Melanistic Tigers
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
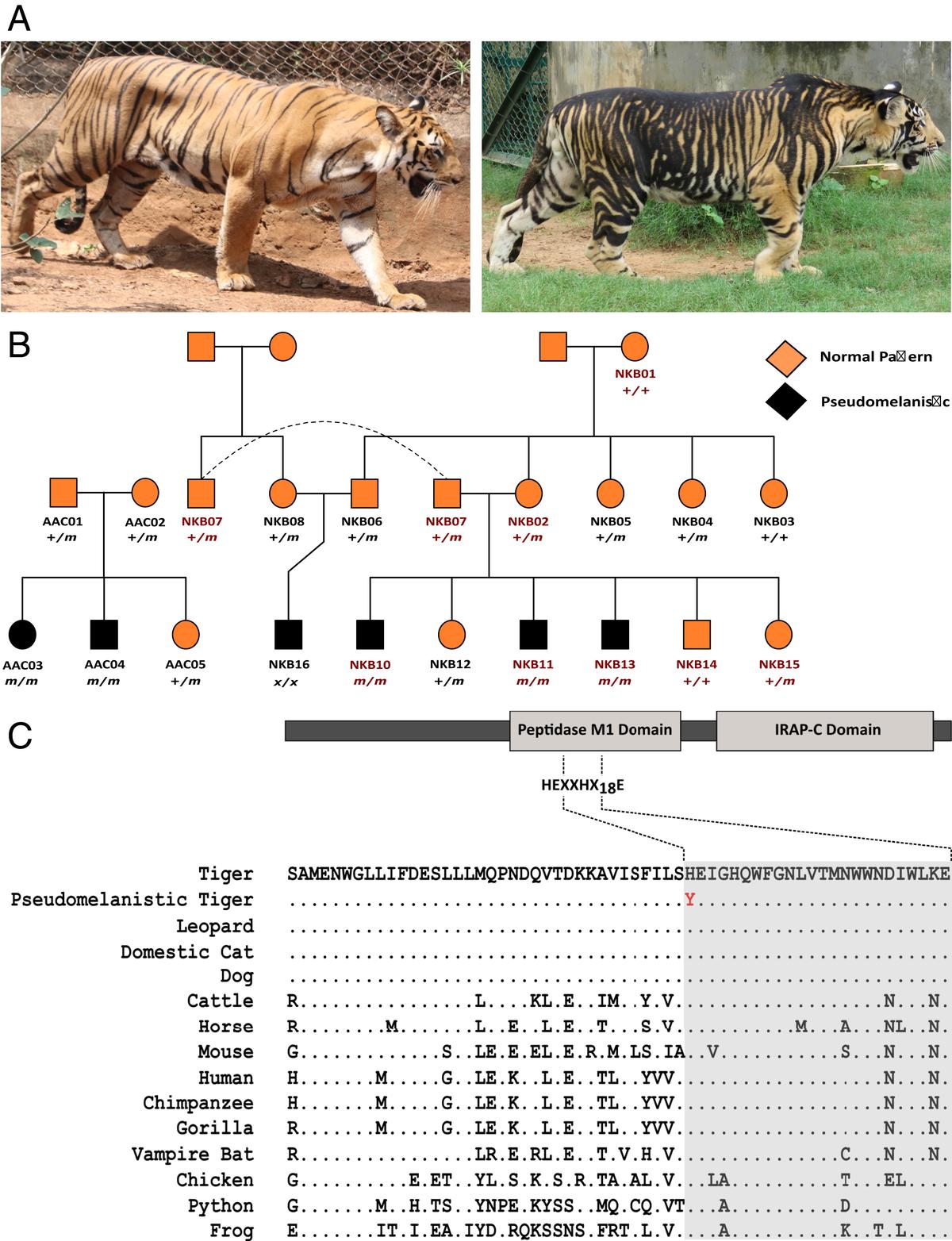
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
PM rolls out Ayushman Bharat for Citizens aged 70 and above

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has expanded the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) to provide health coverage to citizens aged 70 years and above, regardless of their income or economic status. This move is aimed at addressing the healthcare challenges faced by India's elderly population, which has been growing rapidly.
Key Highlights of the Ayushman Bharat Expansion:
- Health Coverage for Elderly:
- Ayushman Vaya Vandana Card: This new health card offers Rs 5 lakh annually for individuals aged 70 and above. The coverage is shared within the family, so if there are multiple elderly beneficiaries in one household, the total cover will be split.
- Scope: This initiative is designed to provide a safety net for elderly people, many of whom had previously been unable to access treatment due to high costs.
- Significance of the Scheme:
- India’s elderly population is rapidly growing, with the number of people over 60 expected to reach 319 million by 2050, up from 103 million in 2011.
- The expansion of PM-JAY to include those aged 70+ is a critical step in making universal health coverage more inclusive as India’s population ages.
- Eligibility and Registration:
- Individuals aged 70 years and above must register on the PM-JAY portal or through the Ayushman app. Those who already have an Ayushman Bharat card must complete an eKYC process to receive the new card and coverage.
- Exclusions: The scheme is not available in Delhi and West Bengal, as these states have not adopted the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- Financial Details:
- The initial outlay for this expansion will be Rs 3,437 crore, covering the remainder of the current financial year and the next year.
- Cover for Overlapping Health Schemes: Elderly individuals who are already covered under other government schemes (e.g., CGHS, Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme) will have the option to either continue with their current coverage or choose Ayushman Bharat. Those with ESIC or private insurance can access both Ayushman Bharat and their existing cover.
- Coverage Scope:
- The expansion is expected to benefit approximately 6 crore individuals across 4.5 crore families.
- Existing Coverage: Around 1.78 crore elderly people are already covered under the scheme. Additional coverage will be provided to those not currently included in the scheme.
- Interoperability with Other Schemes:
- Those under the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or other similar schemes will need to choose between their current insurance and the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- However, individuals enrolled in Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) can have both their existing cover and the Ayushman Bharat coverage.
- Rollout and Reach:
- The scheme will be implemented across 33 states and Union Territories, except Delhi, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Over 29,600 hospitals, including more than 12,600 private facilities, are empanelled to provide treatment under PM-JAY.
Other Key Announcements:
- U-WIN Portal: A pan-India digital platform for routine vaccinations, aimed at enhancing the efficiency of vaccination programs.
- Critical Care Facilities: The Prime Minister also launched critical care infrastructure, including new facilities in AIIMS Bhubaneswar, Kalyani, and super-specialty units in Himachal Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
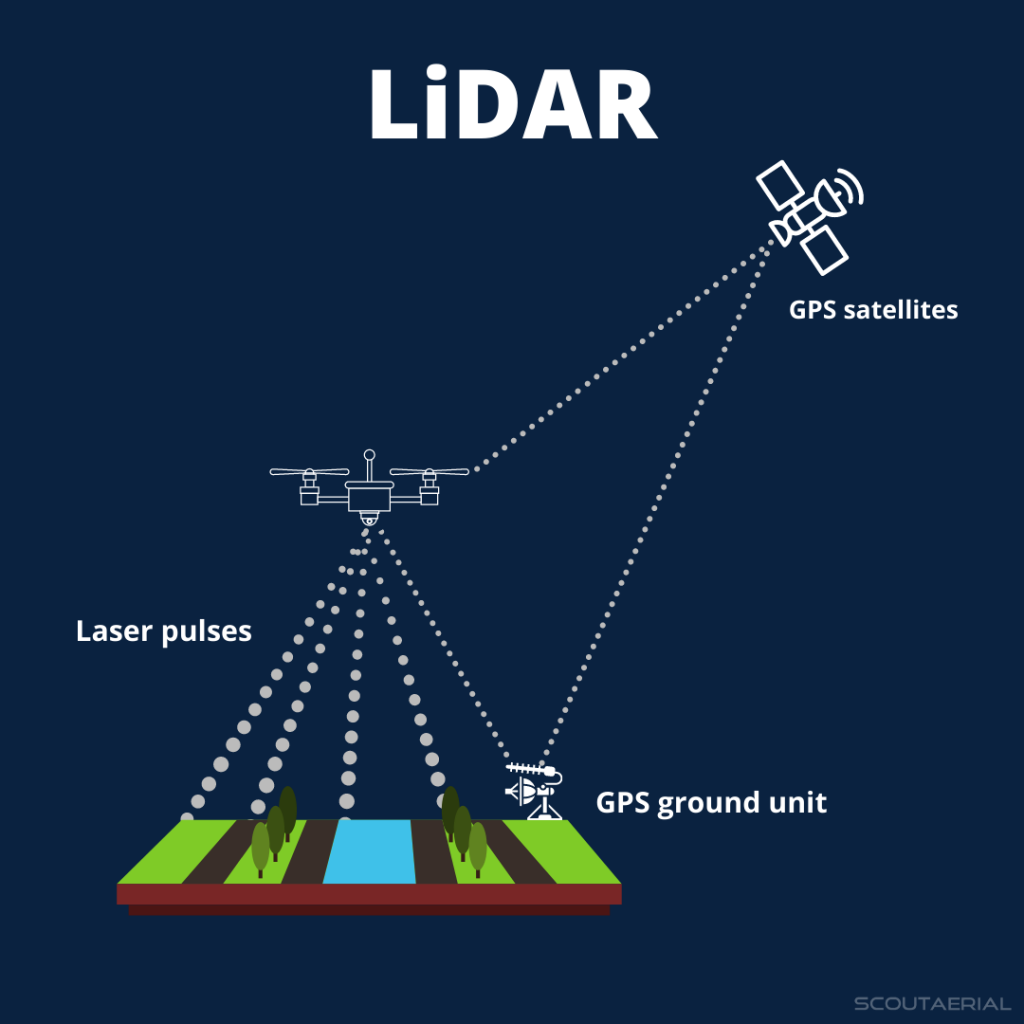
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
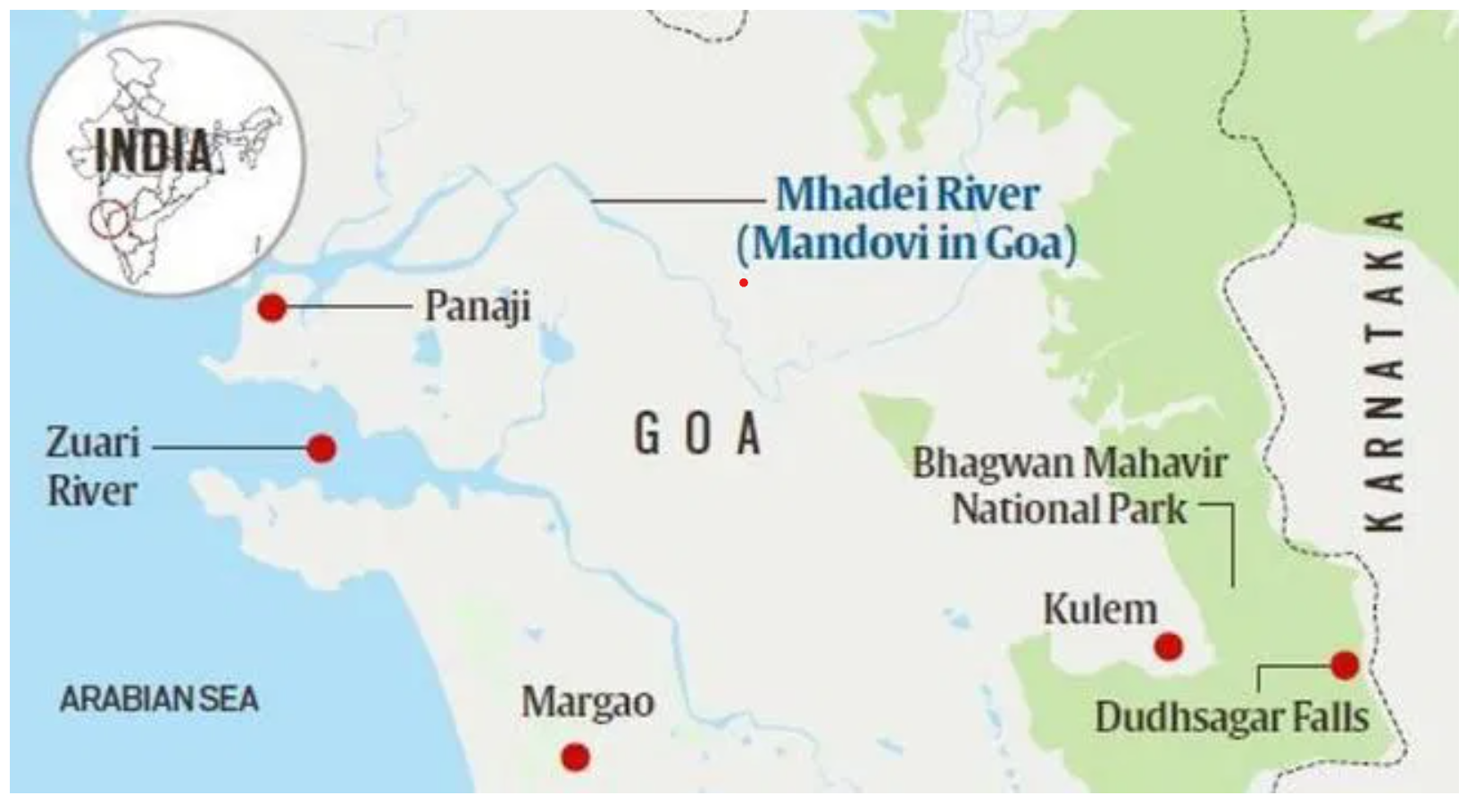
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
