Ethylene Oxide
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Singapore Food Agency (SFA) has issued a recall on Indian spice brand Everest’s fish curry masala after detecting an ‘excessive’ amount of ethylene oxide–a pesticide–in it.
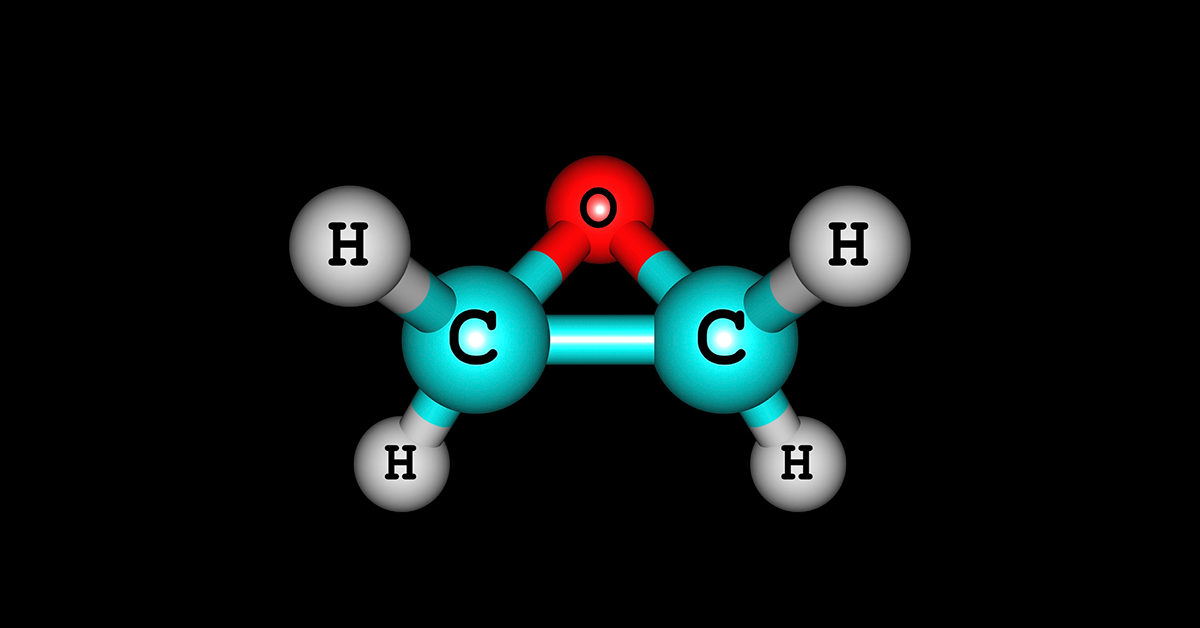
What is Ethylene Oxide?
- Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a slightly sweet odor and It dissolves easily in water.
- It is widely used in various industries due to its versatile properties.
- Its primary applications include the production of other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol for antifreeze and polyester, as well as the sterilization of medical equipment.
- It also has minor applications in agriculture.
- In this sector, it's used as a fumigant to control insect pests in stored agricultural goods, such as food commodities, to protect them from infestation.
- This usage makes up less than 1% of its applications, and it is combined with other gases to minimize potential toxicity to humans and the environment.
- While ethylene oxide plays a significant role in many industrial processes, it also poses health risks to those exposed to it.
- Potential health effects range from mild symptoms like headaches, nausea, and respiratory issues, to more severe problems such as cancer and reproductive harm.
- To minimize exposure risks, industries and facilities that use ethylene oxide are subject to environmental regulations and required to implement safety measures.
- These measures include emission-reducing and monitoring devices, on-site testing, site-specific operating parameters, and regular reporting and record-keeping.
- Despite these precautions, workers in factories that produce or use ethylene oxide, as well as people living near these facilities, may still face potential health risks.
How Do Pesticides Harm Our Bodies if Present in Food?
- Pesticides, designed to ward off unwanted organisms in agriculture, can pose extensive risks to human health if they find their way into our food chain.
- Even a brief exposure to some of them can cause acute poisoning and symptoms, including diarrhea, dehydration, and skin irritation.
- Some insecticides like Resmethrin, Cypermethrin, and Fenvalerate have been connected to chronic health issues, which include reproductive complications, immune system disruption, pores, and skin infection, and interference with the endocrine system.
- Even low-level exposure over the years can cause critical health implications.
How Long-term Issues Can be Combated?
- Some steps can be taken to mitigate the risks associated with pesticides and ethylene oxide exposure.
- It’s critical to prevent the runoff of insecticides into storm drains, which can contaminate water sources.
- While using insecticides, it’s essential to consider the characteristics of the application site to minimize unintended exposure.
- Attention to the geological factors and groundwater depth can prevent pesticide seepage into water reservoirs.
- By implementing these measures and maintaining strict regulations, we can minimize the health risks posed by these chemical substances.
Salas y Gómez
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
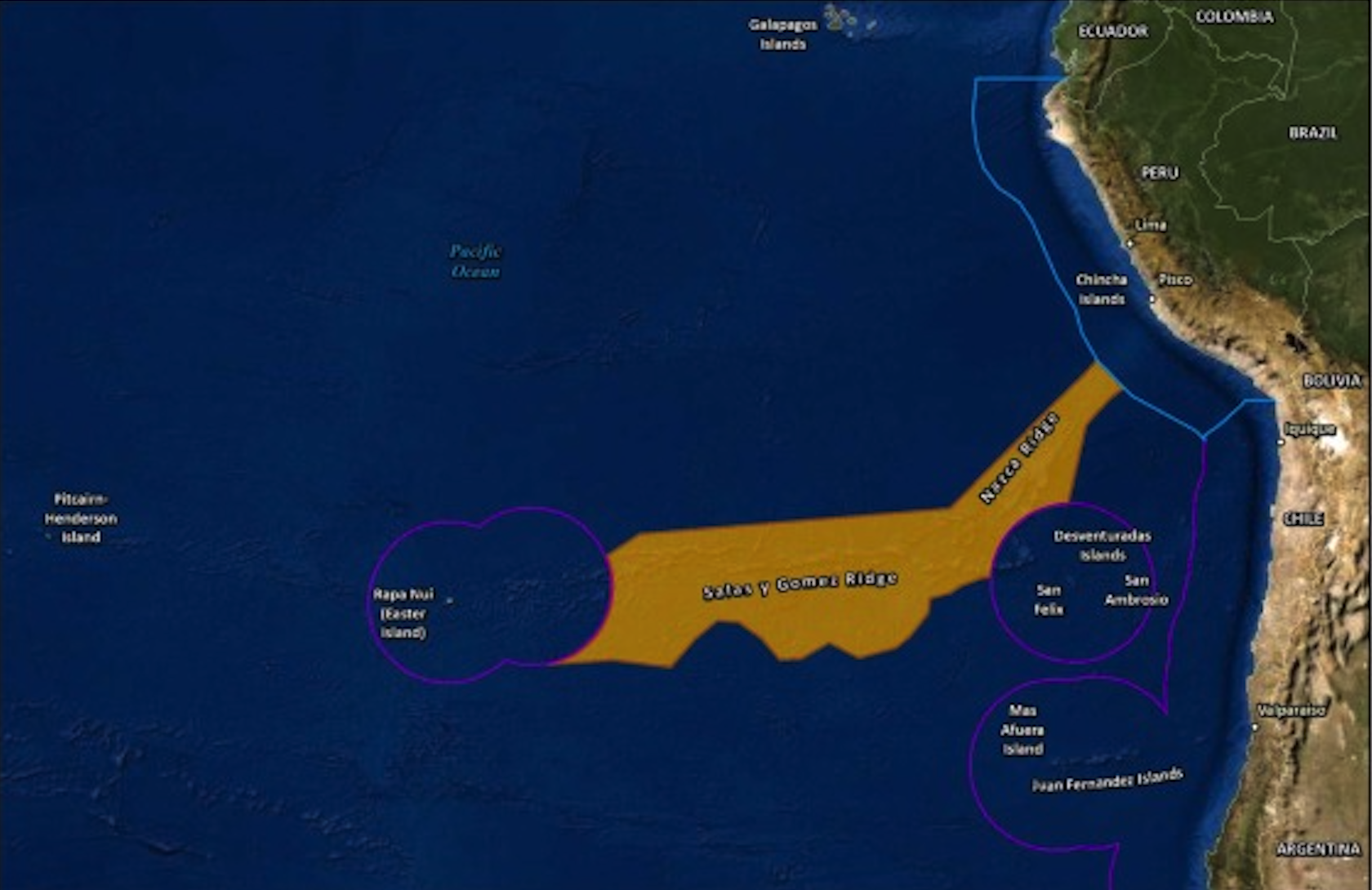
An international team of scientists last week announced they discovered 160 species when exploring 10 seamounts and two islands on the 2,900-kilometre-long ocean ridge Salas y Gómez.
What is ‘Salas y Gomez’?
- Salas y Gómez is a remarkable underwater mountain chain in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- This 2,900-kilometer-long range stretches in a west-east orientation, connecting the East Pacific Rise and the Nazca Ridge.
- The western end of the chain lies within Chile's Exclusive Economic Zone near the Easter Islands, while the eastern part extends into areas beyond national jurisdiction and touches upon the national waters of Chile and Peru.
- The region is characterized by unique ecosystems isolated by the Atacama Trench, the Humboldt Current System, and an extreme oxygen minimum zone.
- Salas y Gómez and Nazca ridges are known for their extraordinary biodiversity, hosting some of the highest levels of marine endemism on Earth.
- Given the ecological significance of this underwater mountain range, there is a growing interest in designating Salas y Gómez and its surrounding areas as high-seas marine protected areas upon the ratification of the UN High Seas Treaty.
- This initiative aims to safeguard the region's unique ecosystems and contribute to global marine conservation efforts.
About the United Nations High Seas Treaty:
- The United Nations High Seas Treaty is a legal framework, or a set of legal tools, designed to protect the oceans that are beyond any country’s territory.
- The high seas are defined as the waters that are 200 nautical miles from any national jurisdiction; they are international open waters that all countries can use for marine business such as shipping, fishing, and marine research.
- The treaty’s formal name is the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Treaty, or BBNJ Treaty for short.
Key Facts About the High Seas Treaty:
- The treaty was to be negotiated under the United Nations Convention on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982.
- It took 19 years to reach an agreement on it.
- Before now, laws to protect ocean waters and biodiversity beyond countries’ territorial boundaries only protected 1.2% of the high seas.
World Craft Council International

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Crafts Council International (WCCI), a Kuwait-based organization working on the recognition and preservation of traditional crafts across the globe, has picked Srinagar for mapping its craft clusters before its final nomination as the World Craft City (WCC) from India this year.
About World Crafts Council:
- World Crafts Council AISBL is an international non-profit organization dedicated to fostering the preservation, promotion, and advancement of global craftsmanship and traditional crafts.
- It was founded by Ms. Aileen Osborn Vanderbilt Webb, Ms. Margaret M. Patch, and Smt Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay at the 1st World Crafts Council General Assembly in New York on June 12, 1964.
- Since its inception, the World Crafts Council AISBL has been affiliated with UNESCO under Consultative Status for many years.
- Its mission is to empower artisans, celebrate cultural diversity, and contribute to sustainable development by supporting the rich tapestry of global craftsmanship and preserving languishing crafts from extinction.
- Headquarters: The current headquarters for the term (2021-2024) is located in Kuwait.
Objectives:
- The main objective of the World Crafts Council AISBL is to strengthen the status of crafts in cultural and economic life.
- The Council aims to promote fellowship among craftspersons by offering them encouragement, help, and advice.
- It fosters and assists cultural exchange through conferences, international visits, research studies, lectures, workshops, exhibitions, and other activities.
- The WCC also seeks to foster wider knowledge and recognition of the craftspeople's work with due regard to the diversified cultural and national backgrounds and traditions of its members.
- In carrying out these principles, the Council shall consult with governments, national and international institutions, societies, and individuals.?
India has only 3 cities designated as World Craft City:
- Mysuru (Kinnal paintings, Sandalwood carvings, Rosewood Inlay, etc.)
- Mamallapuram (Stone Carving continuing since the Pallava dynasty (275 CE to 897 CE)
- Jaipur (Kundan Jadai (Gem setting), Meenakari Jewellery, Lac-based craft, Gotta Patti Work, etc.)
About the World Craft City Programme:
- The World Craft City Programme, initiated in 2014 by the World Crafts Council AISBL (WCC-International), recognizes the significance of local authorities, artisans, and communities in global cultural, economic, and social advancement.
- By establishing a vibrant network of craft cities worldwide, it embraces the ideals of the creative economy and acknowledges the valuable contributions of local entities to comprehensive development.
- Notably, Jaipur (Rajasthan), Mamallapuram (Tamil Nadu), and Mysore have already been designated as craft cities under this initiative in India.
National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time ever, the Central government has released a curriculum advisable to be taught to children aged three to six years old, thus giving an impetus to pre-school learning in 14 lakh anganwadis across the country.
About National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024:
- The National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024 introduces Aadharshila, a comprehensive 48-week curriculum tailored for children aged three to six years attending anganwadis.
- Developed through collaboration among the Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the Department of School Education and Literacy, the Ministry of Education, the NCERT, the Institute of Home Economics at Delhi University, and civil society organizations, Aadharshila serves as a foundational learning framework.
??Key Features:
- The curriculum introduces a weekly play calendar, initiating with four weeks of academic activities facilitating the transition from home to Anganwadi centers through engaging play.
- Over the subsequent 36 weeks, children engage in diverse activities such as storytelling, rhymes, arts, and crafts, fostering exploration, free play, conversation, creation, and appreciation.
- Storytelling themes promote values like conflict resolution, responsibility, and cooperation.
- Children delve into topics including colors, shapes, numbers, senses, family, and friends, enhancing skills in listening, following instructions, counting, and recognizing sounds, alongside exploring themes like seasons and festivals.
- The final eight weeks focus on reinforcing previous learnings through worksheets and performance observation.
- Activities and timetables are age-specific, with detailed material requirements, variations, teacher notes, curricular goals, and competency assessments.
- The curriculum spans three years, targeting at least 48 weeks of learning, fostering skills crucial for Grade 1 transition such as listening, vocabulary, imagination, and social development.
- Special provisions ensure screening, inclusion, and referrals for children with disabilities in all activities.
- The national framework lays the foundation for states to develop culturally relevant curricula, addressing future schooling challenges effectively.
Vasuki Indicus

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fossils recovered from Kutch in Gujarat may have belonged to the spine of one of the largest snakes to have ever lived, according to new research from the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee.
Highlights of the Vasuki Indicus Discovery:
- A nearly 50-foot-long snake species, one of the longest and largest in recorded history, once existed in the Indian subcontinent.
- The reptile, Vasuki indicus, lived in India nearly 47 million years ago, fossil remains found from Gujarat’s Panandhro Lignite Mine in Kutch suggest.
- This giant snake, named Vasuki indicus, is estimated to have reached 15 meters in length, exceeding even a T-Rex.
- Scientists found 27 vertebrae, some even in their original position within the spine. They believe Vasuki resembled a large python and lacked venom.
- The species was given the specific name of Vasuki indicus in acknowledgment of the country of its origin, India.
- Vasuki is revered as the king of the snakes in Hindu mythology and is worshiped on special days like Nag Panchami.
About Vasuki Indicus:
- Vasuki indicus belongs to the Madtsoiidae family, and thrived during a “warm geological interval".
- Researchers suggest that the warm tropical temperatures of Gondwanaland, averaging around 28°C, may have contributed to the substantial size and growth of this giant reptile.
- There is a recognized correlation suggesting that higher ambient temperatures can enable larger growth in animals.
- Madtsoiids were also found in Europe and Africa, besides Asia.
- Vasuki indicus represents a large lineage of Madtsoiidae that originated in the Indian subcontinent and then spread to southern Eurasia, before reaching North Africa around 50 million years ago, that’s nearly 15 million years after the dinosaurs went extinct.
- Madtsoiidae, an extinct lineage of terrestrial snakes, thrived on the Indian subcontinent over a span of approximately 100 million years, from the Late Cretaceous to the Late Pleistocene, dating from roughly 98 million to 11,000 years ago.
- During the Late Cretaceous period, the supercontinent Pangea had fragmented into two major landmasses:
- Laurasia, encompassing North America, Europe, and Northern Asia to the north; and
- Gondwanaland to the south, which included present-day Africa, Antarctica, South America, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- The fossils of Vasuki indicus extracted from the early Lutetian grey shale layers of the Naredi Formation at the Kutch mine include an “excellently preserved, partial vertebral column”.
- The discovery sheds light on the biogeographic patterns of dispersion and diversification within the Madtsoiidae, particularly across the Gondwanan continents.
- The presence of this giant snake in the Eocene of India indicates a complex history of faunal exchanges between the Indian subcontinent and other landmasses prior to complete integration into the Eurasian plate.
