Exercise PoorviPrahar

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
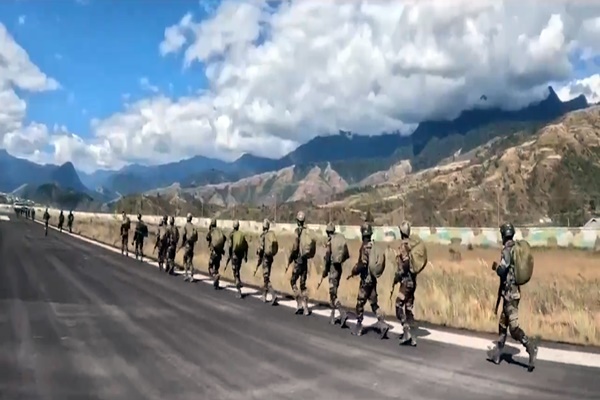
- From November 10 to 18, 2024, the Indian Army is conducting a high-intensity tri-services exercise named PoorviPrahar in the forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The exercise aims to enhance the combat effectiveness and coordination between the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force, focusing on integrated joint operations in the challenging mountainous terrain of the region.
About Exercise PoorviPrahar
Objective: The primary goal of Exercise PoorviPrahar is to hone the combat readiness and synergy across the three branches of the Indian Armed Forces. It is designed to improve their ability to conduct integrated joint operations, especially in the difficult terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, which is crucial due to the region's strategic location along India's eastern frontier.
Key Features of the Exercise:
- Multidomain Integration:The exercise involves land, air, and sea operations, demonstrating India's capability to conduct multi-domain operations. This showcases the Indian Armed Forces' preparedness to tackle threats across all three domains simultaneously.
- Advanced Military Platforms:
- Aircraft: Advanced fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft.
- Helicopters: Including Chinook heavy-lift helicopters and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH Rudra).
- Artillery: The exercise makes use of the M777 Ultra-Light Howitzers, which provide mobility and precision firepower in rugged terrains.
- Swarm Drones and Loitering Munitions: These cutting-edge technologies enable precision strikes and enhanced situational awareness, contributing to more flexible and adaptive operations.
- Technological Integration:
- The exercise integrates next-generation technologies like Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and First-Person View (FPV) Drones. These tools enhance operational flexibility, improve situational awareness, and enable precision in strike capabilities, marking a significant advancement in India's military technology.
- Operational Coordination:A core component of the exercise is the development of a Common Operating Picture (COP). This system integrates real-time data from land, air, and sea operations, improving coordination and decision-making. The system relies on AI-driven analytics and satellite communications, enabling rapid information sharing and quicker response times.
- Tactical Focus on Mountain Warfare:Arunachal Pradesh, with its mountainous and rugged terrain, is the perfect setting for honing skills required for mountain warfare. The region’s proximity to India’s border with China makes it a critical area for India’s defense strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Integrated Joint Operations: The exercise focuses on improving the coordination between the Army, Navy, and Air Force to execute seamless operations across land, air, and sea.
- Advanced Technology Integration: The exercise features the use of Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and AI-driven systems to enhance precision, situational awareness, and overall operational flexibility.
- Mountain Warfare Expertise: Conducted in the mountainous terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, the exercise is crucial for preparing the Indian Armed Forces to operate effectively in such challenging landscapes.
- Strategic Posture: The exercise reaffirms India’s ability to defend its Eastern frontier and maintain a robust defense posture in the face of potential threats in the region.
Unified Complex Radio Antenna
- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- India and Japan recently signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) to co-develop the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for deployment on Indian Navy ships. This pact marks a significant milestone as it is India's first military technology transfer agreement with Japan.
- The deal follows a 2015 agreement on the transfer of defense equipment and technology, further strengthening defense ties between the two countries.
- The UNICORN mast is a cutting-edge communication and radar system designed to enhance the stealth characteristics of naval vessels. This agreement is seen as an important step towards deepening India-Japan defense cooperation.
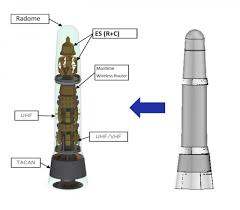
What is UNICORN?
The UNICORN mast is an advanced, integrated antenna system that combines several communication and radar components into a single conical structure or radome (a radar-absorbing dome). It is designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of ships, improving their stealth capabilities.
Key features of the UNICORN mast include:
- Integration of multiple antennas: It consolidates various antennas used for tactical data links, communications, and navigation systems (e.g., TACAN - Tactical Air Navigation System).
- Stealth enhancement: By reducing the number of exposed components and consolidating them into a single radome, the mast significantly lowers the ship’s radar signature, making it harder to detect.
- Improved performance: The mast design minimizes mutual interference between antennas, enhances maintainability, and increases lightning resistance.
- Space efficiency: It saves valuable below-deck space and reduces ship-building time by integrating multiple systems into one mast.
The UNICORN system is currently deployed on Mogami-class frigates of the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force.
India-Japan Defense Cooperation
- 2015 Defense Technology Transfer Agreement: This pact established a framework for defense cooperation between India and Japan, paving the way for joint projects like the UNICORN mast.
- Bilateral Military Exercises:
- Veer Guardian 2023: A bilateral exercise conducted between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), which deepened defense interoperability between the two nations.
- Tarang Shakti 2024: The first multilateral air exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force, with Japanese fighter aircraft participating.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Development: Japan has also provided financial aid for infrastructure development in India’s strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands, contributing to enhancing India’s maritime security in the region.
Red-Headed Vulture

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
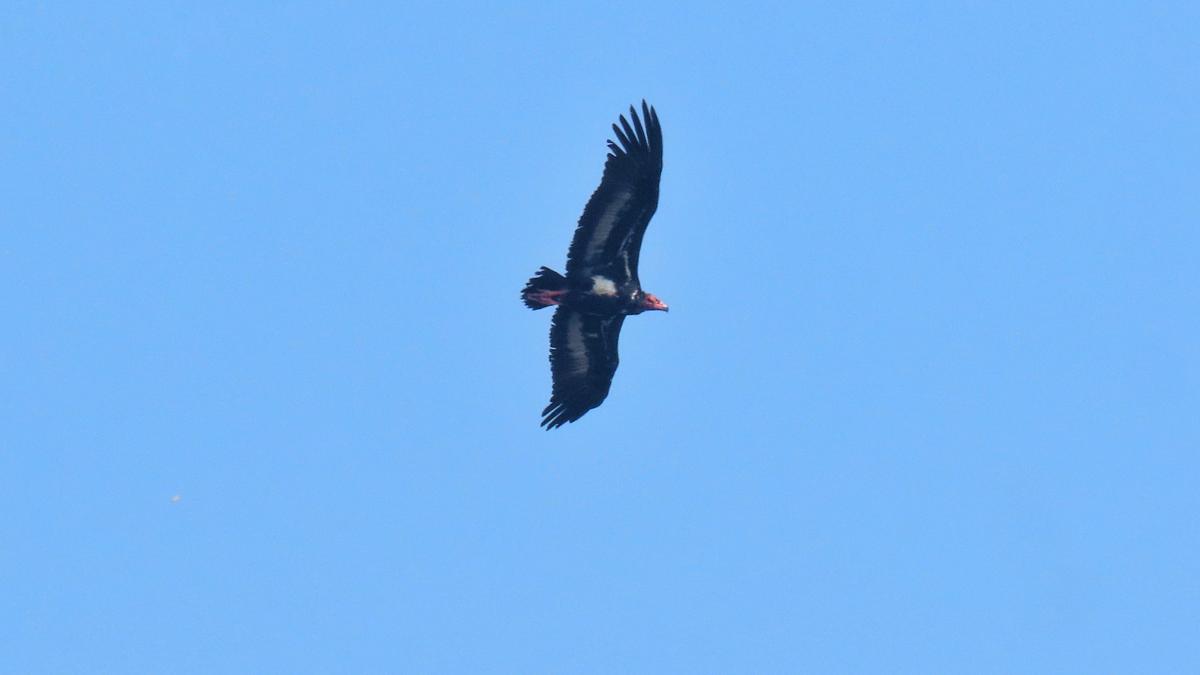
- The Red-Headed Vulture, a critically endangered species, has been sighted for the first time in Kasaragod, Kerala, marking an important addition to the region’s avian biodiversity. This rare sighting occurred at Manhampothikunnu near Mavungal. Prior to this, the species was predominantly seen in the Wayanad region of Kerala.
- This discovery brings the total number of bird species recorded in Kasaragod to 407, showcasing the district's growing avian diversity.
About the Red-Headed Vulture:
- The Red-Headed Vulture (also known as the Asian King Vulture or Pondicherry Vulture) is one of the rarest and most critically endangered species of vultures in India. It is known for its distinctive scarlet red head and black body with a white patch on the abdomen.
- Physical Features: The bird is medium-sized, weighing around 5 kg, with a wingspan of up to 2.5 meters and a length of 80 cm. It is typically solitary, often found alone or with a mate.
- Distribution: Historically found in Central India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, the Red-Headed Vulture’s numbers have drastically declined in recent decades.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: The Red-Headed Vulture is classified as Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: It is listed under Schedule 1, offering it the highest level of legal protection.
- CITES: The species is also listed in Appendix II, indicating that it requires international conservation efforts to prevent it from becoming endangered.
Threats to Vultures:
- Diclofenac Poisoning: The significant decline in vulture populations in India, including the Red-Headed Vulture, is primarily due to the widespread use of diclofenac (a veterinary drug) to treat livestock. When vultures consume the carcasses of treated animals, they ingest the toxic drug, leading to kidney failure and death.
- Other threats include pesticide contamination, lead poisoning, habitat loss, and collisions with man-made structures like power lines and wind turbines.
Conservation Efforts in India:
- India has undertaken various efforts to protect vultures, including banning diclofenac in 2006 and expanding the ban to other harmful drugs like ketoprofen and aceclofenac in 2023.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres (VCBCs): These centers are focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs for vultures, helping to increase their populations. The Jatayu Conservation and Breeding Centre in Uttar Pradesh is one of the latest initiatives, set up to protect and rehabilitate vultures.
- Vulture Safe Zones have been created across India, providing safe habitats for vulture species to recover.
- Vulture Restaurant Initiative: In some regions, safe feeding centers (such as in Jharkhand) have been established, where vultures are provided uncontaminated carcasses, reducing their exposure to toxic substances.
- Legal Protection: Several species of vultures, including the Red-Headed Vulture, are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring stringent legal measures against poaching and habitat destruction.
Global Conservation Efforts:
- India’s vulture conservation initiatives are part of a broader international effort under the SAVE (Saving Asia’s Vultures from Extinction) programme, which involves multiple regional and global organizations working to protect vulture species in South Asia.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
