Ramesh Chand Panel
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
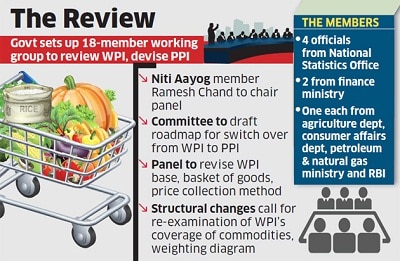
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
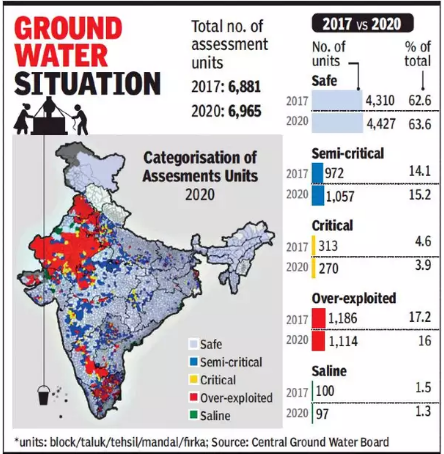
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
