Himalayan Black Bear (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
An animal keeper died after being attacked by a Himalayan black bear in the animal’s enclosure of Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) here recently.
About Himalayan Black Bear:
- The Himalayan black bear (Scientific Name: Ursus thibetanus laniger) is a subspecies of the Asian black bear found in the Himalayas of India, Bhutan, Nepal, China, and Pakistan.
- In India, habitat covers the entire Himalayan range from Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh, extending to hilly areas in other northeastern states.
- Habitat: Thrives in heavily forested regions with broadleaved and coniferous forests.
- It utilizes orchards, agricultural fields, and human habitats to navigate between forest patches.
- Physical Features: Possesses soft and shiny fur, featuring a distinctive white V patch on the chest.
- Average length ranges from 1.4 to 1.7 meters, weighing between 90 to 200 kg (higher weight typically before hibernation).
- Life Span: In the wild, their life expectancy is approximately 25 to 30 years.
- Diet: Omnivorous nature, consuming acorns, nuts, fruit, honey, roots, and various insects like termites and beetle larvae.
- Behavior: Primarily diurnal by nature but often shifts to a nocturnal lifestyle to avoid human contact.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List classification: Vulnerable
- Due to encroachment of human population, forest fires and the timber industries; these have all reduced the bear's habitat.
- There is also a high mortality rate among the newborn.
ISRO's AstroSat (PTI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's AstroSat space telescope has achieved a significant milestone by detecting more than 600 Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB), each marking the death of a massive star or merging of neutron stars.
About ISRO’s AstroSat:
- AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- One of the unique features of the AstroSat mission is that it enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is expected to be 5 years.
- It carried a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- The scientific objectives of AstroSat’s mission are:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
- At present, all the payloads are operational and are observing the cosmic sources.
Rythu Bandhu Scheme (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission recently canceled the Telangana government's approval to give money to farmers through the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
About Rythu Bandhu Scheme:
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme, also known as the Farmer's Investment Support Scheme (FISS), was initiated by the Telangana government in 2018.
- Objectives:
- Provide timely cash grants for the initial investment needs of farmers.
- Prevent farmers from falling into the debt trap.
- Financial Assistance: Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer per season directly transferred to their accounts.
- Distribution: Biannual support for both kharif and rabi harvests.
- Usage: Farmers can use funds for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labor, and other field operations of their choice.
- Eligibility: Open to all resident land-owning farmers, including those in forest areas with a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR).
- Special Inclusion: Farmers in forest areas, mainly from Scheduled Tribe communities, with a ROFR document, are eligible for benefits.
- It’s India's first direct farmer investment support scheme, providing cash directly to beneficiaries.
Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a new plant species belonging to the 'Impatiens' genus (Balsaminaceae) has been identified in the Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Tirunelveli.
About Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- The Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, is situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- This reserve combines three major sanctuaries:
- The Kalakkad Sanctuary
- The Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of the Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The Agasthyamalai Hills, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu, forms the sanctuary's core and is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- This reserve is also recognized as the “River Sanctuary,” with 14 rivers originating from it.
- Flora: The flora in this region exhibits a gradual transition from dry thorn forest to dry deciduous, moist deciduous, and a patch of West Coast wet evergreen forests at higher elevations.
- Fauna: Diverse fauna includes species such as Lion-tailed Macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Nilgiri Pipit, Grey Headed Bulbul, Blue Winged Parakeet, and more.
Details about the New Plant Species:
- The species, named 'Impatiens Karuppusamyi,' pays tribute to S. Karuppusamy for his significant contributions to the taxonomy of South Indian angiosperms.
- This particular plant is exclusively found in the Agasthyamalai region within the southern Western Ghats.
- Belonging to the scapigerous group (stemless group), the plant is observable only during the monsoon season, lasting for a few weeks.
- Impatiens, a genus comprising over 1,000 flowering plant species, is widely distributed across tropical Africa, Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, and China.
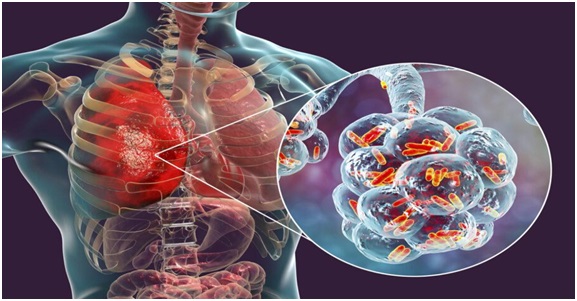
Mycoplasma Pneumonia (Indian Express)
- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause illness by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It is a common cause of pneumonia in children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- Most people with respiratory infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae don’t develop pneumonia.
- For this reason, MP is known as an atypical pneumonia and is sometimes called walking pneumonia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can include:
- Fever, Cough, Headache, Sore throat, Fatigue, Muscle aches, and Shortness of breath
- In most cases, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mild and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- However, some people may develop more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- It spreads through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine to prevent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection however there are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection.
