Melting Glaciers Threaten Gulf Stream Collapse by 2025 (India Today)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, a recent study has sounded the alarm on the potential collapse of the Gulf Stream by 2025.
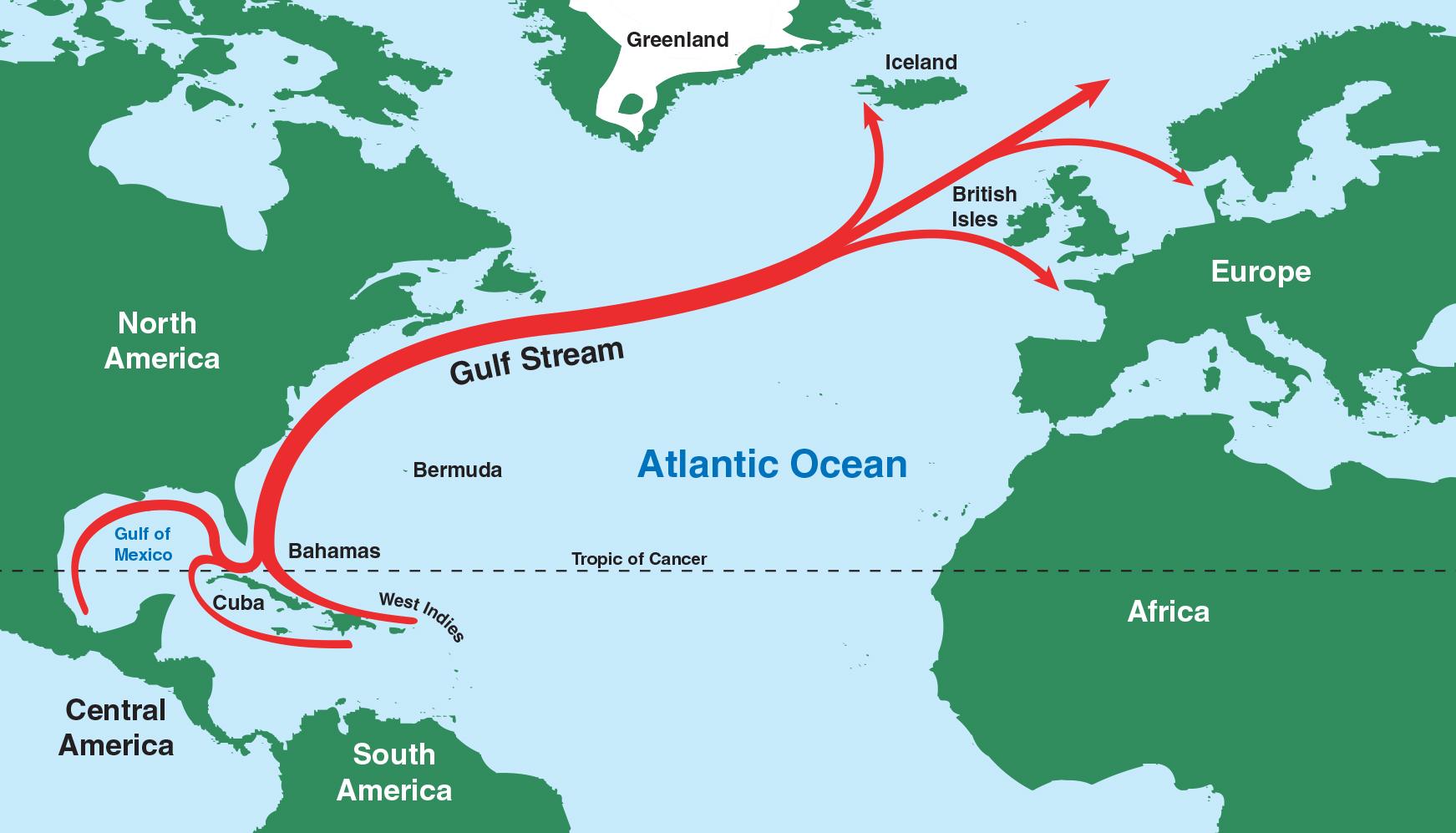
What is the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is a strong ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico into the Atlantic Ocean.
- It extends all the way up the eastern coast of the United States and Canada.
What Causes the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is caused by a large system of circular currents and powerful winds, called an oceanic gyre.
- There are five oceanic gyres on Earth.
- The Gulf Stream is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre.
- The ocean is constantly in motion, moving water from place to place via currents.
- The Gulf Stream brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico all the way up to the Norwegian Sea.
- As the warm water comes in, colder, denser water sinks and begins moving south—eventually flowing along the bottom of the ocean all the way to Antarctica.
How Does the Gulf Stream Impact Weather and Climate?
- This strong current of warm water influences the climate of the east coast of Florida, keeping temperatures there warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer than the other southeastern states.
- Since the Gulf Stream also extends toward Europe, it warms Western European countries as well.
- In fact, England is about the same distance from the equator as the cold regions of Canada, yet England enjoys a much warmer climate.
- If it weren’t for the warm water of the Gulf Stream, England would have a much colder climate.
How Long Have We Known About the Gulf Stream?
- We’ve known about the Gulf Stream for more than 500 years.
- In 1513, Spanish explorer Ponce de Leon noted that there was a strong current in this location.
- A few years later, Ponce de Leon’s ship pilot realized that the Gulf Stream could help speed up the sailing trip from Mexico to Spain.
- In the late 18th century, Benjamin Franklin became the first to chart out the path of the Gulf Stream on a map.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
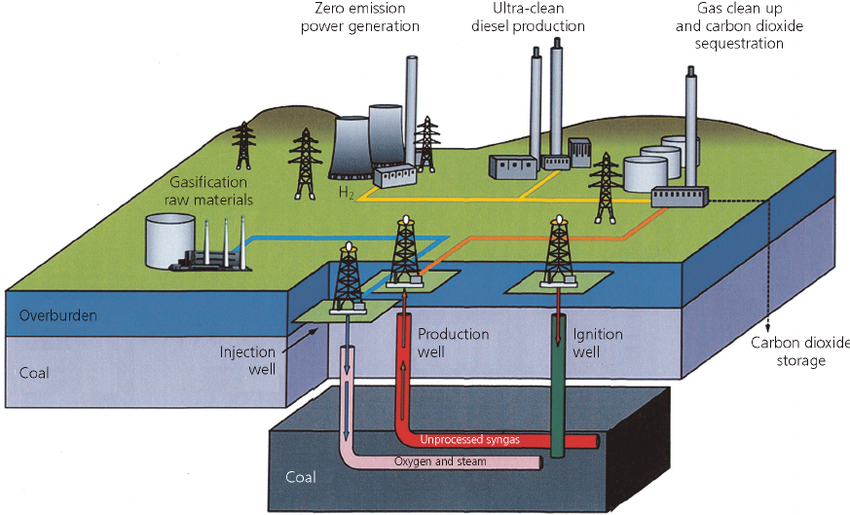
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
The Global Pulses Conference (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Pulses Conference, an annual meeting of pulses producers, processors and traders, suggested that India augment the production of pulses to meet the nutritional requirements.
About the Global Pulses Confederation (GPC):
- The Global Pulses Confederation (GPC) serves as a global representative body for the pulse industry.
- Stakeholders: It encompasses various stakeholders within the pulse industry, such as growers, researchers, traders, government entities, processors, and consumers.
- Headquarters: The GPC is based in Dubai and operates under the licensing of the Dubai Multi Commodity Centre (DMCC).
- The Global Pulses Conference, held annually, took place in New Delhi this year.
Key Observations from the Conference:
- Self-Sufficiency Target: India aims to achieve self-sufficiency in pulses production by 2027, having already attained this status in chickpeas and various other pulse crops, with minor gaps remaining in pigeon peas and black gram.
- Decadal Growth: Pulse production has witnessed a significant 60% growth, increasing from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government has guaranteed farmers a minimum support price set at 50% above the actual cost of production, ensuring lucrative returns on investment.
- Current MSP rates reflect remarkable increases, such as 117% in masoor, 90% in moong, and substantial hikes in chana dal, toor, and urad compared to a decade ago.
- Government Initiatives: Efforts include the introduction of new seed varieties and the expansion of tur and black gram cultivation to bolster production.
- Importance of Pulse Crops: Pulse cultivation not only enriches soil health but also provides nutritional benefits, particularly for smallholding farmers.
- Improved cultivation practices promise widespread benefits for all stakeholders involved.
Status of Pulse Production in India:
- Production Trends: Over the past decade, pulse production in India has surged by 60%, escalating from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Global Standing: India boasts the distinction of being the world's largest producer, consumer, and importer of pulses. It contributes 25% to global production, consumes 27% of the world's total, and imports 14%.
- Agricultural Landscape: Pulses occupy approximately 20% of the foodgrain area in India and contribute 7-10% to the nation's total foodgrain production.
- Cultivation Seasons: While pulses are cultivated in both Kharif and Rabi seasons, Rabi pulses account for over 60% of the total production.
- Variety Distribution: Among pulse varieties, Gram leads the production, comprising roughly 40% of the total output, followed by Tur/Arhar at 15-20%, and Urad/Black Matpe and Moong each contributing approximately 8-10%.
- Self-Sufficiency: India has achieved self-sufficiency in chickpeas (chana) and various other pulse crops, with minor shortfalls, observed only in pigeon peas (tur) and black gram.
DoT Unveils 'Sangam: Digital Twin' Initiative (TOI)

- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications has introduced the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative, which aims to transform infrastructure planning and design through innovation and the integration of advanced technologies.
What is Sangam: Digital Twin initiative?
- Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling monitoring, simulation, and analysis for adaptive outcomes.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' consists of two stages:
- The first is exploratory for creative exploration, and
- The second is for the practical demonstration of specific use cases, creating a future blueprint for collaboration in future infrastructure projects.
- The initiative aligns with advancements in communication, computation and sensing over the past decade, fostering a collaborative approach to reshape infrastructure planning and design.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin and next-gen computational technologies to break silos and promote a whole-of-nation approach.
- The new initiative aims to transform ideas into solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualisation and realisation, and fostering advancements in infrastructure.
- Sangam encourages a holistic approach to innovation, uniting stakeholders to harness unified data and collective intelligence.
- It is aimed at creating an ecosystem that maximises the value of technological advancements for development.
- Sangam aims to demonstrate the practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions, providing a model framework for collaboration and a future blueprint for scaling successful strategies in future projects.
- The platform also offers a blog for pre-registered participants to connect, share insights, and engage in discussions.
Significance of Digital Twins:
- Facilitates remote monitoring, making it applicable for use in hazardous operations.
- Enhances predictive capabilities, assisting in making informed policy decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency, thereby ensuring the maintenance of output quality.
- Assists in urban planning by generating various simulations and forecasts.
The Schengen Area in Europe (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kosovo recently achieved visa-free entry to the Schengen zone in Europe, the world's largest area of unrestricted movement. Now, citizens of Kosovo can visit the Schengen zone as tourists for up to 90 days within 180 days.
Why Kosovo's Schengen Application Was Delayed for Years?
- Despite the European Commission's clearance of Pristina's readiness to address issues like illegal migration and corruption in 2018, Kosovo faced prolonged delays in obtaining Schengen visa-free status.
- The primary obstacle stemmed from opposition from various EU members who did not acknowledge Kosovo's unilateral declaration of independence from Serbia in 2008.
- Moreover, Kosovo lacks legal statehood recognition from the UN and is not acknowledged by key global players like Russia and China.
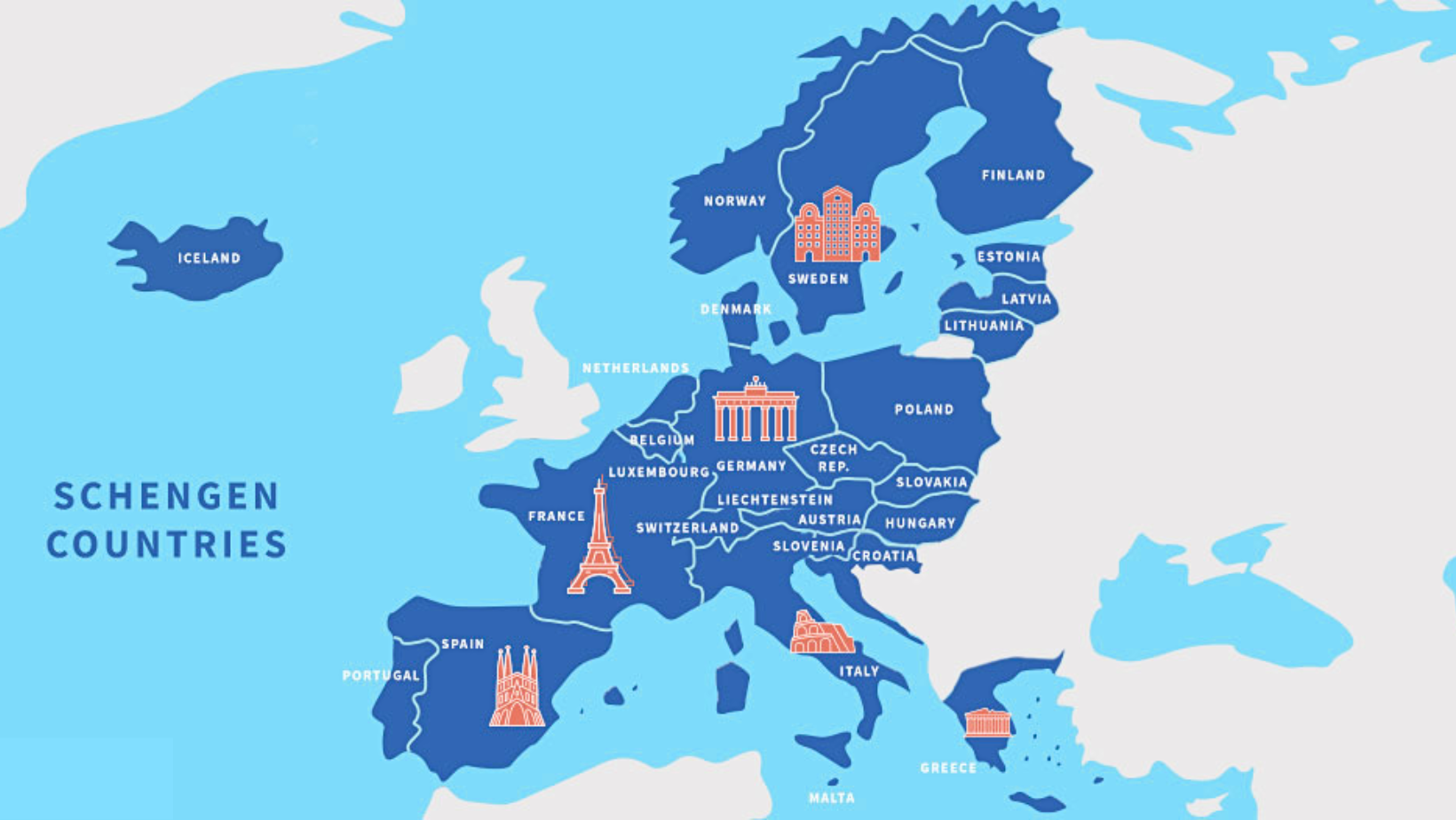
What is the Schengen Zone?
- The Schengen Zone is an area that encompasses much of Europe and enables visa-free and border-free travel within it.
- The Schengen zone is named after the Schengen Agreement, which was signed in 1985 in Schengen, Luxembourg.
- The Schengen Zone acts as a single jurisdiction that allows travellers to cross borders without stopping for any border checks and therefore enables those who live close to international borders to come and go with ease.
- It currently includes 27 countries in Europe, though not all are members of the European Union.
- The exceptions are Norway, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and Iceland.
- Croatia, an EU member since 2013, joined Schengen in 2023, while Romania and Bulgaria, EU members since 2007, will gain partial Schengen entry from 31 March 2024.
Is Admission to Schengen Mandatory for EU Members?
- When the Schengen agreement took effect in 1995, only seven of the entire 15-member union at the time joined the passport-free area.
- Today, 23 of the 27 EU states are part of the passport-free zone, excluding Cyprus, Romania, Bulgaria and Ireland.
- The Schengen area comprises 27 countries, including four non-EU members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Norway.
- It is important not to confuse the status of the four countries with the recent entry of Kosovo and the other five western Balkan entrants which are not counted among the Schengen 27 members.
What are the Advantages of the EU’s Border-free Policy?
- For nationals of any country, the benefit is the freedom to travel with a single Schengen visa to other European nations within the borderless area.
- For EU states, the Visa-free borderless travel, alongside the single currency adopted by 20 EU countries, is the most visible symbol of European integration.
What are the Challenges Faced by the Schengen Region?
- The Schengen region faced significant challenges, particularly during the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis of the past decade.
- The influx of migrants from conflict areas in Africa and West Asia, coupled with the rise of anti-immigrant sentiments fueled by far-right populist parties in Europe, added strain to the region.
- At one point, there were discussions within the EU about potentially excluding Mediterranean border countries from the Schengen Area, as some individual states considered reintroducing border controls unilaterally.
