Data | Sharp rise in Indians illegally crossing U.S. northern border from Canada (The Hindu)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the last ten years, the number of unauthorized Indian migrants entering the U.S. has surged significantly, climbing from a mere 1,500 a decade ago to an astonishing 96,917 in 2023, as reported by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
What are the Implications for India Amidst the Surge in Illegal Migrants?
- Bilateral Relations: The surge in illegal migration poses potential challenges to bilateral relations between India and the USA, impacting areas such as trade negotiations, security cooperation, and strategic partnerships.
- Economic Factors: India faces the risk of a brain drain, as skilled individuals seek illegal entry, potentially affecting sectors with a demand for skilled labour and impacting the country's economy.
- The outflow of skilled and educated individuals through illegal migration can have adverse effects on India's economy, leading to a depletion of talent and expertise.
- Labour Market Challenges: The departure of skilled or semi-skilled workers may create labour shortages in specific sectors, affecting India's workforce and economic productivity.
- Policy Repercussions: India may need to institute stringent policies to address the root causes of illegal migration, potentially diverting resources and attention from other developmental priorities.
What are the Causes Behind the Surge in Illegal Indian Migrants to the USA?
- Pull Factors: The USA's reputation for offering improved employment prospects, higher wages, and career advancement acts as a significant attraction for migrants.
- The allure of quality education and prestigious academic institutions in the USA attracts students and families in search of educational opportunities.
- The desire to reunite with family members or relatives already settled in the USA motivates some migrants to seek illegal entry for proximity to loved ones.
- Push Factors: Numerous push factors, including limited job opportunities and economic prospects in India, drive individuals to seek better employment opportunities abroad.
- Social conflicts or a lack of confidence in India's governance structure may prompt some individuals to search for a more stable environment elsewhere.
- Visa Backlogs and Alternative Routes: Smugglers adapt their methods, providing sophisticated services to facilitate illegal entry into America.
- Prolonged visa backlogs prompt individuals to explore alternative, albeit illegal, pathways to enter the USA due to extended waiting times and limited legal entry options.
- Global Migration Trends: The overall increase in global migration post-pandemic contributes to this surge as individuals seek improved opportunities and security in different countries.
- Misinformation: Social media and deceptive travel agencies disseminate misinformation, misleading desperate migrants and encouraging them to embark on perilous journeys guided by multiple facilitators across continents.
- Desperate migrants may undertake complex, multi-leg journeys through various continents and countries, facing numerous risks and challenges along the way.
What can be Done?
Prioritizing economic stability, job creation, and social welfare programs to alleviate distress and offer improved opportunities within India. Initiating diplomatic dialogues to comprehend and address concerns that contribute to migration, fostering collaboration with other nations to safeguard the rights of migrants.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
NASA all set to launch of PACE mission to study air quality, key climate factors and more (NASA)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
NASA is ready to enhance our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere with the upcoming Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, scheduled for launch in early 2024.
What is NASA's PACE Mission?
- The mission will leverage advanced polarimeters to investigate the intricate interactions of light, aerosols, and clouds, enhancing our understanding of their impact on both air quality and climate.
- Beyond aerosol analysis, the PACE mission will delve into the study of ocean colour.
- At its core, the Ocean Colour Instrument (OCI) serves as the primary science instrument for PACE, designed to measure the ocean's colour across a spectrum ranging from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared.
- The mission includes two polarimeters:
- The Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and
- The Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2)
- Working in tandem, these instruments offer complementary spectral and angular sampling, ensuring polarimetric accuracy and extensive spatial coverage.
- This integrated approach aims to deliver enhanced atmospheric correction and a comprehensive dataset on aerosols and clouds, surpassing the capabilities of OCI alone.
- The collaborative payload of OCI, SPEXone, and HARP2 is poised to achieve significant breakthroughs in aerosol-cloud-ocean research.
What are Aerosols and their Effect?
- Aerosols are comprised of liquid or solid particles suspended in a gaseous or liquid medium.
- In the atmosphere, these particles are predominantly found in the lower layers (< 1.5 km) since aerosol sources are terrestrial.
- However, specific aerosols may extend into the stratosphere, particularly those ejected by volcanoes at high altitudes.
- Sources of Aerosols:
- Natural Sources: Generated from breaking waves (sea salt), wind-blown mineral dust from the surface, and volcanic emissions.
- Anthropogenic Aerosols: These include sulphate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols, primarily originating from fossil fuel combustion.
- Effects of Aerosols:
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry.
- Reduction of Visibility.
- Significance for Air Quality and Human Health: Aerosols can adversely affect the heart and lungs.
- Role as Nuclei: Serve as nuclei for cloud droplets or ice crystals in ice clouds.
Mumps outbreak: Worrying symptoms to watch out for, preventive tips (India TV)
- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A mumps outbreak has recently been reported in several states across the country, causing concern among public health officials.
What is Mumps Disease?
- Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
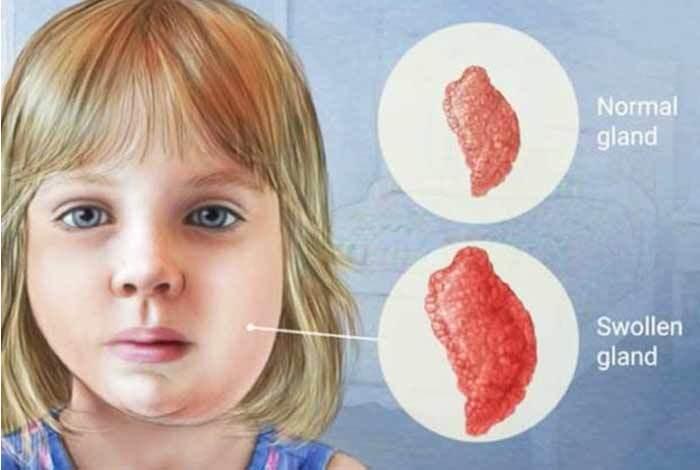
- It typically involves painful swelling in the parotid salivary glands, located on the sides of the face below and in front of the ears.
- These swollen glands often give the infected person a characteristic "chipmunk-cheek" appearance.
- Humans are the only known host for the mumps virus, which is spread via direct contact or by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of infected individuals.
- Transmission of mumps: Mumps is spread through contact with the saliva or respiratory droplets of an infected person. This can happen through coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing utensils, or close contact.
- Symptoms:
- Mumps typically manifest after an incubation period of 2 to 4 weeks, starting with nonspecific symptoms like myalgia, headache, malaise, and low-grade fever.
- Within days, these initial symptoms progress to the swelling of the parotid salivary glands, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with other salivary glands affected in 10% of cases.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and effective for most people.
- Other preventive measures include practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your coughs and sneezes.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for mumps. Most people recover on their own within a few weeks.
- Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as with pain relievers and fever reducers.
- In general, mumps is a mild, self-limiting disease that resolves without lasting effects.
- However, complications can arise, including encephalitis or sensorineural deafness.
- Orchitis, a painful inflammation of the testes, occurs in approximately 20% of young adult males who contract mumps.
The Hindu Parliament security breach | 14 Opposition MPs suspended from House amid face-off (LiveMint)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Fourteen MPs have been suspended for "unruly conduct" as stormy scenes played out in Parliament in the wake of the massive security breach recently.
Context:
- A total of 14 MPs, 13 from Lok Sabha and one from Rajya Sabha, were suspended from Parliament on Thursday for the remainder of the Winter Session.
- This follows after stormy scenes played out in Parliament on Thursday, December 14, in the wake of the massive security breach a day before.
- Earlier in the day, TMC member Derek O'Brien was suspended from the Rajya Sabha for the remainder of the Winter session for "unruly behaviour" and "misconduct".
Suspension of MPs:
- The Presiding Officer, whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, plays a crucial role in maintaining order for the smooth functioning of the House.
- Empowered to uphold proper proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman has the authority to compel a Member to withdraw from the House, ensuring the orderly conduct of parliamentary affairs.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer/Chairman acts?
- In Lok Sabha: Rule 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business empowers presiding officers to direct an MP to withdraw for disorderly conduct.
- The suspended Member must remain absent for the remainder of the day's sitting.
- Rules 374 and 374A are invoked for more persistent disruptions.
- Rule 374 allows the Speaker to name legislators for continued disruptions, leading to a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Rule 374A, added in December 2001, facilitates automatic suspension for five days or the remaining session part.
- In Rajya Sabha: Rule 255 grants the Chairman the authority to immediately direct withdrawal for disorderly conduct.
- Rule 256 enables the Chairman to name members persistently disregarding the Chair's authority or abusing Council rules.
- The House may then pass a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot suspend members without a formal motion.
Judicial Oversight in MP Suspension Cases:
- While Article 122 of the Indian Constitution shields parliamentary proceedings from judicial review, there are instances of courts intervening in legislative procedures.
- In a case involving the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly's 2021 Monsoon Session, where 12 BJP MLAs were suspended for a year, the Supreme Court stepped in.
The Court ruled that the assembly's resolution had legal limitations and was only applicable for the duration of the Monsoon Session, underscoring the judiciary's role in assessing the legality and effectiveness of legislative actions.
