La Nina impacted air quality in India in the winter of 2022
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study suggests that monsoon rainfall over India, which is strongly influenced by El Niño and La Niña events—alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean impacting global weather may also affect air quality in the country.
Key Findings of the New Study on the Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- According to the researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Studies (Bengaluru) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (Pune), the strong influence of El Niño and La Niña events on monsoon rainfall over India, driven by the alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns.
- Remarkably, this study marks the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been directly linked to a La Niña event, suggesting an indirect connection to climate change, which intensifies the severity of El Niño and La Niña occurrences.
- Traditionally, northern Indian cities, notably Delhi, face elevated concentrations of PM2.5 pollutants from October to January.
- However, the winter of 2022 witnessed a notable deviation from this trend, with northern cities experiencing cleaner air than usual, while western and southern cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai saw worsened air quality.
- Specifically, Delhi observed a 10% reduction in PM2.5 concentrations, contrasted with a 30% increase in Mumbai and a 20% rise in Bengaluru.
- The researchers, investigating this anomaly, identified the potent effects of the La Niña event, notably stronger than typical occurrences, leading to significant changes in wind circulation patterns over India.
- This impact became pronounced in the third year of La Niña, suggesting a cumulative effect that may amplify over time.
- While La Niña events are associated with improved air quality in northern India, the study emphasizes the need for further research to understand the potential impacts of El Niño events, which may produce contrasting effects on air quality across the country.
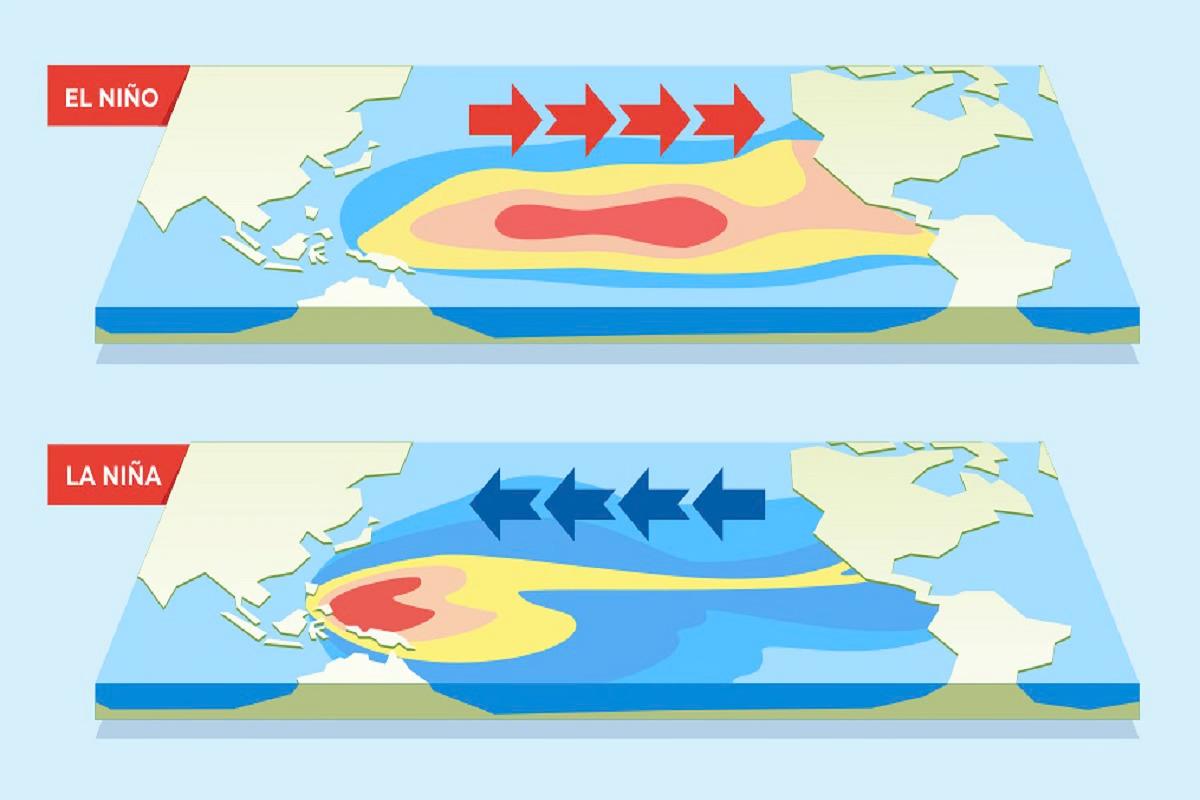
What are El Niño and La Niña?
- El Niño refers to a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Similarly, a La Niña occurs when the band of water spreads east to west and is cooler.
- Both phenomena affect the weather worldwide and can have drastic effects on economies that depend on rainfall.
- Together, El Niño and La Niña make up a cyclical process called the El Niño Southern Oscillation.
- An El Niño year creates a global warming crisis in miniature because the warm water spreading across the tropical Pacific releases a large amount of heat into the atmosphere.
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, El Niño events often correlate with below-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to drought conditions in some regions, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- El Niño can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing warmer temperatures during El Niño events.
- La Niña: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, La Niña events often correlate with above-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to increased precipitation in some regions, potentially causing flooding, while other areas may experience drought conditions.
- La Niña can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing cooler temperatures during La Niña events.
Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- Altering Wind Patterns: During the winter of 2022, the typical north-westerly winds, carrying agricultural pollutants from Punjab and Haryana towards Delhi and the Gangetic plains, were disrupted.
- Instead, wind circulation shifted to a north-south direction, diverting pollutants away from Delhi.
- Consequently, pollutants bypassed Delhi, travelling over Rajasthan and Gujarat towards southern regions.
- Modifying Local Wind Circulation near Mumbai: In Mumbai, the local wind circulation, which alternates between land-to-sea and sea-to-land flows every few days, experienced prolonged unidirectional winds.
- This sustained wind pattern prevented the dispersal of pollutants from the city, leading to their accumulation within Mumbai's atmosphere throughout the winter of 2022.
- These changes in wind patterns, influenced by La Niña, significantly impacted air quality dynamics in India, highlighting the intricate relationship between climate phenomena and regional atmospheric conditions.
Gold Hunt by Villagers Reveals Ancient Harappan Settlement in Gujarat

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The newly discovered Harappan settlement at Lodrani village in the Kutch region of Gujarat has sparked widespread interest in the fascinating remains of this ancient civilisation, making it an important site for archaeological exploration and research.
Features of Harappan site Morodharo:
- Morodharo is a fortified settlement of the Harappan era, with the fortification measuring 102 m to the west and 58 m north to the south.
- The thickness of the wall is 3.3 m on average.
- Morodhara has a 10x10 m platform on the southwest side and a well on the northeast side.
- Burial cairns have been found at Morodharo.
- A cairn is an intentionally constructed mound of stones, typically created for marking a location or serving as a burial mound.
- Harappan pottery with perforated jar sherds, reserved slipware and terracotta cakes have also been unearthed.
- All these items have a striking resemblance to those found in Dholavira.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization, also known as the Indus Valley civilization was South Asia's first urban civilization, flourishing concurrently with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- It encompassed the most extensive territory, covering approximately 800,000 square kilometres, compared to its contemporaries.
- Prominent cities during the Harappan period included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in present-day Pakistan, along with Dholavira, Lothal, and Surkotada in Gujarat, India, among others.
- Urban planning in Harappan cities followed a meticulous grid layout, with streets intersecting at right angles, dividing the cities into neat rectangular blocks.
- The streets and alleys were deliberately designed for efficient movement, accommodating carts and pedestrians, often featuring covered drains alongside.
- For defence and security, the cities were enclosed by sturdy walls made of mud bricks, shielding against intruders and natural calamities.
- Each city was structured into an elevated citadel and a lower town, with the former housing monumental structures like granaries and administrative buildings.
- Residential areas comprised multi-story brick houses clustered around courtyards, some equipped with private wells and well-ventilated bathrooms.
- A sophisticated drainage system ensured efficient waste disposal, with individual house drains connected to street-level drainage networks.
- Granaries and storage facilities were strategically positioned to manage surplus agricultural yields, reflecting advanced urban planning and resource management.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Hundred years ago, Satyendra Nath Bose changed physics forever
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2024, we commemorate the centenary of Bose's pivotal discovery of the precise equations governing the behaviour of collections of photons, fundamental particles of light.
About Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974) was an eminent Indian physicist renowned for his pioneering contributions to theoretical physics, notably in the realms of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics.
- His groundbreaking research laid the groundwork for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theoretical elucidation of Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Bose's profound insights not only advanced the understanding of fundamental physics but also played a pivotal role in refining the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
- His visionary work eventually paved the way for significant discoveries in particle physics, including the identification of the Higgs Boson, colloquially referred to as the "God Particle."
Major Contributions of Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Foundation of Bose-Einstein Statistics and Bosons: In 1924, Bose formulated a revolutionary explanation for Planck's law of black-body radiation using quantum mechanics principles, introducing the concept of "Bose-Einstein statistics."
- This theory delineates the behaviour of particles known as "bosons," characterized by integer spin.
- Bose-Einstein statistics elucidate how bosons, such as photons and atoms, preferentially occupy the same quantum state, a behaviour distinct from fermions governed by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- This groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for understanding particle behaviour at low temperatures and foretold the existence of the Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Prediction of Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose's collaboration with Einstein in statistical mechanics led to the theoretical prediction of the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), a revolutionary concept in quantum physics.
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, at ultra-low temperatures approaching absolute zero, bosons can congregate in the lowest energy state, forming a condensed state.
- Often dubbed the "fifth state of matter," BEC occurs when bosons lose sufficient energy to coalesce into a single quantum state, creating a cohesive "super-particle" cloud.
- Experimental confirmation of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, decades after Bose's theoretical proposal, garnered Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001.
- Together with Meghnad Saha, he published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- His dedication to research and scientific integrity earned him numerous accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan and the Fellowship of the Royal Society.
