AMRUT scheme

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Around 36% of India’s population is living in cities and by 2047 it will be more than 50%. The World Bank estimates that around $840 billion is required to fund the bare minimum urban infrastructure over the next 15 years.
About Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT):
- AMRUT was launched to enhance the quality of life by providing basic civic amenities, especially benefiting the poor and disadvantaged.
- The mission focuses on infrastructure development to deliver better services to citizens.
- AMRUT covers 500 cities, including all cities and towns with a population of over one lakh that have notified Municipalities.
About AMRUT 2.0:
- AMRUT 2.0 will promote circular economy of water through development of City Water Balance Plan (CWBP) for each city focusing on recycle/reuse of treated sewage, rejuvenation of water bodies and water conservation.
- It will help cities to identify scope for projects focusing on universal coverage of functional water tap connections, water source conservation, rejuvenation of water bodies and wells, recycle/reuse of treated used water, and rainwater harvesting.
- Based on the projects identified in CWBP, Mission envisages to make cities ‘water secure’ through circular economy of water.
The target in the second phase of AMRUT is to:
-
- Improve sewage and septic management
- Make cities water-safe
- Ensure no sewage drains into rivers
- AMRUT 2.0 focuses on enhancing sewerage and septic management to make all Indian cities water secure.
Aim:
- Achieve 100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 urban local bodies by providing about 2.68 crore tap connections.
- Achieve 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities by providing around 2.64 crore sewer or septage connections.
Principles and Mechanism:
- Adopt principles of the circular economy to promote conservation and rejuvenation of surface and groundwater bodies.
- Promote data-led governance in water management and leverage the latest global technologies and skills through a Technology Sub-Mission.
- Conduct 'Pey Jal Survekshan' to encourage competition among cities for better water management.
Coverage:
- Extend coverage from 500 cities in the first phase to 4,700 cities and towns.
- Benefit more than 10.5 crore people in urban areas.
Analysis of the AMRUT Scheme:
Performance of the Scheme:
- As of May 2024, the AMRUT dashboard reports that ?83,357 crore has been disbursed. This funding has facilitated:
- 58,66,237 tap connections
- 37,49,467 sewerage connections
- Development of 2,411 parks
- Replacement of 62,78,571 LED lights
Criticism of the Sheme:
Despite these achievements, significant issues persist:
- Approximately 2,00,000 people die annually due to inadequate water, sanitation, and hygiene.
- In 2016, India's disease burden from unsafe water and sanitation was 40 times higher per person than China's, with minimal improvement since then.
- Large volumes of untreated wastewater increase disease vulnerability.
- Around 21 major cities are expected to run out of groundwater. A NITI Aayog report predicts that 40% of India's population will lack access to drinking water by 2030.
- Nearly 31% of urban households lack piped water, and 67.3% are not connected to a piped sewerage system.
- The average urban water supply is 69.25 litres per person per day, far below the required 135 litres.
- Air quality in AMRUT cities and other urban areas continues to worsen.
- While the National Clean Air Programme was launched in 2019 to address air quality, AMRUT 2.0 focuses primarily on water and sewerage issues.
Challenges:
The AMRUT scheme has faced several fundamental challenges:
- Project-Oriented Approach: The scheme adopted a project-oriented rather than a holistic approach.
- Lack of City Participation: It lacked significant involvement from elected city governments, being driven instead by bureaucrats, parastatals, and private companies.
- Governance Issues: Governance was dominated by non-elected officials, violating the 74th constitutional amendment.
- The apex committee was led by the MOHUA secretary, and state committees were headed by chief secretaries, excluding people's representatives.
- Private Nexus: The scheme favored a private nexus of consultants and professionals, sidelining local elected officials.
- Water Management: Effective water management in cities requires consideration of climate, rainfall patterns, and existing infrastructure, which the scheme did not adequately address.
- Inefficient Sewage Treatment: Sewage treatment plants were inefficiently designed, with faecal matter traveling longer distances than the average worker's commute.
- Urban Planning: Driven by private players and real estate developers, urban planning often led to the disappearance of water bodies, disrupted stormwater flows, and a lack of proper stormwater drainage systems.
Way Forward:
To improve the AMRUT scheme:
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implement nature-based solutions.
- Comprehensive Methodology: Adopt a comprehensive methodology that integrates all aspects of urban development.
- People-Centric Approach: Focus on a people-centric approach, involving local communities in decision-making.
Empower Local Bodies: Empower local bodies to take a leading role in governance and implementation.
New Light-based Tool to Detect Viral Infections

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A viral infection can stress cells and change their shapes and sizes. Researchers have built a tool to detect these changes.
About the new Tool:
- A team of researchers has developed an innovative method to detect viral infections in cells using only light and principles of high-school physics.
- The key insight is that viral infections can stress cells, causing changes in their shapes, sizes, and other features.
- As the infection progresses and the body becomes diseased, these changes become more pronounced.
- The researchers have found a way to translate these cellular changes into recognizable patterns that can indicate whether a cell is uninfected, virus-infected, or dead.
- For example, virus-infected cells tend to be elongated and have clearer boundaries compared to uninfected cells.
- By analyzing the patterns of light interacting with cells, this method can non-invasively differentiate between uninfected, virus-infected, and dead cells.
- This approach has the potential to revolutionize viral disease diagnosis and monitoring, providing a simple, cost-effective, and powerful tool for detecting viral infections at the cellular level.
Significance:
- This light-based approach to detecting viral infections offers several significant advantages over the current standard methods:
- Accuracy: The new light-based technique can detect viral infections with equal or even greater accuracy compared to existing standard methods that rely on chemical reagents.
- Cost-effectiveness: The equipment required for this new method costs only around one-tenth of the $3,000 (approximately Rs 2.5 lakh) needed for the standard chemical-based approach, making it a far more affordable option, especially for resource-constrained settings.
- Rapid results: The light-based method can identify virus-infected cells in just about two hours, significantly faster than the 40 hours required by the current standard method.
- This time efficiency can be crucial in situations where rapid detection is essential, such as during a virulent disease outbreak.
- Early detection: By enabling the early detection of viral infections at the cellular level, this new technique could prove invaluable in containing the spread of highly contagious viral diseases, such as a severe influenza outbreak.
What are Viruses?
- Viruses are microscopic organisms capable of infecting various hosts such as humans, plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
- Structurally, they consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protective shell called a capsid, with some viruses also possessing an envelope.
- Unable to reproduce independently, viruses rely on host cells to replicate by utilizing the cell's machinery.
- Common types include influenza viruses, human herpesviruses, coronaviruses, human papillomaviruses, enteroviruses, flaviviruses, orthopoxviruses, and hepatitis viruses.
- Viruses are responsible for causing illnesses such as flu, the common cold, and COVID-19.
Dag Hammarskjold Medal

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Indian peacekeeper who lost his life serving under the UN flag is among over 60 military, police and civilian peacekeepers to be honoured posthumously with a prestigious medal for their service and supreme sacrifice in the line of duty.
What is Dag Hammarskjold Medal?
- The Dag Hammarskjold medal is a prestigious honour commemorating the ultimate sacrifice made by United Nations peacekeepers.
- Established in 1997, it pays tribute to those who have lost their lives while serving in UN peacekeeping missions under the organization's operational control and authority.
- This posthumous award is presented annually on Peacekeeper's Day at a solemn ceremony held at the United Nations headquarters in New York.
- Each member state that has had military or police personnel perish during peacekeeping duties receives the medal in recognition of their fallen compatriots.
- The medal bears the name of Dag Hammarskjold, the second Secretary-General of the United Nations, whose own life was tragically cut short in 1961 while working to resolve the Congo crisis.
- In naming this honour after him, the UN commemorates both his exceptional leadership and the courageous individuals who have followed in his footsteps by making the ultimate sacrifice for the cause of global peace and security.
India’s Role in Peacekeeping:
- India is currently the second largest contributor of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping after Nepal.
- India is followed by Uganda with 5,764 personnel, and Bangladesh with 5,393.
- These personnel are deployed across 12 UN peacekeeping missions across the world.
- Traditionally, India has always been among the biggest contributors of UN peacekeepers.
- Since 1950, approximately 2, 86,000 Indian soldiers have served in the UN across the globe.
- UN peacekeeping missions are mandated under Article 99 by which the Secretary-General is granted the authority to independently address potential global conflicts or threats.
- Also seen as a very robust diplomatic tool, it is also a way in which the Secretary-General flags the issue to the UN Security Council.
- The functions of UN peacekeeping operations range from maintaining peace and security to escorting humanitarian relief, upholding human rights, supporting the fight against gender-based violence to assist in the restoration of the rule of law and facing the complex crises of today from climate change to pandemic.
Microcephaly
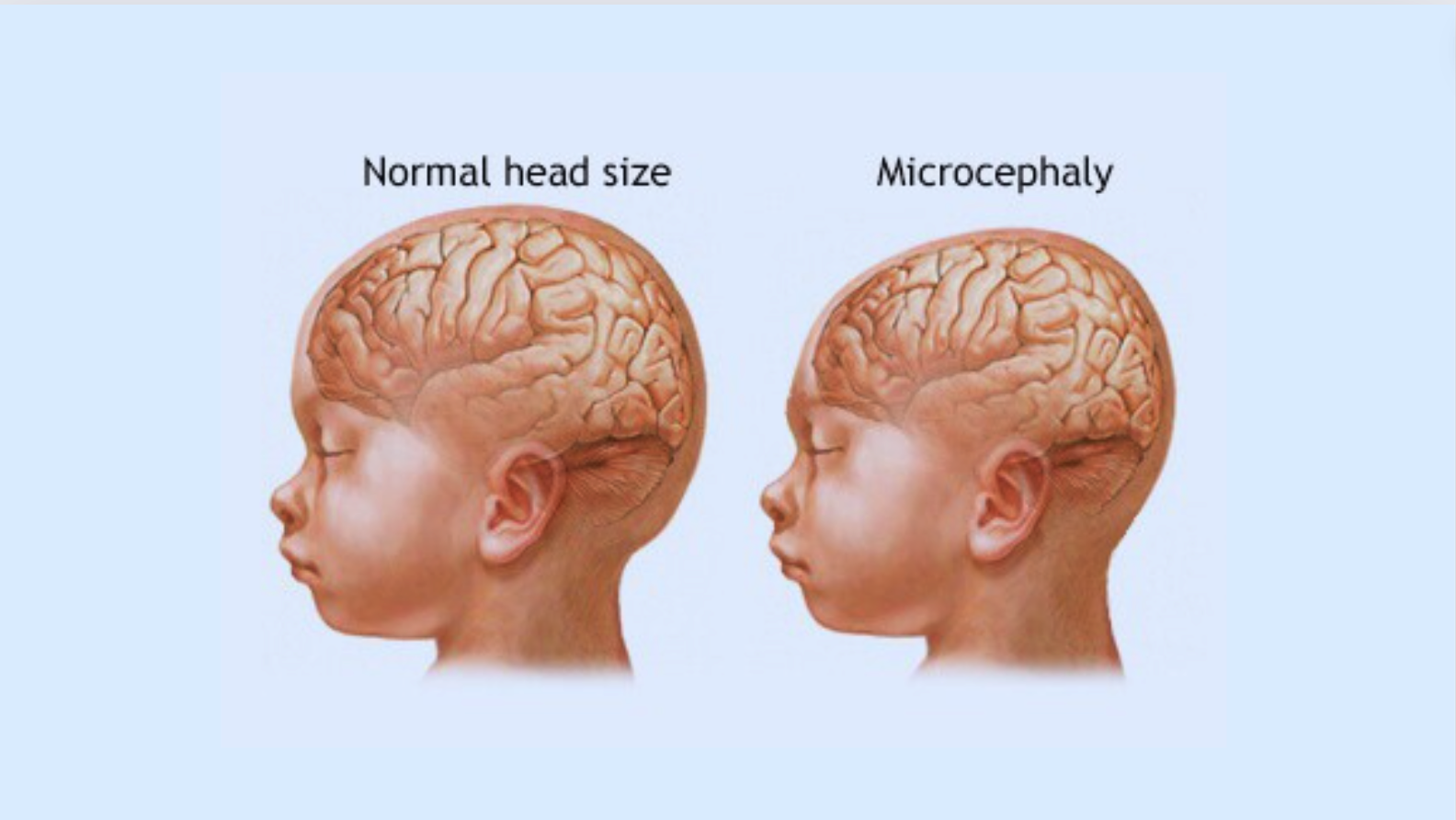
- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study recently revealed that a gene called SASS6 and its variants have been implicated in a developmental process that causes microcephaly.
What is Microcephaly?
- Microcephaly is a condition where a baby's brain and head do not develop properly during pregnancy or after birth.
- While rare, it can have profound impacts on a child's cognitive and physical abilities.
- Several factors can disrupt normal brain growth, including infections the mother contracts while pregnant, exposure to toxic substances, genetic disorders, lack of proper nutrition, and injuries before or around the time of birth.
- Infants with microcephaly are born with abnormally small heads compared to others of the same age and sex.
- This small head size indicates an undersized brain.
- As they grow older, many children with microcephaly experience significant developmental delays and disabilities.
- Common symptoms include intellectual disability, impaired motor skills and speech, vision and hearing problems, seizures, and unusual facial features.
- Some cases may show no obvious symptoms at birth, only for challenges to emerge over time.
- Treatment: Unfortunately, there is no cure for microcephaly itself.
- However, early intervention programs, therapies, and educational supports can help manage symptoms and maximize the child's developmental potential within their abilities.
- While microcephaly's causes are varied, maintaining good health before and during pregnancy gives a baby the best chance for proper brain growth.
Preventing prenatal infections, avoiding toxins, getting prenatal screening for disorders, and ensuring adequate nutrition all reduce microcephaly risk.
eMigrate Project

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Ministry, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Common Services Centers eGovernance Services India Limited have signed a Memorandum of Understanding today to provide the eMigrate services through CSC in the country.
What is the eMigrate Project?
- eMigrate project is undertaken to assist mainly the blue-collar workers going to Emigration Check Required (ECR) countries.
- The project was conceptualized to address issues faced by migrant workers by making the emigration process online seamless and also to bring foreign employers registered recruitment agents and insurance companies on one common platform aimed at promoting safe and legal migration.
- Over the years, the number of Indians going abroad for employment has been increasing as well as the contribution of remittances sent by them has been significant.
- Under this MoU, the eMigrate Portal of MEA would be integrated with CSC’s portal, to provide the following eMigrate services to the citizens through CSCs:
- Facilitate registration of applicants on the eMigrate portal through CSCs.
- Facilitation of uploading and processing of the required documents for the applicants on the eMigrate portal through CSCs.
- Facilitate and support booking for medical and other services required by migrant workers or applicants registered on the eMigrate portal through CSC.
- Creating awareness about eMigrate services amongst citizens across India.
About Common Service Centre (CSC):
- Common Services Centers (CSCs) are an integral part of the Digital India mission.
- The CSCs are frontend service delivery points for the delivery of digital services to the citizens, especially in rural and remote areas across the country.
- This helps in contributing towards the fulfilment of the vision of Digital India and the government’s mandate for a digitally and financially inclusive society.
- Currently, more than 5.50 lakh CSCs are delivering more than 700 digital services to citizens in assisted mode with enhanced ease and convenience.
- Apart from delivering essential government and public utility services, CSCs also deliver a range of social welfare schemes, financial services, educational courses, skill development courses, healthcare, agriculture services, digital literacy, etc.
