India Ranks 93 on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023 (The Hindu)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
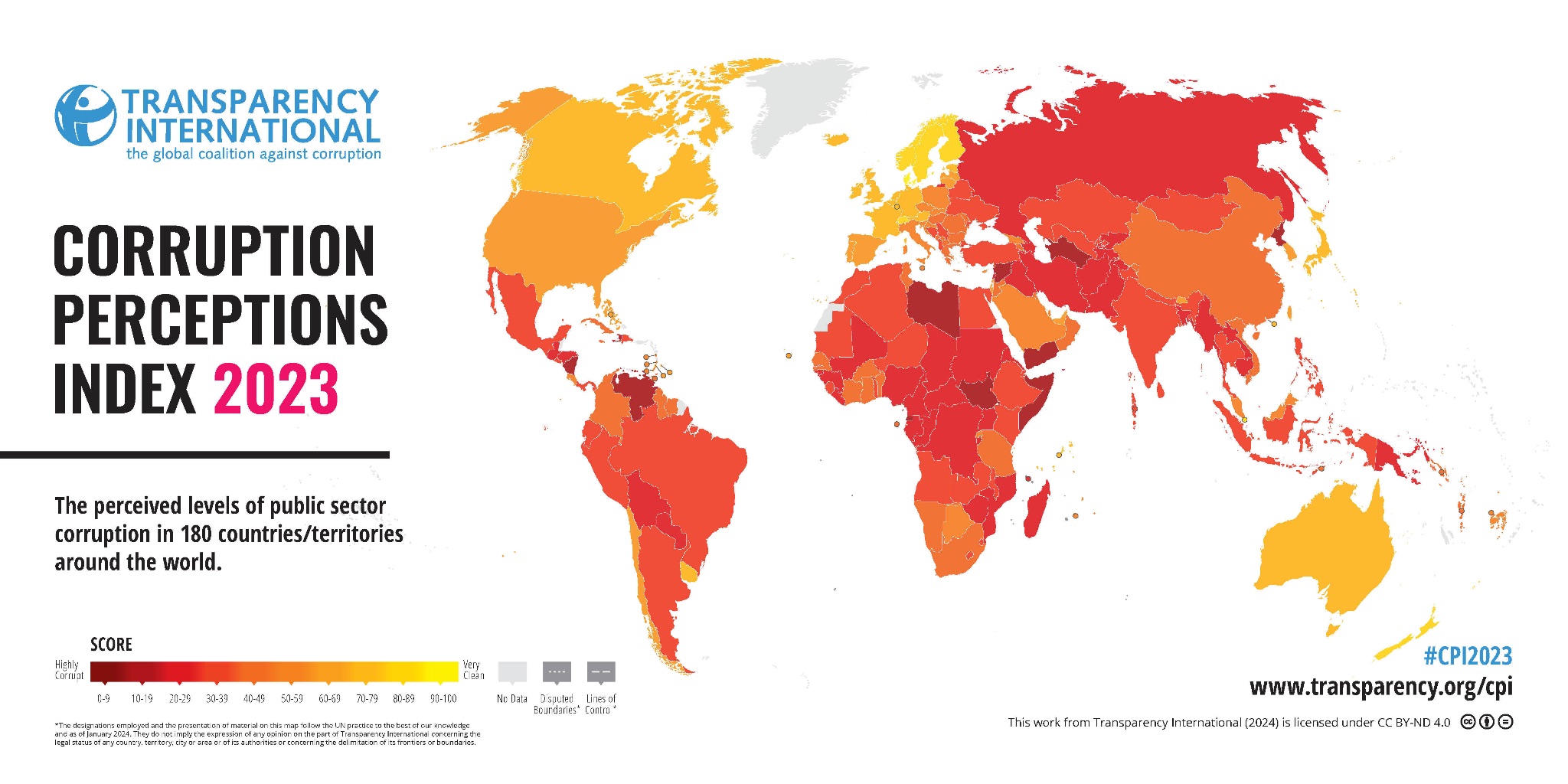
India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 as its overall score remained largely unchanged, according to a Transparency International report.
Key Facts About Corruption Perceptions Index 2023:
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 tied with Maldives, Kazakhstan, and Lesotho also ranking at 93 out of 180 countries.
- In 2023, India's overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40.
- India's rank in 2022 was 85.
- Denmark (90) tops the index for the sixth consecutive year, with Finland and New Zealand.
- In South Asia, both Pakistan (133) and Sri Lanka (115) grapple with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
- Bangladesh (149) emerges from the least developed country (LDC) status, with economic growth supporting a continued reduction in poverty and improving living conditions.
- China (76), with its aggressive anti-corruption crackdown, has punished more than 3.7 million public officials for corruption over the last decade.
- Somalia (11), Venezuela (13), Syria (13), South Sudan (13) and Yemen (16) take the bottom spots in the index.
What is the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)?
- The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) scores and ranks countries/territories based on how corrupt a country’s public sector is perceived to be by experts and business executives.
- It is a composite index, a combination of 13 surveys and assessments of corruption, collected by a variety of reputable institutions including the World Bank, World Economic Forum, private risk and consulting companies, think tanks and others.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and the results are given on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International, an independent nonprofit organization that aims to fight corruption, especially in the public sector.
- Transparency International is a global independent, nongovernmental nonprofit organization (NPO) that aims to stop corruption by promoting transparency in various sectors of society.
- The organization's international secretariat is located in Berlin and it has national chapters in more than 100 countries.
- The agency is funded through donations from governments, individuals, private donors, and other organizations.
- The organisation conducts research, and advocacy work, and undergoes various projects in its fight against corruption.
- In 1995, the organization created the first Corruption Perceptions Index, ranking 45 countries based on how much corruption they were perceived to have in the public sector.
Economic Impact of Corruption:
- Corruption continues to be a big hurdle to political, economic, and social development.
- Those who are economically challenged are the most affected by the effects of corruption and related fraud.
- That's because they often rely heavily on public services and can't afford to pay bribes.
- The International Finance Corporation also cites increases in the cost of business as a result of corruption.
Elon Musk's Neuralink implants Brain Chip in First Human (Indian Express)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Elon Musk announced his brain chip company, Neuralink, has completed its first implant on a human patient.
What is Neuralink?
- Neuralink is an upcoming medical device called a brain-computer interface that can help paralysed persons or amputees regain some sense of movement.
- It will decode signals from a part of the brain that plans movements.
- These signals will then be used to control external devices such as computers and mobile phones, allowing the participants to browse the web or play online games with just their thoughts even as their limbs are immobile.
- Under the PRIME Study (short for Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface) an N1 implant will be surgically placed by an R1 robot in the brain.
- The N1 implant has 1,024 electrodes distributed across 64 threads that are thinner than human hair.
- The R1 robot has been designed to insert these threads very accurately in a specific region of the brain.
Current Scenario in the Brain-Computer Interface?
- Recent breakthroughs in brain-computer interfaces have led to remarkable advancements, including systems capable of translating neural signals into speech at nearly the speed of natural speech and bi-directional interfaces that offer sensory feedback to the brain.
- In a notable development, researchers in Switzerland documented a case involving a man paralyzed from the waist down who regained the ability to walk.
- This feat was achieved through the use of a digital bridge that bypassed the damaged portion of his spinal cord.
- By employing a brain-spine interface, the signals from his brain were converted into stimulation for his spine, enabling him to walk again.
- While it may take several years before such devices are commercially available, the scientific progress in this field is remarkable.
- These advancements hold promise for individuals paralyzed due to accidents, offering potential mobility with the assistance of spinal implants.
What are the Challenges?
- One of the main challenges of the technology is establishing the connection between the brain and the chips, allowing it to reliably interpret the signals from the brain.”
- The use of conventional electronics for developing brain-computer interfaces results in a “mismatch with the soft tissue of the brain.”
- This can lead to tissue damage and immune response to the sensors.
- Flexible electronics with tissue-like properties can help build interfaces that do not face these problems.
- It can also help the systems adapt to changes in the brain volume during development, ageing and disease.
Eravikulam National Park to Close From February 1 for Nilgiri Tahr Breeding Season (The Hindu)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
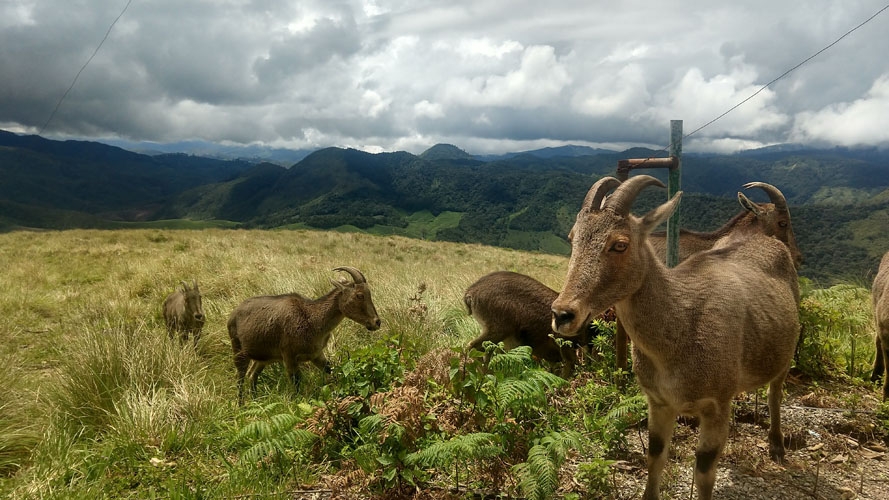
The Eravikulam National Park (ENP), the natural habitat of the Nilgiri tahr, will be closed for the calving season of the species from February 1 to March 31.
About Eravikulam National Park:
- Eravikulam National Park also known as Rajamala National Park, is located in Kerala's Idukki district.
- The park is administered under the Kerala Forest and Wildlife Department and became a National park in 1978.
- It is a 97 km2 national park located along the Western Ghats, Kerala.
- Anamudi, the highest peak in south India was located on the southern side of the park.
- This is also the land of "Neelakurinji", a flower that blooms once in twelve years.
- Wildlife in the Park: The park holds the maximum viable population of the endangered Nilgiri Tahr including other little-known fauna Nilgiri marten, ruddy mongoose, small clawed otter, dusky striped squirrel etc.
- Flora: Important flora includes Microtropis ramiflora, Actinodaphne bourdilloni, Pittosporum tetraspermium, Chrysopogon Zelanieus, Strobilanthus Kunthianus (Neela Kurinji) etc.
- Mostly the park is busted with rolling grasslands, but several patches of shola forests are also found in the upper part of the valley.
- The shola grasslands are exceptionally rich in balsams and orchids including the long thought extinct variety Brachycorythis wightii.
- The Atlas moth, the largest of its kind in the world, is seen in this park.
Key Facts about Nilgiri Tahr:
- Nilgiri Tahr is a rare mountain animal found only in the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Scientific Name: Nilgiritragus hylocrius
- Local Name: Varayaadu
- They are famous for their ability to climb steep cliffs, which has earned them the nickname Mountain Monarch.
- It is the official state animal of Tamil Nadu.
- Distribution: Nilgiri Tahrs are mainly found in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, covering only about 5% of the Western Ghats.
- Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the largest population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
- Habitat: They live in open grasslands at elevations between 1200 and 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
- Characteristics: Nilgiri Tahrs have a sturdy body with short, coarse fur and a rough mane.
- Both males and females have curved horns, with males having larger horns, up to 40 cm long.
- Adult males have a light grey area on their backs, known as a 'saddle,' hence the name 'saddlebacks.'
- They have a short grey-brown or dark coat.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972: Schedule I
Employer Rating Survey to Assess Women Participation in Workforce (Business Standard)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
To bolster the representation of women in the workforce and advance gender equality, various ministries of the central government issued a series of advisories and surveys on Tuesday, aimed at industries and employers.
About the Survey:
- This survey aims to evaluate the prevalence of women-friendly practices across the nation's workplaces.
- The government is collecting information on several key aspects, including the establishment of internal complaints committees (ICC) for preventing sexual harassment, the provision of childcare facilities, ensuring pay equity, offering flexible or remote work options for women, and providing safe transportation during late hours.
- Additionally, various ministries of the Central government have issued advisories to enhance women's representation in the workforce.
Factors Affecting Low Women Workforce Participation:
- Cultural and Social Norms: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations often discourage women from pursuing full-time employment due to responsibilities for caregiving and homemaking, limiting their participation in the workforce.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to quality education can hinder women from acquiring the necessary skills and qualifications for certain jobs, further reducing their workforce participation.
- Gender Pay Gap: Disparities in wages between men and women discourage women from entering or remaining in the workforce, contributing to lower participation rates.
- Structural Constraints: India's manufacturing and service sectors often have rigid structures that limit employment opportunities, particularly in the informal sector where many women work.
- Security Concerns: Instances of sexual harassment in the workplace create safety concerns for women, acting as a barrier to their participation in the labour force.
Government Initiatives Supporting Women's Empowerment:
- Code on Wages, 2019: Ensures equal pay for equal work without discrimination based on gender, fostering fairness in wage practices across establishments.
- Code on Occupational Safety, Health And Working Conditions (OSH), 2020: Proposes amendments to improve employment conditions for women workers, particularly in above-ground mines, ensuring their safety and well-being.
- Maternity Benefit Act, 2017: Enhances maternity benefits and fosters a healthier work environment for pregnant and nursing women, promoting their well-being and work-life balance.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK): A national organization offering microfinance services to empower economically disadvantaged women, supporting their livelihood projects and economic independence.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Focuses on creating sustainable self-employment opportunities for rural women through skill training, capacity building, and financial assistance, enabling them to engage in income-generating activities.
- MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Guarantees 100 days of wage employment annually to rural households, actively encouraging women's participation and ensuring equitable employment opportunities.
Way Forward
Continued government initiatives aimed at empowering women in the workforce through skill development and expanded employment opportunities have yielded positive results, as evidenced by the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the Labour Bureau in 2023. This survey indicated a notable increase in women's participation, rising from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23.
Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre has proposed repealing the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 and bringing in a new law for the stamp duty regime in the country.
What is Stamp Duty?
- A stamp duty is essentially a government tax, which is levied to register documents, like an agreement or transaction paper between two or more parties, with the registrar.
- Usually, the amount specified is fixed based on the document’s nature or is charged at a certain percentage of the agreement value stated in the document.
- Stamp duties can be levied on bills of exchange, cheques, promissory notes, bills of lading, letters of credit, policies of insurance, transfer of shares, debentures, proxies and receipts.
- Accepted as valid evidence in a court of law, stamp duties are levied by the Centre but appropriated by the concerned states within their territories under Article 268 of the Constitution.
Notable Provisions of the Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023:
Several provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 have now become “redundant” or “inoperative” Therefore, the ministry has proposed repealing the existing Act and substituting it with new legislation to “reflect the present realities and objectives.”
- The draft Bill has introduced provisions for digital e-stamping.
- “Electronic stamp” or “e-stamp” means an electronically generated impression denoting the payment of stamp duty by electronic means or otherwise, according to Section 2 (18) of the Bill.
- There are also provisions for digital signatures.
- Section 2 (17) of the Bill states that the words “executed” and “execution”, used for instruments, will mean “signed” and “signature” and include attribution of electronic records and electronic signatures, as defined under the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
- The IT Act defines “electronic records” as “data, record or data generated, image or sound stored, received or sent in an electronic form or micro film or computer generated microfiche.”
- Meanwhile, digital or electronic signature refers to the authentication of any electronic record by a subscriber through an electronic method or procedure.
- The draft Bill also proposes to raise penalties.
- It seeks to increase the maximum penalty amount from Rs 5,000 to Rs 25,000 for contravening any provisions of the law and impose Rs 1,000 per day for repeated offences.
What is the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899?
- The Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 is a fiscal or money-related statute that lays down the law relating to tax levied in the form of stamps on instruments recording transactions.
- Under Section 2 of the Act, an instrument includes every document by which any right or liability is or purports to be, created, transferred, limited, extended, extinguished or recorded.
- According to this Act, a “stamp” has been defined as “any mark, seal or endorsement by any agency or person duly authorised by the State Government, and includes an adhesive or impressed stamp, for the purposes of duty chargeable under this Act”.
- Section 3 of the 1899 Act prescribes that certain instruments or documents shall be chargeable with the amount indicated in Schedule 1 of the Act.
- These include bills of exchange or promissory notes.
