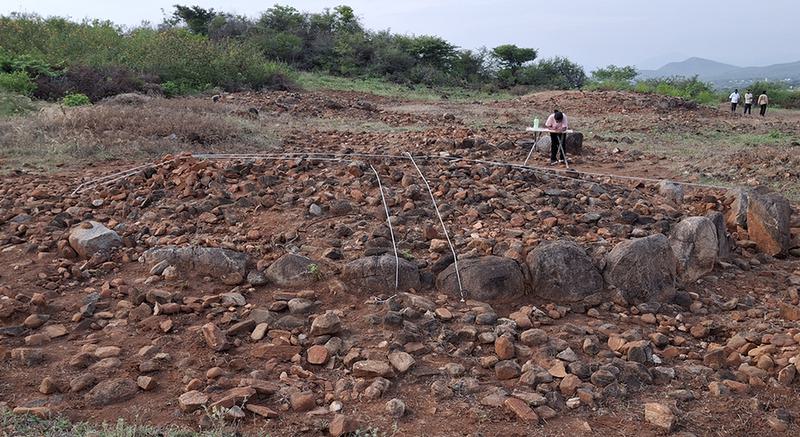
Doddalathur Megalithic Burial Site

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore have embarked on an excavation of megalithic burial sites in Chamarajanagar district.
- Location: Doddalathur village, Hanur taluk, Chamarajanagar district, situated in a valley by the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges.
- Team: A group of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore, in collaboration with the Mythic Society, Bengaluru.
- Excavation Focus: Exploration of megalithic burial sites corresponding to the Iron Age (approximately 1200 BC to 300 CE).
- Site Features:
- Burials consist of circles made of large boulders, referred to as "megalithic."
- A small hillock is located to the west of the village.
- Historical Significance:
- The site was discovered by C. Krishnamurti of the Archaeological Survey of India in 1961.
- Originally contained over 1,000 burials, many of which have been lost due to agricultural expansion and development.
- Despite disturbances, many burials remain intact and are considered suitable for excavation.
- Goals of the Project:
- To enhance understanding of megalithic-Iron Age culture in southern Karnataka's hilly regions.
- To provide practical field training for archaeology students.
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024, Commencing at Visakhapatnam on 08 Oct Hosted by India, USA, Australia and Japan in Participation.
Background
- Origins: Initiated in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between the United States and Indian Navy.
- Evolution: Has grown into a key multilateral exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and addressing maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific region.
Participating Naval Assets
- India: Various platforms, including:
- Guided missile destroyers
- Multi-purpose frigates
- Submarines
- Fixed-wing maritime reconnaissance aircraft
- Fighter aircraft and helicopters
- Australia:
- HMAS Stuart (Anzac Class Frigate)
- MH-60R helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- United States:
- USS Dewey (Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer)
- Integral helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Japan:
- JS Ariake (Murasame-class Destroyer)
Focus Areas of the Exercise
- Operational Enhancements:
- Discussions on special operations
- Surface, air, and anti-submarine warfare
- Subject Matter Expert Exchange (SMEE)
- Maritime Operations:
- Anti-submarine warfare
- Surface warfare
- Air defense exercises
- Emphasis: Improving situational awareness in the maritime domain.
Special Events
- Distinguished Visitors’ Day: Scheduled for October 9, 2024.
- Hosted by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Eastern Naval Command.
- Joint Press Conference: Co-chaired by heads of delegations from all participating nations during the Harbour Phase.
Significance
- Comprehensive Exercise: Malabar 2024 is expected to be the most detailed edition to date, featuring complex operational scenarios and enhanced cooperation among the naval forces of the participating countries.GS Paper
DefConnect 4.0

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
- DefConnect 4.0 was inaugurated by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on October 7, 2024, at Manekshaw Centre, Delhi Cantonment.
- Organizer: Hosted by Innovations for Defence Excellence - Defence Innovation Organisation (iDEX-DIO) under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
Purpose and Focus
- Advancing Indigenous Innovation: Aims to enhance India’s defense ecosystem by promoting self-reliant defense technologies.
- Participants: Involves Armed Forces, Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), start-ups, MSMEs, academia, incubators, investors, and policymakers.
Technology Showcase
- Exhibitions: iDEX innovators showcased cutting-edge technologies, products, and capabilities.
- Collaboration and Dialogue: Encourages partnerships and discussions to drive defense innovation and long-term collaborations.
Special Sessions
- Budget Insights: Focused on key takeaways from recent budget announcements impacting the defense innovation ecosystem.
- Semiconductor Domain: Highlighted initiatives and opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Path Forward: Vision for 2047
- Viksit Bharat Goal: Aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in defense innovation by 2047.
- Government Initiatives: Supports local talent and indigenous solutions through programs like iDEX.
iDEX Impact
- Defence India Start-up Challenges: 11 editions launched, garnering over 9,000 applications.
- Collaborations: Engages with over 450 start-ups/MSMEs on significant defense projects.
- Contribution to Self-Reliance: Supports the goal of achieving self-reliance in the defense and aerospace sectors.
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Increasing Frequency of Typhoons in Southeast Asia
- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Overview of Typhoons
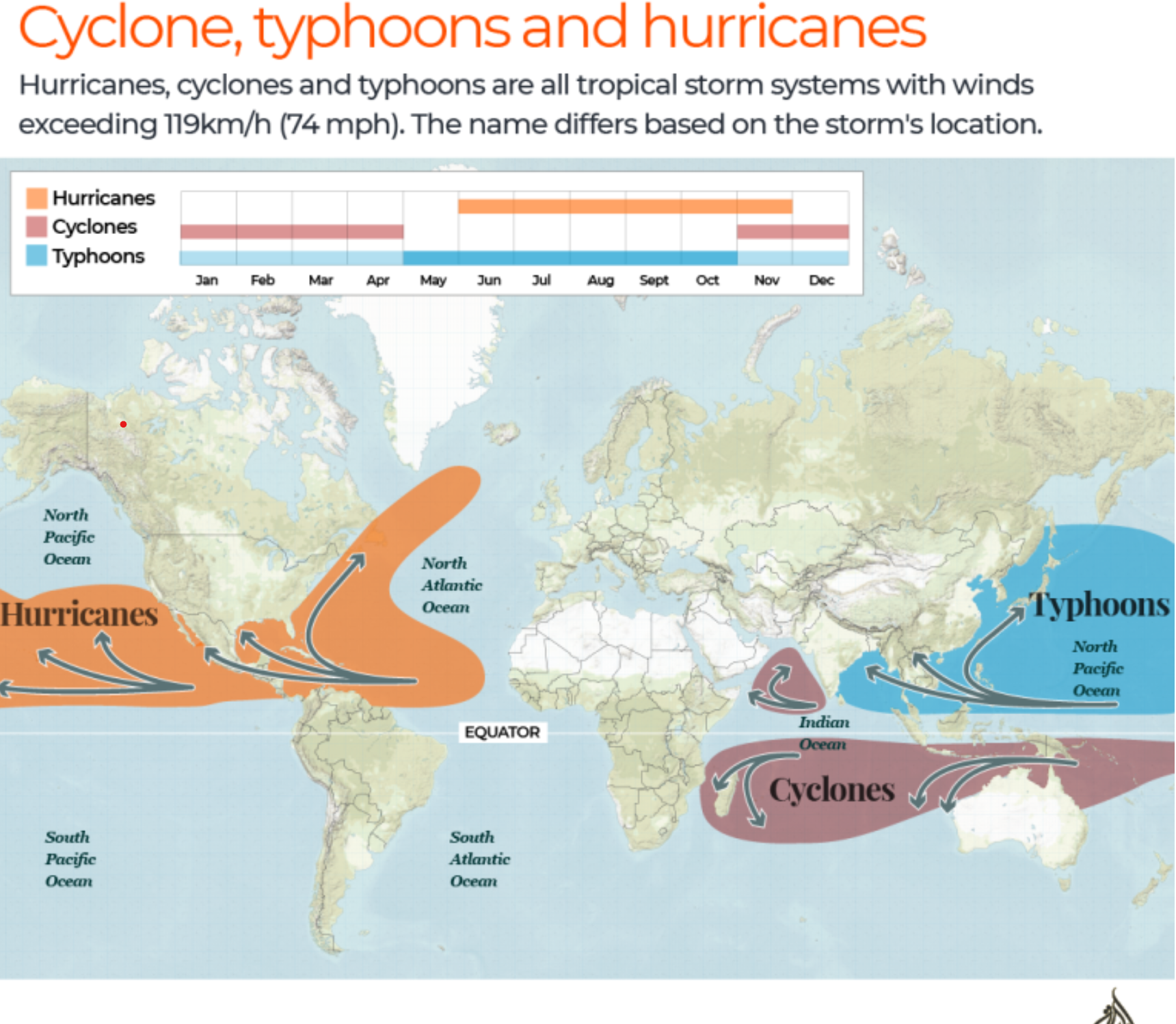
- Definition: A typhoon is a type of cyclone with wind speeds of 119 km/h or more, forming over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Mechanism: As warm, moist air rises from the ocean, it creates a low-pressure system, leading to the characteristic circular wind patterns: anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Recent Typhoon Events
- Typhoon Yagi: The most powerful tropical cyclone in Asia in 2024, with peak winds of 260 km/h. It caused significant destruction across Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, displacing around 631,000 people and resulting in over 500 fatalities.
- Typhoon Bebinca: Reached wind speeds of 151 km/h, classified as a Category 1 storm, impacting eastern China with heavy rainfall and forcing evacuations for over 414,000 residents.
- Typhoon Shanshan: Affected Japan, bringing severe weather conditions.
Why are Typhoons more frequent?
- Rising Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Global warming has raised ocean temperatures, providing more energy for typhoon formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Circulation Changes:
- Alterations in patterns, such as the weakening of the Walker Circulation, affect the frequency and paths of typhoons.
- El Niño and La Niña Effects:
- The El Niño-Southern Oscillation significantly influences typhoon activity. El Niño years often lead to increased typhoon occurrences in Southeast Asia, while La Niña can enhance cyclone activity in the Western Pacific.
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Higher global temperatures result in more evaporation, adding moisture to the atmosphere, which fuels stronger storms and increases rainfall intensity.
- Geographical Vulnerability:
- Southeast Asia’s location near warm ocean currents makes it a hotspot for typhoon activity, particularly along its extensive coastlines.
- Marine Heat Waves:
- Climate change has led to more frequent marine heat waves, causing extreme ocean warming, which contributes to intensified storms.
- Weaker Land-Sea Temperature Gradients:
- Changes in temperature differences between land and sea can prolong storm duration and severity.
- Urbanization and Environmental Degradation:
- Rapid urban development and the destruction of coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, diminish natural barriers against storm impacts.
Humanitarian Impact and Response
- The increasing intensity and frequency of typhoons have precipitated severe humanitarian crises in affected regions. The need for international cooperation in disaster response has become critical, involving collaboration among governments, civil societies, and humanitarian organizations to provide aid and support for those affected.
- Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind the rising frequency of typhoons is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and enhance community resilience in Southeast Asia.
