India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
The ‘Architecture Nobel’: Why Pritzker laureate Riken Yamamoto’s work stands out

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Japanese architect Riken Yamamoto was this week declared winner of the 2024 Pritzker Architecture Prize, the highest international award in the field, which is sometimes referred to as the “Architecture Nobel”.
About Pritzker Architecture Prize:
- The Pritzker Architecture Prize is an international prize awarded each year to a living architect or a group of architects for significant achievements.
- It was established by the Pritzker family of Chicago in 1979 through their Hyatt Foundation, which until today is responsible for the prestigious award.
- The idea behind the Pritzker Prize is to honor contemporary architects “whose built work demonstrates a combination of those qualities of talent, vision, and commitment, which has produced consistent and significant contributions to humanity and the built environment through the art of architecture.”
- The award consists of a bronze medallion and a prize money of 100,000 USD.
- It is conferred during a ceremony held at an architecturally significant site throughout the world.
- The prize, which is also known as the Nobel Prize of architecture, is awarded “irrespective of nationality, race, creed, or ideology”.
- Nominations come from a range of architects, academics, and critics and the jury consists of five to nine experts.
History of the Prize:
- The idea for the Pritzker Prize came from Jay and Cindy Pritzker, who wanted to encourage and stimulate a greater public awareness of architecture, while also inspiring more creativity in the profession.
- The name Pritzker comes from the family who are based in Chicago and own the Hyatt Hotels.
Riken Yamamoto's Notable Works:
- Yamamoto, the ninth laureate from Japan, is known for his iconic architectural designs, such as the Hiroshima Nishi Fire Station (2000), featuring a transparent façade with glass walls and floors, offering passersby a glimpse inside.
- His design of the Koyasu Elementary School (2018) incorporates spacious, open terraces that facilitate arts education in dance, music, and painting while fostering student interaction.
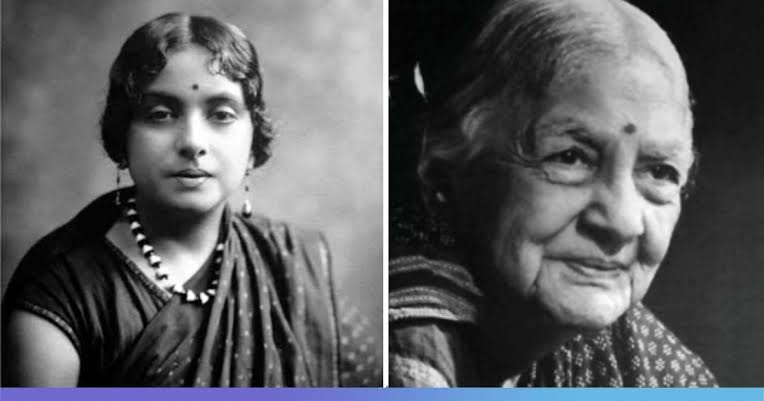
Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay, the unsung feminist freedom fighter in the history of India

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Post-Independence, the revival of the crafts sector began with Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay who strongly championed the handicrafts movement for the role it could play in social and economic upliftment.
About Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay:
- Kamaladevi was born in April 1903 in a liberal Chitrapur Saraswat Brahmin family in Mangalore (now Mangaluru).
- She completed her primary education at the local St Ann’s Convent.
- Growing up in a land with a rich cultural heritage, especially of the music and dance form Yakshagana, she developed a taste for traditional art forms.
- After her father’s untimely death, Kamaladevi moved to her maternal uncle’s house.
- There, she met renowned freedom fighters, including Gopalkrishna Gokhale, Srinivasa Shastri, Ramabai Ranade and Annie Besant.
- Kamaladevi was married off at the age of 14 and widowed two years later.
- Unperturbed by these life events, she joined Queen Mary’s College in Madras (now Chennai) for higher studies.
- There, she met Sarojini (Chattopadhyay) Naidu’s brother Harindranath Chattopadhyay which led to their wedlock.
- However, their marriage ended over incompatibility issues and this, too, created history – Kamaladevi was the first legal divorce granted through an Indian court of law.
- Kamaladevi played a prominent role in political reforms and India’s freedom struggle.
- She was the first woman to contest the Madras provincial elections.
- Though she lost by a narrow margin, she got recognition and was appointed secretary of the All-India Women’s Conference.
- She joined Indian National Congress in 1927 and was elected to the All-India Congress Committee within a year.
- During the Salt March to Dandi, she convinced Gandhi to give women equal opportunity to be in the forefront of the march.
- Later, she joined Seva Dal and trained women activists.
- However, the British government banned Seva Dal and threw Kamaladevi into jail.
- There, she contracted jaundice. Having experienced the pathetic condition of the prison hospital, she built a hospital for inmates upon release.
- Kamaladevi got attracted to socialism and took up the problems of laborers and peasants.
- During World War II, she visited America and met several political activists, mostly blacks, and shared with them India’s non-violent approach to freedom struggle.
- The British got wind of her activism and banned her from returning to India.
- Unmoved, Kamaladevi continued on her journey, visiting South Africa, China, Japan and Vietnam.
- Kamaladevi was inarguably the embodiment of women’s empowerment.
- She was an advocate of female sexual freedom and birth control.
- Her remarriage after widowhood and legal divorce from her second marriage were symbolic of her self-empowerment.
- She acted in many films (a Kannada film, too) when the film industry was not considered a respectable place for women.
- Indeed, Kamaladevi’s immense travel and experiences shaped her as a secular, socialist world citizen.
- Such were her ideals that led to her building the city of Faridabad to rehabilitate some 50,000 craftsmen who moved to India from Pakistan during Partition.
- Post-independence, she helped revive Indian handicrafts and built institutions for a ‘New India’-- to name a few, the National School of Drama, Bharatiya Natya Sangha, Lady Irwin College, Sangeet Natak Academy, Central Cottage Industries Emporium, World Craft Council, Craft Council of India, and the Delhi Craft Council.
- Kamaladevi was a prolific writer, too and wrote 18 books altogether, touching upon women’s issues, Indian handicrafts and her foreign visits.
- She published her autobiography, “Inner Recesses, Outer Spaces: Memoir” (1986).
- She received several awards in recognition of her public service, like Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan, the Ramon Magsaysay Award and the UNESCO Award.
- She died in Mumbai on October 29, 1988, aged 85.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
