India’s Polio Eradication Journey

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's achievement of becoming polio-free in 2014 stands as one of the most remarkable successes in global public health. This milestone, which was celebrated worldwide, represents decades of consistent efforts, collaboration, and innovative strategies, culminating in the elimination of wild poliovirus in the country.
Key Milestones in Polio Eradication
- Pulse Polio Programme Launch (1995):
- The Pulse Polio Immunization Programme was a game-changer, initiating large-scale vaccination campaigns across India, with the first nationwide campaign held on 2nd October 1994 (Gandhi Jayanti) in Delhi.
- The campaign used the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) and reached over 1 million children.
- The slogan "Do BoondZindagi Ki" (Two drops of life) became synonymous with India’s polio eradication efforts.
- Routine Immunization and System Strengthening:
- The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), which launched in 1985, made polio one of the first diseases targeted for elimination. UIP is now one of the world’s largest immunization programs, aiming to provide vaccines against 12 preventable diseases, including polio.
- Cold chain management was improved through systems like the National Cold Chain Training Centre (NCCTE) and Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN), ensuring proper storage and distribution of vaccines.
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) Introduction (2015):
- As part of the Global Polio Endgame Strategy, India introduced the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) in 2015 to provide enhanced protection, particularly against type 2 poliovirus.
- This move followed the global transition from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV (which excludes the type 2 strain) and helped ensure continued protection against all forms of polio.
- Surveillance Systems:
- India implemented Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) Surveillance to track unexplained paralysis in children, a symptom of polio.
- Environmental Surveillance, involving monitoring sewage water for poliovirus strains, played a critical role in identifying potential outbreaks and residual poliovirus transmission.
- Political Will & Community Engagement:
- Strong political commitment from both central and state governments ensured sustained resources and focus on the program.
- Community participation was also vital, with health workers and volunteers working to ensure vaccination coverage in the most remote areas.
The Final Leap: Certification and Maintenance
- 2011 marked the last case of wild poliovirus in Howrah, West Bengal, and India ramped up its surveillance and response efforts to ensure no further cases.
- India achieved polio-free certification from the World Health Organization (WHO) on 27th March 2014, after meeting strict criteria, including three years without wild poliovirus transmission and robust surveillance systems.
Post-Certification Efforts: Keeping Polio at Bay
Even after achieving polio-free status, India remains vigilant to maintain this achievement:
- Annual National Immunization Days (NID) and Sub-National Immunization Days (SNID) are held regularly to boost immunity levels and ensure no child is missed.
- Continuous surveillance and vaccination at international borders help prevent the risk of re-importation of the virus.
- Mission Indradhanush (MI), launched in 2014, aims to increase immunization coverage to 90%, focusing on hard-to-reach areas and improving vaccine coverage.
Ongoing Commitment to Immunization
India’s immunization programs continue to evolve:
- New vaccines like Rotavirus, Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV), and Measles-Rubella (MR) are being added to protect against other vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Mission Indradhanush’s intensified phase has played a crucial role in improving vaccination rates, particularly in underserved areas.
High-Altitude Sickness

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
In September, a trekker from Idukki, Kerala, died in Uttarakhand while attempting to scale Garur Peak due to respiratory failure. Every year, numerous tourists like this succumb to the effects of high-altitude sickness in the pristine but challenging inner Himalayas. These regions present hidden dangers due to their extreme altitudes, where thinner air and reduced oxygen can lead to potentially fatal conditions.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
- Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) occurs when the body struggles to acclimatize to high altitudes, typically above 8,000 feet (2,400 meters), where oxygen levels are lower.
- As altitude increases, oxygen levels decrease, leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). Early symptoms include:Headache, Nausea, Fatigue&Shortness of breath
- If untreated, AMS can develop into:
- High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE): Fluid accumulation in the lungs, leading to severe breathing problems.
- High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE): Fluid in the brain causing confusion, hallucinations, or coma.
- Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate descent to lower altitudes.
Infrastructural Issues
- Many Himalayan regions lack adequate healthcare facilities beyond major towns like Shimla.
- Leh is an exception, with specialized facilities for high-altitude ailments, but most areas lack preventive health measures.
- Implementing health screenings at entry points to high-altitude zones (like Kinnaur or Lahaul-Spiti) could significantly improve prevention and response to AMS.
Mandatory Registration System for Tourists
- Tourist Registration: A system where tourists must register before entering remote mountain areas would allow authorities to monitor movements and provide timely medical assistance.
- Benefits:
- Quick emergency responses by having data on tourists' locations.
- Research support: Tracking demographic patterns and risk factors to better understand how altitude impacts different populations.
Early Intervention for High-Altitude Sickness
- Gradual Ascent: To allow the body to acclimatize, gradual ascent is crucial. Every 3-4 days, take a rest day and avoid increasing sleeping altitude by more than 500 meters/day.
- Medications: Doctors recommend:
- Acetazolamide to promote better oxygenation.
- Dexamethasone for reducing inflammation in severe cases.
- For those with a history of HAPE, Nifedipine may be used preventively.
- However, no medication guarantees immunity from AMS. Travelers with pre-existing conditions should consult a doctor before traveling.
Treatment Strategies
- Descent: The best treatment for AMS is to descend to lower altitudes (300-1,000 meters), where symptoms improve rapidly.
- Additional Measures: If available, supplemental oxygen or a portable hyperbaric chamber can help in emergencies.
- Medications like acetazolamide and dexamethasone can provide short-term relief but are not substitutes for descent.
Policy Recommendations
- Medical Infrastructure: Establish state-of-the-art medical facilities in high-altitude regions of the Himalayas.
- Research: Set up research centers to study high-altitude illnesses.
- Air-ambulance Services: Equip states with air-ambulance services for rapid medical evacuation in emergencies.
- Health and Safety Information: Provide accessible information on government websites and at check-in points to educate tourists on preventing and managing AMS.
Preventive Measures Before Scaling the Himalayas
- Acclimatization: Gradual ascent is essential for preventing AMS.
- Health Checks: Get a medical check-up to assess risk factors before travel.
- Medications: Consult a doctor for potential preventive medications.
- Hydration and Rest: Stay hydrated and take ample rest during the ascent.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be aware of early symptoms like headaches or nausea and stop ascending if they occur.
By addressing these measures, the risks associated with high-altitude sickness can be mitigated, improving safety for tourists and trekkers in the Himalayas.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
SanyuktVimochan 2024

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
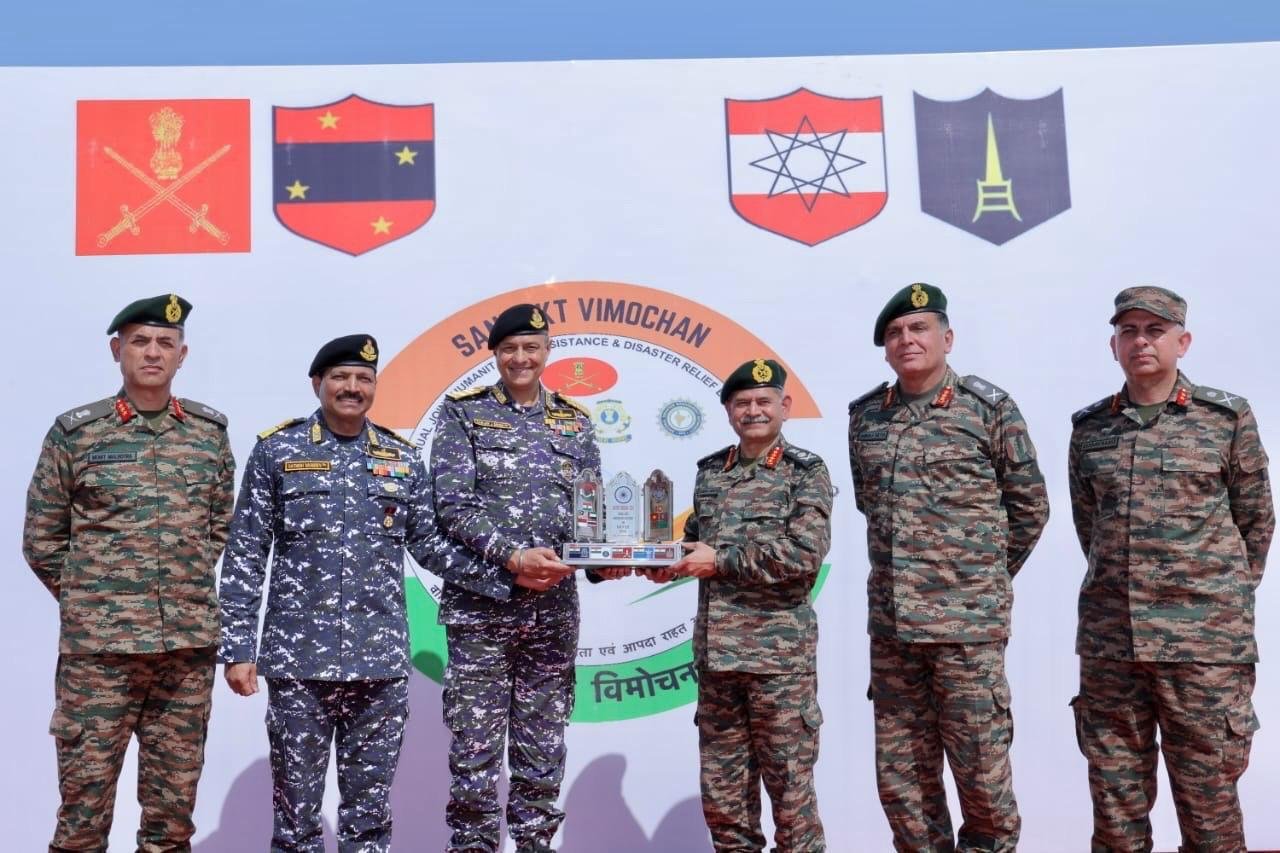
Recently, the Indian Army successfully conducted the Multilateral Annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise, 'SanyuktVimochan 2024' at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
Key Highlights:
- Conducted by: Konark Corps of Southern Command, Indian Army.
- Day 1: Tabletop Exercise (TTX)
- Theme: 'Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat'.
- Focused on simulating a cyclone scenario affecting the Okha-Porbandar coastline.
- Discussed disaster relief strategies and interagency cooperation to improve response readiness.
- Attended by senior officials from NDMA, Armed Forces, State Disaster Management, and industry representatives, including delegates from nine foreign countries.
- Day 2: Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- Held at Chowpatty Beach, Porbandar.
- Simulated Disaster Scenario: Coordinated response to a cyclone, showcasing joint operations by:
- Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, NDRF, SDRF, and other Central and State agencies.
- Key actions demonstrated:
- Requisition and Surveillance: Civil administration’s request for Armed Forces' assistance, followed by area surveillance.
- Rescue Operations: Insertion of personnel to rescue casualties.
- Casualty Evacuation: Use of resources to evacuate and assist victims.
- Resuscitation and Rehabilitation: Restoration efforts for affected citizens.
- Industrial Display &Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative:
- Showcased indigenous HADR equipment from Indian defense industries.
- Highlighted technological advancements and self-reliance in disaster management.
- SanyuktVimochan 2024 enhanced India's disaster response capabilities, ensuring a coordinated and effective approach to humanitarian assistance.
- The exercise also bolstered India’s leadership in global disaster relief, contributing to international best practices and collaborative efforts in humanitarian assistance and disaster response.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
