Sycamore tree (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a 300-year-old sycamore tree in England, renowned for its beauty and exceptional location, was felled by a teenager.
About Sycamore Tree:
- Location: Situated within a hollow between two hills, at a break in the Hadrian Wall, an ancient stone structure near the border of England and Scotland in Northumberland, northern England.
- These 'breaks' are essentially channels that were naturally carved by extensive meltwater flows beneath ancient ice sheets, thousands of years ago.
- As they mature, sycamore trees can grow impressively tall, reaching heights of up to 35 meters.
- They are commonly found in the UK and feature leaves reminiscent of maple trees.
- Initially, the bark is dark pink-grey and smooth when young, but over time, it becomes textured, developing small plates.
- Sycamores have a remarkable lifespan and can survive for as long as 400 years.
- Distribution: Native to central, eastern, and southern Europe, it's believed that the introduction of sycamore trees to the UK occurred either during the Roman era or in the Tudor period around the 1500s.
Greater sand-plover (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A Greater sand-plover (Charadrius leschenaultii), typically found along seashores, was recently observed in an urban reservoir within Coimbatore.
About Greater Sand-Plover:
- Known for its impressive long-distance migrations.
- Physical Characteristics:
- A medium-sized plover featuring a lengthy and robust bill.
- Breeding adults display a dark mask and an orange chest, neck, and forehead, with females being somewhat less vibrant than males.
- Non-breeding birds and juveniles exhibit sandy brown plumage on top and white underneath, including a white throat and 'eyebrows.'
- Notably, unlike some Lesser Sand-Plovers, the Greater Sand-Plover never sports a black boundary around the throat.
- Breeding habitat includes high-elevation regions, favoring arid, open environments, often near water sources.
- During winters, it can be found along coastal mudflats and estuaries.
- Breeding season typically spans from April to May in central Asia, late March to late May in Turkey, and up to late June in Armenia.
- During the non-breeding season, it migrates to the shores of the Indian and Australian Oceans.
- The bird sustains itself on a diet comprising beetles, worms, crustaceans, mollusks, other insects, and their larvae.
- Preferred Habitat: Mudflats and sandy shores.
- Behavior/Ecology: Tends to associate with other shorebirds, particularly the Lesser Sand Plover.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concern
Pygmy hog (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a total of eighteen pygmy hogs, which were bred in captivity, were set free within the Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve located in western Assam.
About Pygmy Hog:
- It holds the distinction of being the world's smallest and rarest wild pig species.
- Remarkably, it's among the few mammals that construct their own dwellings, complete with a 'roof.'
- Considered an indicator species, its presence serves as a barometer for the well-being of its primary habitat, which consists of tall and moist grasslands.
- Habitat: Pygmy hogs thrive in untouched expanses of grassland dominated by early-stage riverine ecosystems.
- These areas typically feature dense tall grass interspersed with a rich variety of herbs, shrubs, and young trees.
- Currently, the only viable population of these hogs in the wild resides in the Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I
Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Madurai Bench of the Madras High Court has recently issued a notice to the State regarding a public interest litigation petition. This petition aims to request a directive to limit the access of individuals and vehicles into the Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve.
About Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- Established as a Tiger Reserve in 1988.
- Comprises three primary sanctuaries:
- Kalakad Sanctuary
- Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The core area of the sanctuary is the Agastya Malai Hill Range, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- This range is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- Often referred to as the 'River Sanctuary,' it serves as the source for as many as 14 rivers.
- Terrain: Characterized by undulating landscapes with numerous valleys and porous rock formations.
- Vegetation:
- Varies from thorny shrub jungles to lush evergreen forests.
- Apart from forests, the reserve also includes savannah woodlands, grasslands, and even tea and coffee plantations.
- Flora: Notable species encompass Sarcandra, Paphiopedulum druryi, Hopea parviflora, Hopea utilis, Calophylum elatum, Cullenia exarillata, and more.
- Fauna: Home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, rusty spotted cats, wild dogs, sloth bears, elephants, gaurs, sambar deer, spotted deer, mouse deer, Nilgiri langurs, slender lorises, bonnet macaques, lion-tailed macaques, among others.
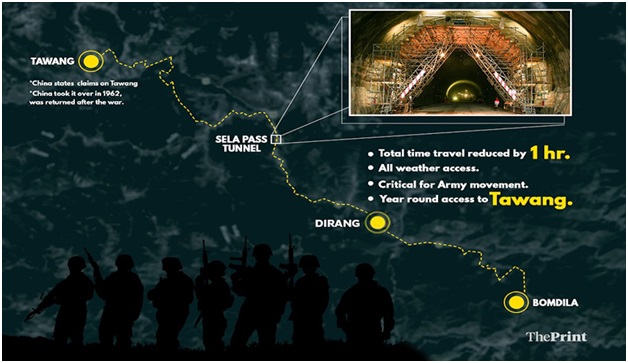
Sela Tunnel Project (Times of India)
- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The officials from BRO (Border Roads Organization) recently announced that they have almost finished about 96 percent of the work on the strategically important Sela Tunnel. It's expected to be officially opened by the end of this year.
About Sela Tunnel Project:
- Location: Situated in the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- When it's finished, the Sela tunnel will be the world's longest two-lane tunnel, located at an altitude above 13,000 feet.
- Its purpose is to provide year-round connectivity between Guwahati in Assam and Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This tunnel is being constructed underneath the Sela Pass as part of NH-13, a segment of the Trans-Arunachal Highway system.
- The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is responsible for its construction under Project Vartak, which began on April 1, 2019.
- Project Details:
- Tunnel 1: This tunnel is 980 meters long and has a single tube.
- Tunnel 2: A two-lane tunnel that spans 1555 meters, equipped with an emergency escape tunnel.
- Roads: The road leading to Tunnel 1 is 7100 meters long, the road connecting the two tunnels is 1340 meters long, and the road leading to Tunnel 2 is 340 meters in length.
