India to use SpaceX rocket to launch communications satellite (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is gearing up for the launch of its communication satellite GSAT-20, weighing 4,700kg, an initiative marking India's entry into a new era of satellite technology.
Context:
- The commercial arm of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will launch GSAT-20 (renamed as GSAT-N2), on-board SpaceX’s Falcon-9 during the second quarter of 2024.
- ISRO's current flagship rocket, the LVM3, holds a maximum carrying capacity of four tons.
- Falling short by 700kg for the GSAT-20.
- This satellite will cater to cellular backhaul service needs particularly to remote and unconnected regions.
What is GSAT 20 Satellite?
- GSAT-20 is an Indian geostationary Ka-band high-throughput communications satellite.
- GSAT 20 is built on the I-3K unified modular bus with electric-only propulsion.
- It will be India's first satellite to rely entirely on electric propulsion, which can be five to six times more efficient than chemical-based propulsion.
- It features a Ka × Ka high-throughput communications payload with 70 Gbps throughput utilizing 32 spot beams with each 2 polarisations providing broadband services across the Indian region.
- The satellite was initially set for a 2020 launch on a GSLV Mk.3 (2) rocket but got moved up to 2019 on an Ariane-5ECA+.
- In 2021, the plan returned to a GSLV Mk.3 (2) launch.
- In early 2024, a contract with SpaceX was signed for a Falcon-9 v1.2 (Block 5) launch.
What is SpaceX’s Falcon-9 Rocket?
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX “for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond".
- It is the world’s first orbital-class reusable rocket.
- Reusability allows SpaceX to re-fly the most expensive parts of the rocket, which in turn drives down the cost of space access," it added.
- Till now, it has undertaken 285 launches, 243 landings, and 217 re-flights.
Centre, SEBI will regulate short selling, Solicitor-General tells Supreme Court (The Hindu)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court judgement records a statement made by Solicitor General Tushar Mehta that the Union government and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) will take measures to regulate short selling.
What is Short Selling?
- Short selling is a financial strategy where an investor or trader borrows securities, such as stocks, from a broker and sells them in the market with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price in the future.
- Short selling is regulated by a circular notified by SEBI in December 2007.
- This technique is employed by individuals who anticipate a decline in share prices, aiming to profit from their predictions.
- The process involves selling shares that the trader does not own.
- To initiate a short position, the trader borrows shares from a broker, who lends them with an agreement for return at the settlement time.
- The borrowed stocks are then sold at the prevailing market rate, creating a short position.
- Subsequently, the trader waits for the prices to decrease before buying back the shares to close the position.
- The ultimate goal of short selling is to 'sell high and buy low.'
- Profits are made when share prices fall, and the trader benefits from the difference between the selling and repurchasing prices.
- Conversely, if the trader's analysis is incorrect and share prices rise, they incur a loss.
How Does Short Selling Work?
Short selling is an activity that allows market participants to profit from the fall in the price of a financial instrument. It involves borrowing an asset from a broker, selling it in the market, and then repurchasing it later at a hopefully lower price to return it to the lender.
- Borrowing the Asset: The trader borrows the asset (usually stocks) from a broker or another trader.
- This borrowed asset is typically done through a margin account, where the investor agrees to certain terms and pays a fee or interest for the borrowed amount.
- Selling the Asset: After obtaining the borrowed asset, the trader immediately sells it on the market.
- This is where they take advantage of their belief that the asset's price will decrease.
- Waiting for Price Drop: The trader waits for the price of the asset to fall. If the price drops as anticipated, the investor can buy back the asset at a lower price.
- Repurchasing the Asset: Once the price has dropped, the trader uses the proceeds from the initial sale to repurchase the same asset at a lower price.
- Returning the Borrowed Asset: Finally, the trader returns the borrowed asset to the lender, typically the broker, from whom they originally borrowed it.
- Profit or Loss: The profit or loss in short selling is the difference between the price at which the asset was sold and the price at which it was repurchased, minus any borrowing fees, interest, or transaction costs.
Short selling is considered a more advanced and riskier trading strategy, and it requires careful monitoring of market conditions. It is often used by experienced investors or hedge funds seeking to profit from anticipated price declines in specific securities or markets.
A first in 100 years, the Indian Science Congress was postponed amid a tussle between organisers, Govt (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Science Congress, the largest gathering of scientists and students of science in the country and a permanent annual fixture in the calendar of the participant group for more than a century has been postponed.
Postponement of the Indian Science Congress:
- Unprecedented Interruption: The postponement of the Indian Science Congress holds unprecedented significance.
- Since its inception in 1914, the Congress has been an annual event, except for the years immediately following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022).
- Tradition and Prime Ministerial Engagement: A cornerstone of scientific tradition, the Indian Science Congress is inaugurated by the Prime Minister, making it a fixture on the PM's calendar.
- Typically, it stands as the Prime Minister's first public engagement of the new year.
Why has the Science Congress Been Postponed This Year?
- This year's postponement stems from a protracted dispute between the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), the organizing body, and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) within the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The DST, a key funding entity, withdrew support in September 2023, citing financial irregularities.
- The ISCA refuted the allegations and contested the DST's directive prohibiting government funds for Science Congress-related expenses, leading to an impasse that has resulted in the postponement.
- A legal challenge to the DST's decision is currently pending.
What is the Indian Science Congress (ISC)?
- The Indian Science Congress (ISC) is a unique event in the country that serves as a platform for scientific communities to interact with students and the general public on science-related matters.
- Organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), an independent body supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government, the Science Congress is an annual five-day event from January 3 to 7, considered a permanent fixture on the Prime Minister’s calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
- In recent years, the Indian Science Congress (ISC) has faced criticism due to issues such as a lack of substantial discussions, the promotion of pseudoscience, and outlandish claims by certain speakers.
- This has led to concerns among prominent scientists, with some advocating for the discontinuation of the event or, at the very least, the withdrawal of government support.
- While the government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, it does not play a direct role in its organization.
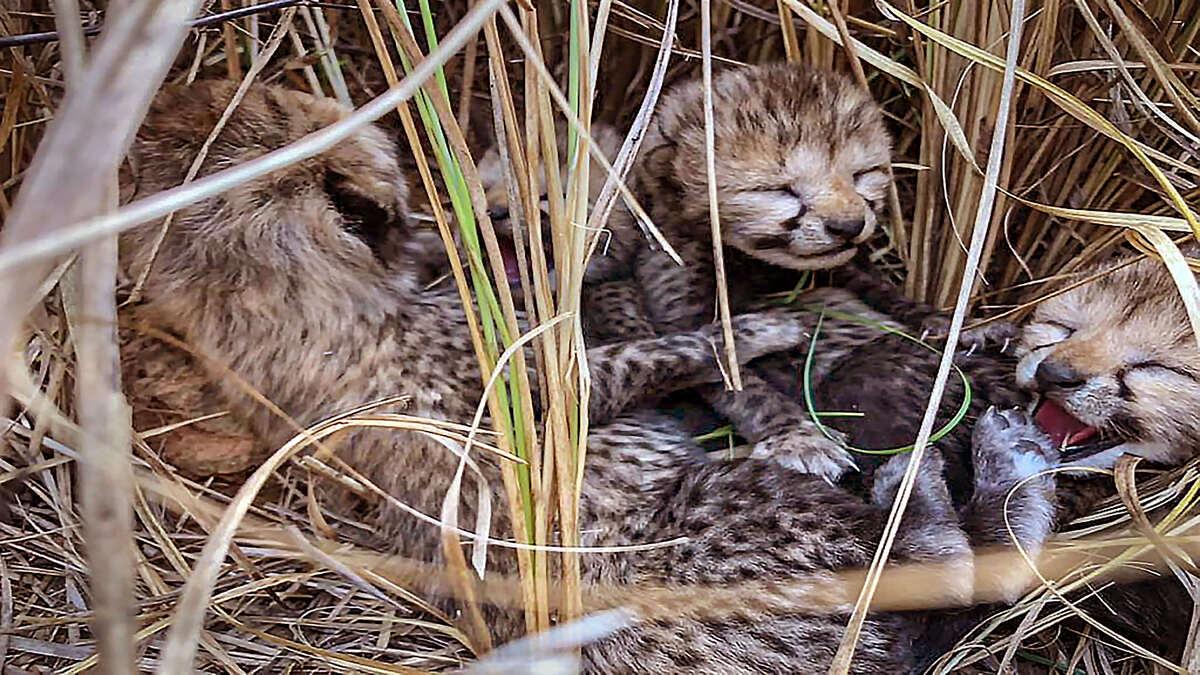
Namibian cheetah Aasha gives birth to 3 cubs in Kuno; ‘indicator that animals are acclimatising’ (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a Namibian cheetah named Aasha has given birth to three cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
About Kuno National Park (KNP):
- Location: Situated in the Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh, Kuno National Park is nestled near the Vindhyan Hills.
- The park is aptly named after the Kuno River, a significant tributary of the Chambal River that traverses its expanse.
- Originally designated as a wildlife sanctuary, Kuno National Park attained the status of a national park in 2018.
- This transformation aligns with its pivotal role in the 'Action Plan for Introduction of Cheetah in India.'
- Vegetation and Flora: Kuno predominantly features a grassland landscape, punctuated by occasional rocky outcrops.
- The flora encompasses a diverse mix, including dominant species such as Kardhai, Salai, and Khair trees.
- The park boasts a rich composition with 123 tree species, 71 shrub species, 32 exotic and climbing species, and 34 bamboo and grass species.
- Fauna: The protected region of Kuno National Park shelters an array of wildlife, including the jungle cat, Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- The park also delights bird enthusiasts with a habitat supporting over 120 bird species.
What is Project Cheetah?
- The Wildlife Trust of India started talks in 2009 to bring the cheetah back to India.
- Over five years, 50 cheetahs will be imported from African nations and placed in various national parks as part of the "Action Plan for Reintroduction of Cheetahs in India."
- Prime Site Selection - Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP): Among the surveyed sites in central Indian states, Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh emerged as the most suitable location.
- This acclaim is attributed to its conducive habitat and ample prey base.
- KNP is deemed capable of supporting 21 Cheetahs, uniquely standing as a wildlife site where villages have been entirely relocated from within the park.
- Moreover, Kuno offers the prospect of harmoniously accommodating four of India's prominent big cats - tiger, lion, leopard, and Cheetah.
- Additional Recommended Sites: The project identifies other potential sites, including Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh), Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary - Bhainsrorgarh Wildlife Sanctuary complex (Madhya Pradesh), Shahgarh bulge in Jaisalmer (Rajasthan), and Mukundara Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan).
- Implementation Progress: As a significant stride in the project's realization, 20 Cheetahs, comprising 8 from Namibia and 12 from South Africa, were introduced to Kuno Palpur National Park last year.
- This marks a historic initiative to establish a free-ranging Cheetah population in India, reviving their presence after a 70-year absence.
PM inaugurates Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Optical Fibre Connection (PIB)
- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently, in Kavaratti, Lakshadweep, inaugurated the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands submarine optical fibre connection (KLI-SOFC) project including various developmental projects worth more than Rs 1,150 crore.
Background-Kochi-Lakshadweep Submarine OFC (KLI) Project:
- The need for digitally connecting the Lakshadweep Islands through a high-capacity submarine cable link with the mainland has been felt for some time.
- Earlier, the only means of communication with the Islands was through Satellite medium, which had limited bandwidth capacity and was not able to meet the growing bandwidth demand.
- In the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Cable (KLI) project submarine cable connectivity from Mainland (Kochi) to eleven Lakshadweep Islands namely, Kavaratti, Agatti, Amini, Kadmat, Chetlet, Kalpeni, Minicoy, Androth, Kiltan, Bangaram and Bitra has been extended.
- The project is funded by the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF), Department of Telecommunication.
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) was the Project Executing Agency and the work was awarded to NEC Corporation India Pvt Ltd.
- Major activities related to the project include Marine Route Survey, Submarine Cable laying, Civil Construction of CLS stations, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of End Terminals (SLTE).
- Highlights of the KLI Project:
- Total link distance: 1,868 kilometres.
- Total cost of project: Rs 1072 crore
???????Benefits of the KLI Project:
- The project will play a significant role in achieving the objective of ‘Digital India’ and ‘National Broadband Mission’ and in rolling out various e-governance projects of the Government of India in Lakshadweep Islands.
- E-Governance, Tourism, Education, Health, Commerce and Industries will get a boost
- It will also help in further improvement in the standards of living of the people on the Island and will accelerate overall social and economic development in these areas.
- The population of Lakshadweep Islands will be provided high-speed wireline broadband connectivity.
- High-speed broadband will be provided through FTTH and 5G/4G Mobile networks.
- The bandwidth created under this project will be available to all Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to strengthen their telecom services in the Lakshadweep Islands.
