Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
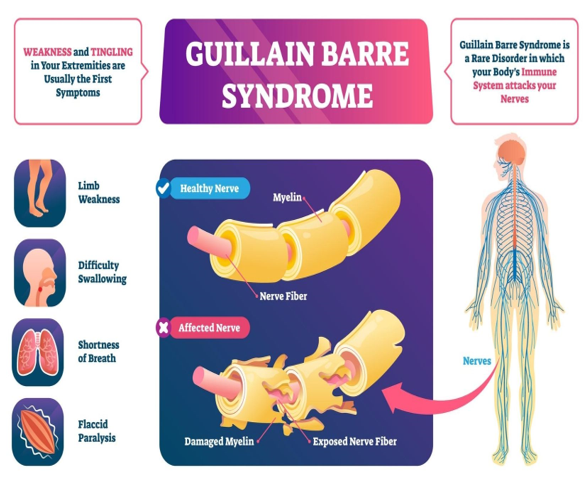
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
Ad Hoc High Court Judges

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
To address the mounting pendency of criminal cases in several High Courts, the Supreme Court of India has suggested invoking Article 224A of the Constitution, which allows the appointment of retired High Court judges on an ad hoc basis.
Constitutional Provision: Article 224A
- Title: Appointment of Retired Judges at Sittings of High Courts.
- Key Provision: The Chief Justice of a High Court, with the consent of the President, may invite retired judges of the same or other High Courts to act as judges temporarily.
- Status: These judges enjoy the powers, jurisdiction, and privileges of regular High Court judges, but are not deemed permanent judges.
Why the Provision is Being Invoked Now:
- Backlog of Cases: Over 40% vacancy rate in High Courts; huge pendency, especially of criminal cases.
- Delays in Regular Appointments: Slow process of regular judicial appointments prompted the Supreme Court to consider alternative mechanisms.
- Underuse of Article 224A: Only three recorded instances of ad hoc appointments since Independence:
- Justice Suraj Bhan – MP High Court (1972)
- Justice P. Venugopal – Madras High Court (1982–83)
- Justice O.P. Srivastava – Allahabad High Court (2007, Ayodhya case)
Judicial Interpretation – Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021):
- The Supreme Court laid down guidelines for invoking Article 224A.
- The process must be routed through the SC collegium (CJI + 2 senior-most judges).
- Trigger Point for Appointment:
- High Court vacancies exceed 20% of sanctioned strength (excluding pending proposals).
- More than 10% of pending cases are over 5 years old.
Procedure for Appointment:
- Consent: Retired judge must agree to serve again.
- Initiation: Chief Justice of the High Court forwards the name.
- State and Centre: Proposal routed through State CM → Union Law Ministry.
- SC Collegium: Must review and approve the name.
- Executive Clearance: Law Ministry → PM → President for final approval.
Term & Allowances:
- Duration: Typically 2–3 years, renewable if required.
- Number of Judges: Suggested 2–5 ad hoc judges per High Court.
- Remuneration: Entitled to allowances as per Presidential order.
- Status: Have full judicial powers during tenure.
Concerns & Safeguards:
- Fear of using ad hoc appointments as a substitute for regular appointments.
- Therefore, SC mandates that regular appointment process must be underway before invoking Article 224A.
- Periodic review and panel creation of eligible retired judges recommended.
M23 Armed Group

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The March 23 Movement (M23), a rebel group active in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has intensified its insurgency in North Kivu province, capturing key areas like Minova and threatening the provincial capital, Goma.
About M23 Armed Group:
- Full Form: March 23 Movement
- Formation: 2012, by mutineers from the Congolese army protesting a failed 2009 peace deal.
- Base of Operations: Eastern DRC, primarily in North Kivu province.
- Activities: Armed rebellion, territorial control, ethnic conflict, disruption of state authority.
External Support:
- Rwandan Involvement:
- UN Reports (2023): Estimated 3,000–4,000 Rwandan troops operating alongside M23.
- Rwanda alleged to have “de facto control” over M23 operations.
- Kigali denies direct territorial aggression claims.
- International Concerns: The group’s resurgence reflects broader regional instability and transnational military dynamics.
Recent Developments (2024):
- Territorial Gains: Capture of Minova; encroachment on Goma, a strategic and densely populated city.
- Humanitarian Crisis:
- Over 2,30,000 displaced since January 2024.
- Influx of injured civilians in hospitals; risk of further displacement and violence.
- Congolese Military Weakness:
- Internal instability and operational setbacks have contributed to M23’s advances.
- The Congolese army acknowledged a “breakthrough” by M23 with external backing.
Geographical Significance of the Region:
- DRC Capital: Kinshasa
- Strategic Location: Borders 9 countries—Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of Congo.
- Topography:
- Rwenzori & Virunga Mountains: Includes active volcanoes (e.g., Mount Nyiragongo).
- Congo River: Vital for transport, hydroelectric power, and biodiversity.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in cobalt, coltan, gold, and other rare minerals—critical to the global tech industry.
- The mineral wealth of North Kivu is a major driver of prolonged conflict.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
India is set to deploy its first human-operated deep-sea submersible as part of the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), marking a significant leap in the country’s marine research and technological capability.
Key Highlights:
- Submersible Deployment (2024):
- India will operate its first human submersible at a depth of 500 meters this year.
- The goal is to reach a depth of 6,000 meters by 2025.
- The project aligns with the timelines of Gaganyaan, India’s first human space mission—showcasing parallel progress in marine and space technology.
- Indigenous Technology:
- The mission is powered by 100% indigenous technology, underlining India’s growing self-reliance in high-end scientific infrastructure.
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM):
- Launched: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Budget: ?4,077 crore over five years
- Framework: One of nine key missions under PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council)
Core Objectives:
- Develop deep-sea technologies, including a manned submersible for ocean exploration.
- Explore and harness ocean resources such as: Polymetallic nodules, Hydrothermal sulphides & Rare earth metals
- Study marine biodiversity for sustainable fisheries and conservation.
- Support India’s blue economy through innovation and research.
- Monitor ocean climate change and develop advisory services.
- Promote marine biology and biotechnology via dedicated marine research stations.
- Harvest renewable energy and freshwater from ocean sources.
Key Components and Technologies:
Matsya6000 Submersible:
- India’s first manned deep-sea vehicle.
- Designed to reach 6,000 meters depth.
- Crew Capacity: Three members
- Developed by: National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai
- Structure: Made of titanium alloy, withstanding 6,000 bar pressure
- Equipped with: Scientific sensors, tools for sampling, viewports, propellers, and acoustic communication systems.
- Combines capabilities of ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) and AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles).
Varaha Deep-Ocean Mining System:
- Developed by NIOT
- Successfully conducted trials at 5,270 meters
- Key to India’s future in deep-sea mining of critical minerals
Strategic Importance:
- Scientific Advancement: DOM places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France, Japan) with human-crewed deep-ocean exploration capacity.
- Economic Potential: Unlocks access to underwater mineral wealth, critical for electronics, defense, and energy sectors.
- Environmental Sustainability: Supports marine biodiversity conservation and promotes sustainable use of oceanic resources.
- Geopolitical Significance: Enhances India’s presence and influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Technological Leap: Strengthens India’s capabilities in underwater robotics, materials engineering, and ocean sciences.
Is Poverty Being Underestimated in India?

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The recent 2023-24 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed a decline in poverty across rural and urban India. However, questions have emerged about whether poverty is being underestimated, due to changes in methodologies, definitions, and data availability.
Evolution of Poverty Measurement in India
- 1970s to 2005: Poverty was defined based on minimum calorie intake; updated every 5 years using NSSO data.
- Tendulkar Committee introduced in response to divergence between NSSO and National Accounts data.
- Post-2011-12: No official poverty estimates or surveys; alternative indices like Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) were used.
Current Data Issues
- Different recall periods in surveys (7-day, 30-day, 365-day) create non-comparability.
- Modified Mixed Recall Period (MMRP) introduced in 2017-18 and improved upon in recent years with three household visits, enhancing recall and thus raising reported expenditures.
- Result: Using older poverty lines on newer, higher expenditure data underestimates poverty.
Diverging Poverty Estimates
- Dr. C. Rangarajan (2022-23): Estimated poverty at around 10%.
- Recent factsheet (2023-24) suggests poverty may have declined to single digits.
- A paper using Rangarajan’s methodology on 2022-23 HCES data estimated 25% poverty, but this is debated.
Reasons for Poverty Reduction
- High GDP growth, increased public expenditure, and improved public delivery systems.
- National Food Security Act covers nearly 80 crore people.
- Broadened definition of poverty now includes non-food items and essential services.
- Decline in poverty estimated around 17-18% between 2011-12 and 2023-24.
Rural-Urban Trends
- Consumption gap between rural and urban areas is narrowing.
- Rural consumption patterns becoming more urban-like.
- 2011 Census definitions outdated — many rural areas are peri-urban in character.
Need for Poverty Line Revision
- Lack of consensus and official backing on methodology hinders creation of a new poverty line suited to current data.
- UNDP’s global poverty line is $2.15/day; India’s poverty was 12.9% in 2019 by that metric.
- NITI Aayog’s estimates do not support 25% poverty claim.
Debate on Multidimensional Poverty Index
- India’s MPI (12 indicators) differs from UNDP’s 10-indicator framework.
- Additions like bank accounts and maternal health are India-specific.
- Criticism: Once indicators (e.g., electricity, bank accounts) are met, they remain met — poverty appears to decline permanently, while income vulnerability is not captured.
