11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
Cicada

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
North American cicadas have life cycles that last for prime numbers of years, putting pressure on the idea that humans created mathematics.
What are Cicadas?
- Classification: Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Physical Features: Hemipteran insects (also known as true bugs) have piercing-sucking mouthparts and two pairs of wings.
- Life Span: Cicadas spend the majority of their life underground, feeding on plant sap. Once they emerge from the soil, they have a short adult life span of about 2 to 4 weeks.
Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Cicadas are typically found in natural forests with large trees and are considered canopy dwellers.
- Global Distribution: Cicadas are found on every continent except Antarctica. The highest genetic diversity of cicadas is found in India and Bangladesh, followed by China.
Cicada Emergence and Life Cycle:
- Life Cycle: Cicadas have a complex life cycle, involving long periods of underground development followed by brief adult emergence.
- Periodical Cicadas: There are species of cicadas that emerge in 13-year and 17-year cycles.
- Broods: Initially, 30 broods were categorized based on geography and emergence times, but currently, only about 15 broods remain active due to some broods becoming extinct.
- Unique Phenomenon: In April 2024, a rare event is expected where a trillion cicadas from two different broods will emerge simultaneously in the Midwest and Southeast regions of the United States.
Cicada's underground Development:
- Feeding on Sap: During their underground phase, cicadas feed on the sap of plants.
- Purpose of Long Development: Researchers believe the long development period helps cicadas evade above-ground predators by keeping them hidden in the soil.
Vulnerability after Emergence:
- Emergence Behavior: Once cicadas emerge, they construct a "cicada hut" to shed their nymphal skins, then climb onto nearby trees or vegetation.
- Predator Vulnerability: Adult cicadas are vulnerable to predators such as turtles and other forest creatures because they are clumsy and defenseless, making them easy prey for predators.
Significance of the 2024 Emergence:
- The coinciding emergence of cicadas from different broods (13-year and 17-year cycles) is a rare event that highlights the complexity and mathematical precision behind the cicada life cycle.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
GQ-RCP Platform
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
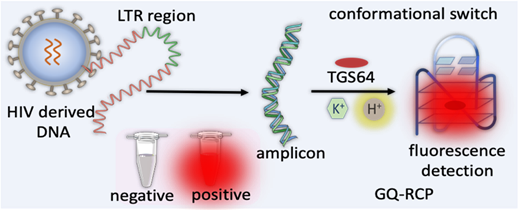
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted better detection of HIV-genome derived G-Quadruplex (GQ).
Key Features of the GQ-RCP Platform
- Technology: GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform developed by Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR).
- Detection Mechanism: Uses a fluorometric test to detect HIV-derived GQ DNA through reverse transcription and amplification.
- Advantage: Increases diagnostic reliability by reducing false positives associated with non-specific DNA probes.
- Process: pH-mediated transition of double-stranded DNA into GQ conformation for targeted detection.
- Flexibility: Initially designed for SARS-CoV-2, now adapted for HIV diagnosis.
About HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, specifically CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections.
- Transmission: Spread through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- AIDS: Without treatment, HIV progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system becomes severely damaged.
- Management: No cure; managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which controls viral replication.
Current HIV Situation in India
- Prevalence: As of 2021, ~2.4 million people living with HIV in India, with a 0.22% adult prevalence rate.
- Demographic Distribution: High prevalence among female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users (5.91%). Women represent 39% of HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: Northeastern states have the highest prevalence (e.g., Mizoram - 2.70%) and southern states (e.g., Andhra Pradesh - 0.67%).
Government Initiatives on HIV
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP): Launched in 1992, aims for prevention, treatment, and care.
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focus on awareness, blood safety, and surveillance.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded interventions for high-risk populations.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Increased targeted interventions and civil society involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Focused on integration of HIV services into public health systems.
- Phase V (2021-2026): Aim to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2026.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) ensures the rights of people living with HIV and access to treatment without discrimination.
- International Support: India receives support from UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and foundations like Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Global Soil Conference 2024
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
- Global Soil Conference (GSC) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- Focused on soil health's importance for food security, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem services.
What is the Global Soil Conference 2024?
- Organizers: Indian Society of Soil Science (ISSS) in collaboration with the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- Objective: Address sustainable soil/resource management challenges and foster global dialogue.
- Theme: "Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services."
Key Highlights of GSC 2024:
- Soil Health Issues:
- Soil degradation threatens productivity and global food security.
- 30% of India's soil is compromised by erosion, salinity, pollution, and organic carbon loss.
- Soil erosion is linked to SDG 15 (Sustainable Development Goal 15), aiming to protect terrestrial ecosystems.
- SDG 15:
- Goals: Promote sustainable land use, combat desertification, halt land degradation, protect biodiversity.
Concerns Regarding Soil Health in India:
- Soil Degradation:One-third of India's land faces degradation due to poor farming practices.
- Soil Erosion & Fertility Loss:
- India loses 15.35 tonnes of soil/hectare annually.
- Results in crop losses, economic damage, and environmental issues like floods and droughts.
- Soil Salinity:Reduces water infiltration, nutrient uptake, and aeration, making land infertile.
- Low Organic Content:
- Organic carbon in Indian soil is 0.54%, which hampers fertility.
- Over 70% of soils are affected by acidity or alkalinity, disrupting nutrient cycles.
- Desertification:Reduces soil fertility, increases erosion, and worsens food insecurity.
- Diversion of Fertile Land:Fertile agricultural land is diverted for non-agricultural purposes.
India's Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme:Provides farmers with soil nutrient information.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:Focuses on efficient water use.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming & Natural Farming Mission:Promotes sustainable farming practices to protect soil health.
