Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
World AIDS Day 2024
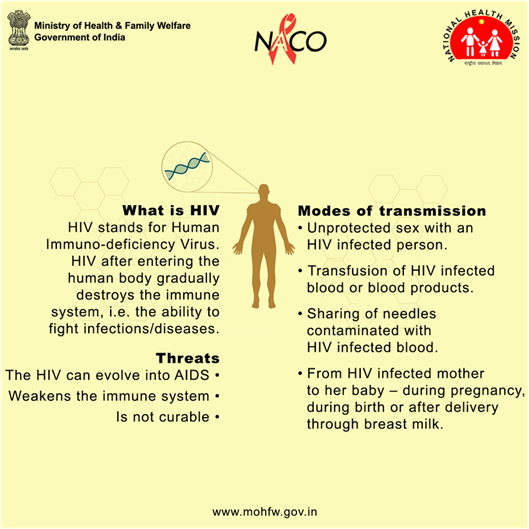
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
World AIDS Day is observed annually on December 1 since 1988 to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS and demonstrate solidarity with affected individuals. It commemorates lives lost to AIDS and highlights progress and ongoing challenges in prevention, treatment, and care.
Key Highlights:
- 2024 Theme: "Take the Rights Path: My Health, My Right!"
- Focuses on healthcare access, human rights, and addressing systemic inequalities in HIV prevention and treatment services.
- Aims to empower individuals to manage their health and reduce stigma.
- Advocates for inclusivity and global cooperation to eradicate AIDS.
Global and National Perspective on HIV/AIDS
- Global Progress:
- According to UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023, significant strides have been made globally in reducing new HIV infections and improving treatment access.
- India has been acknowledged for its robust legal framework and financial investments in HIV control.
- India's HIV Statistics:
- Over 2.5 million people live with HIV in India.
- Annual new infections: 66,400, a 44% reduction since 2010.
- HIV prevalence among adults is 0.2%.
- Free lifelong treatment is provided to over 16 lakh people at 725 ART centers (as of 2023).
India’s Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response
- Early Initiatives:
- India’s response to HIV/AIDS began in 1985 with sero-surveillance and blood safety measures.
- The National AIDS and STD Control Programme (NACP) was launched in 1992, evolving into one of the world’s largest HIV/AIDS control programs.
- Evolution of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness and blood safety.
- Phase II (1999-2007): Introduced direct interventions in prevention, detection, and treatment.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Expanded decentralized management at the district level.
- Phase IV (2012-2017): Increased funding and sustainability of interventions.
- Phase IV Extended (2017-2021): Passage of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017; introduction of the ‘Test and Treat’ policy; and response to the COVID-19 pandemic with IT innovations.
- NACP Phase V (2021-2026):
- Central Sector Scheme with an outlay of Rs. 15,471.94 crore.
- Goals: Reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 from 2010 levels.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis, reduce stigma, and ensure universal access to STI/RTI services for vulnerable populations.
- Key strategies include community-centered approaches, technology integration, gender-sensitive responses, and public-private sector partnerships.
Key Objectives of NACP Phase V
- Prevention & Control:
- Ensure 95% of high-risk individuals access prevention services.
- Achieve the 95-95-95 targets: 95% of HIV-positive individuals know their status, are on treatment, and achieve viral suppression.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis.
- Reduce stigma and discrimination to less than 10%.
- STI/RTI Prevention:
- Universal access to high-quality services for at-risk populations.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
