Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
BharatGen Initiative
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
BharatGen is a pioneering generative AI initiative launched in New Delhi, aimed at revolutionizing public service delivery and enhancing citizen engagement, with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State, in virtual attendance.
- Significance
- Represents India's commitment to advancing homegrown technologies.
- Positions India as a global leader in generative AI, similar to achievements with UPI and other innovations.
- Marks the world's first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model project focusing on Indian languages.
- Leadership and Implementation
- Spearheaded by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Collaboration with the TIH Foundation for IoT and various academic partners, including IITs and IIMs.
- Key figures involved include Prof. Shireesh Kedare (Director, IIT Bombay) and Prof. Ganesh Ramakrishnan (consortium leader).
- Core Objectives
- Deliver generative AI models as a public good, prioritizing socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Address broader needs such as social equity, cultural preservation, and inclusivity.
- Make AI accessible for industrial, commercial, and national priorities.
- Key Features
- Multilingual and Multimodal Models: Capable of handling text and speech in multiple languages.
- Bhartiya Data Sets: Focus on India-centric data collection and training.
- Open-Source Platform: Promotes collaboration and innovation in AI research.
- Ecosystem Development: Fosters a robust AI research community.
- Project Timeline and Impact
- Expected completion in two years, with benefits for government, private, educational, and research institutions.
- Ensures coverage of India’s diverse linguistic landscape through multilingual datasets.
- Emphasis on data sovereignty to strengthen control over digital resources.
- Alignment with National Goals
- Supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
- Aims to strengthen the domestic AI ecosystem for startups, industries, and government agencies.
- Focuses on democratizing access to AI for innovators and researchers.
- Research and Community Engagement
- Data-efficient learning for languages with limited digital presence.
- Development of effective models with minimal data through research collaborations.
- Initiatives to foster an AI research community, including training programs and hackathons.
- Future Roadmap
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
- Extensive AI model development and experimentation.
- Establishment of AI benchmarks tailored to India’s needs.
- Scaling AI adoption across industries and public initiatives.
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise, KAZIND-2024, has commenced in Auli, Uttarakhand, running from September 30 to October 13, 2024.
Key Details:
- Joint Exercise KAZIND-2024 has been held annually since 2016.
- Last edition of the Joint Exercise was held at Otar, Kazakhstan from 30th October to 11th November 2023.
Participants:
- India:
- 120 personnel from KUMAON Regiment of the Indian Army
- Additional support from other arms and Indian Air Force
- Kazakhstan:
- Personnel primarily from Land Forces and Airborne Assault Troopers
Aim:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations
- Focus on sub-conventional scenarios under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
Focus Areas:
- Operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrains
- High physical fitness levels
- Rehearsal and refinement of tactical drills
- Sharing best practices
Tactical Drills:
- Joint response to terrorist actions
- Establishment of a Joint Command Post
- Creation of an Intelligence and Surveillance Centre
- Securing helipad/landing sites
- Combat free fall and Special Heliborne Operations
- Cordon and Search operations
- Employment of drones and counter-drone systems
Outcomes Expected:
- Sharing of tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations
- Development of interoperability between the two armies
- Strengthening of bonhomie and camaraderie
- Enhancement of defense cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
La Nina and North India’s pollution
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research by scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) has underlined the links between climate change, La Niña and air quality.
Key Points on Air Quality Outlook for Delhi and North India
- Delayed La Niña & Monsoon Retreat:
- Erosion of optimism for improved air quality this winter in Delhi.
- Significant pollution challenges anticipated in early winter months.
- Possible relief in December and January, contingent on La Niña strengthening.
- Impact of Stubble Burning:
- If stubble burning occurs at half the intensity of previous years, November air quality may deteriorate.
- Research Insights:
- Study by National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) links climate change, La Niña, and air quality.
- Notable air quality improvement in winter 2022-23 was linked to La Niña conditions.
- Late onset of La Niña contributes to air quality uncertainty.
- Changing Pollution Dynamics:
- Shift from local emission-centric views to broader climatological factors is necessary.
- Air quality in Delhi worsens during winter due to high humidity, calm winds, and poor pollutant dispersion.
- La Niña Delays:
- Delayed La Niña onset means weak winds and stagnant conditions, worsening pollution.
- Expected development between September and November 2024.
- Effects of Stubble Burning:
- North-north-westerly winds could carry pollution from stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana into Delhi.
- Potential Outcomes of Late La Niña Onset:
- If La Niña develops in December or January, may improve air quality slightly.
- However, a longer, severe winter could exacerbate pollution issues due to lower inversion layers.
- NIAS-SAFAR Model Predictions:
- Early La Niña could have worsened air quality in the peninsular region.
- Early onset might have improved northern air quality.
- Link to Climate Change:
- Evidence suggests extreme air pollution correlates with climate change.
- Emphasizes the need for rigorous mitigation efforts and broader airshed management.
- Call for Rethinking Air Quality Strategies:
- Focus on integrating larger climatic factors into air quality policies.
- Prioritize health-centric measures through collaborative efforts with scientific bodies.
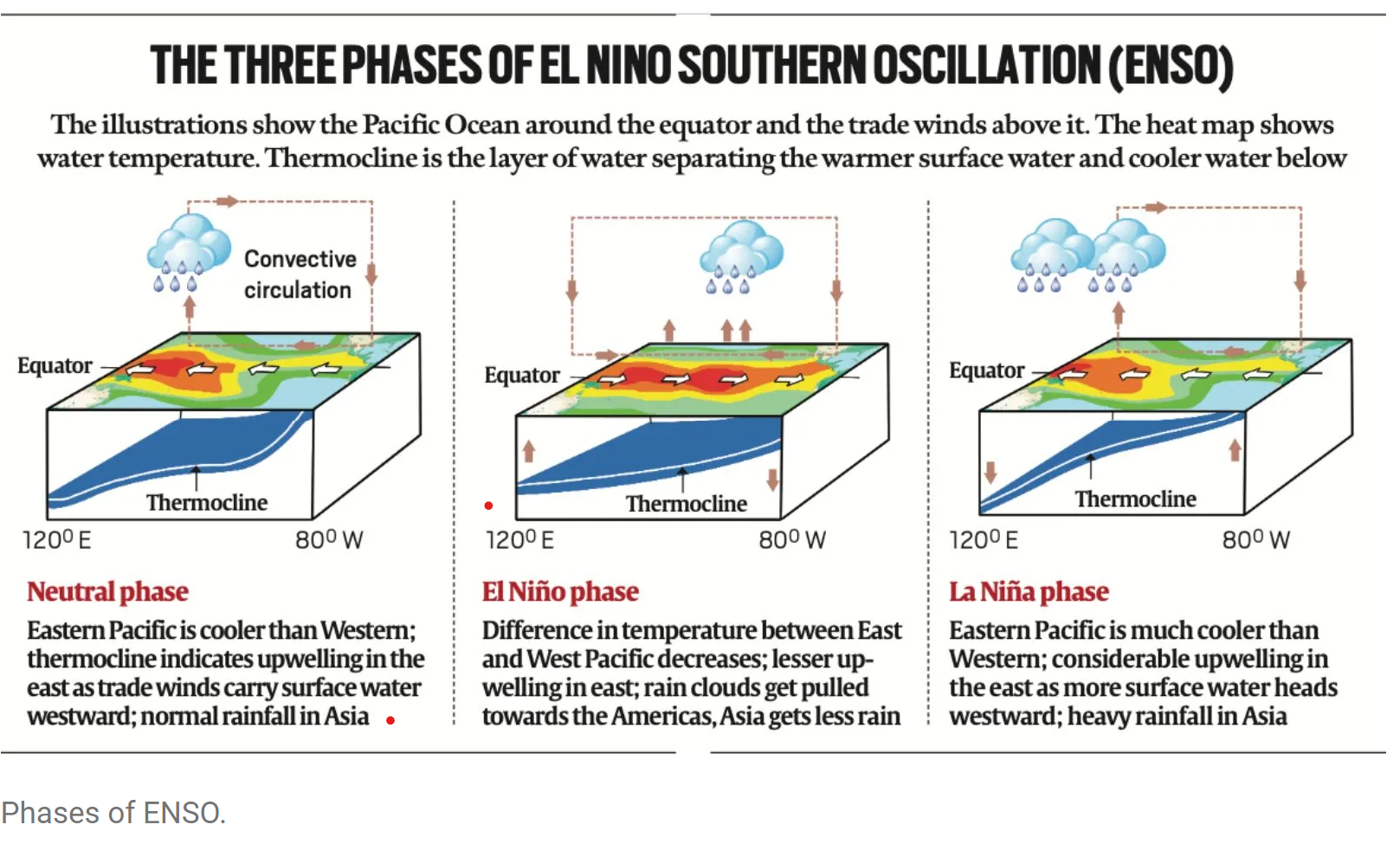
What is La Niña?
- La Niña (or ‘The Little Girl’ in Spanish) is a phase of what climatologists refer to as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a phenomenon that is a key driver of global natural climate variability.
- ENSO is characterised by changes in sea temperatures along the tropical Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric fluctuations overhead. These changes alter and interfere with the global atmospheric circulation, and influence weather worldwide.
- Occurring in irregular cycles of anywhere between two to seven years, ENSO has three phases — warm (El Niño or ‘The Little Boy’ in Spanish), cool (La Niña), and neutral.
- During the neutral phase, the eastern Pacific (off the northwestern coast of South America) is cooler than the western Pacific (around Philippines and Indonesia). This is because prevailing trade winds — caused by Earth’s rotation, between 30 degrees north and south of the equator — move east to west, sweeping warmer surface water along with them. The relatively cool waters from below rise to the surface to replace the displaced water.
- These wind systems weaken in the El Niño phase, leading to lesser displacement of warmer waters off the American coasts. Consequently, the eastern Pacific becomes warmer than usual. The opposite happens in the La Niña phase i.e. trade winds become stronger than usual and push larger quantities of water to the western Pacific.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
