages of Green Deposits:
- Contribution to Climate-Friendly Initiatives: Green deposits empower depositors to actively participate in climate-friendly initiatives, aligning with India's net-zero goals and promoting environmental sustainability.
- Support for Socially Responsible Activities: Although higher interest rates may not be the primary focus, depositors indirectly contribute to socially and environmentally responsible endeavours.
- Their funds play a pivotal role in supporting activities that benefit the community and the planet.
- Positive Environmental Impact: By investing in green deposits, depositors contribute to positive outcomes such as reduced emissions, improved air quality, and sustainable resource allocation.
- These actions foster positive externalities, creating a healthier environment for all.
- Contribution to Reduced Income Inequality: The support for eco-friendly initiatives and fair resource allocation facilitated by green deposits contributes to long-term reductions in income inequality, fostering a more equitable and sustainable society over time.
Challenges Associated with Green Deposits:
- Design Limitations: Flaws in the design of green deposit frameworks may restrict the scope of eligible green projects that banks can invest in, limiting the diversity of environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Perceived Reality vs. Impact: There is a concern that some green investment products may serve more as a psychological boost for investors rather than delivering substantial environmental benefits.
- The actual impact on the environment may not align with the positive perception created.
- Uncertain Project Sustainability: The long-term sustainability of green projects funded by banks remains uncertain, raising questions about the enduring impact of investments in environmentally friendly initiatives.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient awareness among bank staff can result in delays in the process of acquiring green deposits, hindering the seamless integration of eco-friendly financial products into banking operations.
- Lower Interest Rate Perception: Investors often prioritize high returns, and the perception that green deposits may offer lower interest rates could deter them from choosing environmentally conscious financial products.
