AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
eShram portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Labour & Employment (MoLE) stated in a latest update that in the short span of three years since its launch, eShram has registered more than 30 crore unorganised workers, showcasing its rapid and widespread adoption among the unorganised workers.
Key Highlights:
- The Government envisages to establishing the eShram portal as a "One-Stop-Solution" for Country’s unorganised workers.
- During Budget speech 2024-25 it has been announced that, A comprehensive integration of eShram portal with other portals will facilitate such One-Stop-Solution.
- This initiative aims to facilitate access of various social security schemes being implemented by different Ministries/ Departments to unorganised workers through the eShram portal.
- As part of the eShram - One Stop Solution project, Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) has been working to integrate major schemes like Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G), Ration Card scheme etc. for the benefit of the unorganised workers.
What is e-Shram and its purpose?
- e-Shram is a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW) launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Its primary purpose is to facilitate delivery of welfare benefits and social security measures to unorganised sector workers across the country.
- The platform aims to register and provide identity cards to unorganised workers, enabling them to access various government schemes, benefits, and services more efficiently.
Who are unorganised workers?
Any worker who is a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker working in the unorganised sector and not a member of ESIC or EPFO, is called an unorganised worker.
What is unorganised sector?
Unorganised sector comprises of establishment/ units which are engaged in the production/ sale of goods/ services and employs less than 10 workers. These units are not covered under ESIC & EPFO.
What is UAN?
UAN or Universal Account Number is a 12 digit number uniquely assigned to each unorganised worker after registration on e-Shram portal. UAN is a permanent number i.e., once assigned, it will remain unchanged for any worker.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the proposal of Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd to setup a semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat, with an investment of Rs 3,300 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The proposed unit, under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), will produce nearly 60 lakh chips per day.
- The chips produced in this unit will cater to a wide variety of applications which include segments such as industrial, automotive, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, telecom and mobile phones, etc.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of developing indigenous semiconductor capabilities.
- As per the reports, India’s semiconductor market is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, positioning the country as a major global semiconductor hub.
- The first indigenously-developed chip is set to arrive in the country by the end of this year.
- In March, PM Modi laid the foundation stone of three semiconductor projects worth Rs 1.25 lakh crore.
- Tata Electronics is setting up a semiconductor fab in Dholera, Gujarat and one semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- CG Power is setting up one semiconductor unit in Sanand. These units will produce lakhs of direct and indirect jobs.
- These four units will bring an investment of almost Rs 1.5 Lakh crore. The cumulative capacity of these units is about 7 crore chips per day, according to the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- The Programme for Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem in India was notified in 2021 with a total outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
About India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- It is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation that aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- ISM has all the administrative and financial powers and is tasked with the responsibility of catalysing the India Semiconductor ecosystem in manufacturing, packaging, and design.
- ISM has an advisory board consisting of some of the leading global experts in the field of semiconductors.
- ISM has been working as a nodal agency for the schemes approved under the Semicon India Programme.
Semicon India Programme:
- Launched in 2021 with a total budget of Rs. 76,000 crore, the ISM is overseen by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), Government of India. This initiative is part of a broad effort to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem within the country.
- The programme is designed to offer financial support to companies involved in semiconductor and display manufacturing and design. It also aims to foster the creation of domestic Intellectual Property (IP), and to promote and incentivize the Transfer of Technologies (ToT).
- Under this programme, four key schemes have been introduced:
- Scheme for establishing Semiconductor Fabs in India.
- Scheme for establishing Display Fabs in India.
- Scheme for setting up Compound Semiconductors/Silicon Photonics/Sensors Fabs and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP)/OSAT facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
India-Singapore Relations

- 04 Sep 2024
- High-Level Inter-Governmental Contacts:
- Frequent and high-level exchanges, including the Prime Minister's upcoming visit.
- Recent second India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable with senior Indian ministers.
- Key Areas of Cooperation:
- Digitalisation, skills development, sustainability, healthcare, advanced manufacturing, and connectivity.
- Broader contacts include parliamentary and judicial exchanges.
- Economic Ties:
- Singapore is India’s largest trading partner among ASEAN countries and the sixth largest globally.
- Singapore is also the largest source of foreign direct investment (FDI) for India.
- People-to-People Exchanges:
- Large concentration of IIT and IIM alumni in Singapore.
- Historical ties, including the Indian National Army's presence and the contributions of early Indian diaspora in Singapore.
- Regional Policy and Strategic Importance:
- Singapore has supported India’s “Look East” and “Act East” policies.
- Facilitated India’s dialogue partnership with ASEAN.
- Regional implications due to Myanmar’s instability, with India and Singapore both having stakes.
- Defence and Maritime Cooperation:
- Important defence component and maritime collaboration.
- Focus on the Indo-Pacific region amidst growing Chinese influence and new regional architectures like the QUAD.
- Trade and Economic Outlook:
- The visit provides an opportunity to review and expand trade and economic partnerships.
- Potential for increased Chinese FDI into India, with Singaporean entities likely to play a role.
- Complementarities and Challenges:
- Singapore's role as a global trading and investment hub complements India’s economic landscape.
- Highlights India's regulatory and structural inefficiencies, pointing to areas needing improvement for enhanced bilateral cooperation.
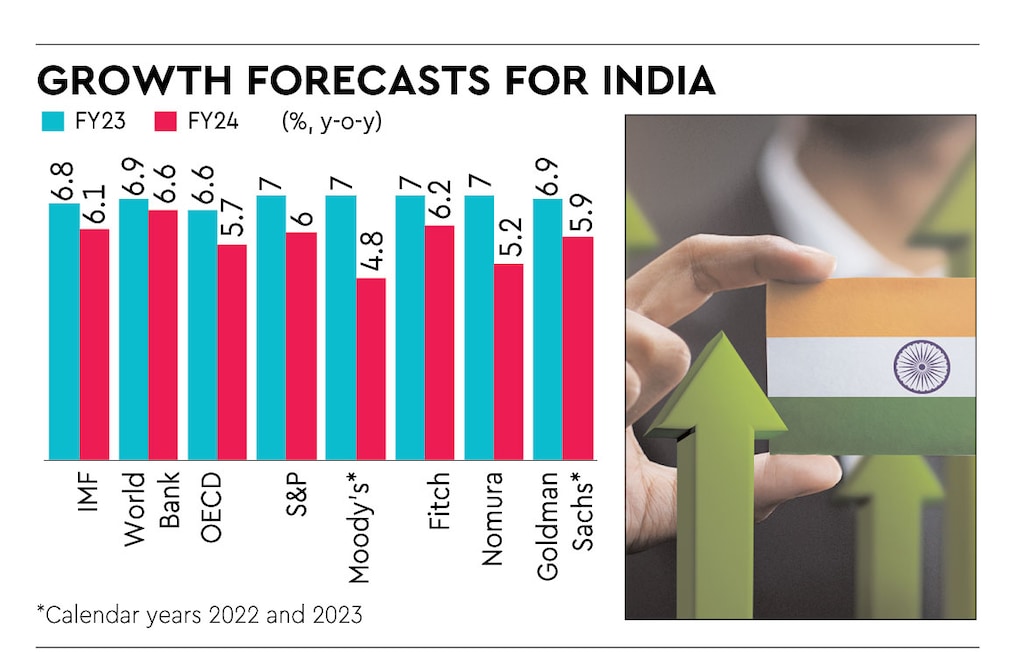
World Bank hikes India's economic projection to 7% for FY 2024-25
- 04 Sep 2024
- The World Bank has forecast a growth of 7% for the Indian economy for the current fiscal year, upping its earlier estimate of 6.6%.
- In its report, India Development Update: India’s Trade Opportunities in a Changing Global Context, the World Bank said India’s growth continued to be strong despite a challenging global environment.
- The World Bank growth projection is in line with those of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- Both the institutions have raised their forecast to 7% for the financial year ending March 2025.
- The India Development Update [IDU] observes that India remained the fastest-growing major economy and grew at a rapid clip of 8.2% in FY 23/24.
- Growth was boosted by public infrastructure investment and an upswing in household investments in real estate.
- On the supply side, it was supported by a buoyant manufacturing sector, which grew by 9.9%, and resilient services activity, which compensated for underperformance in agriculture.
- Reflecting these trends, urban unemployment has improved gradually since the pandemic, especially for female workers. While female urban unemployment fell to 8.5 % in early FY24/25, the urban youth unemployment remained elevated at 17%.
- India’s robust growth prospects, along with declining inflation rate will help to reduce extreme poverty
- India can boost its growth further by harnessing its global trade potential. In addition to IT, business services and pharma where it excels, India can diversify its export basket with increased exports in textiles, apparel, and footwear sectors, as well as electronics and green technology products.
- A recovery in agriculture will partially offset a marginal moderation in industry and all services will remain robust. The rural private consumption will recover, thanks to the expected recovery in agriculture.
- The report also highlights the critical role of trade for boosting growth. The global trade landscape has witnessed increased protectionism in recent years. The post pandemic reconfiguration of global value chains, triggered by the pandemic, has created opportunities for India.
- The IDU recommends a three-pronged approach towards achieving the $1 trillion merchandise export target by reducing trade costs further, lowering trade barriers, and deepening trade integration.
