Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) Results for 2022-23
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the results of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for the financial year 2022-23 (April 2022 to March 2023).
- The fieldwork for this survey was conducted from November 2023 to June 2024.
- The ASI provides critical insights into the dynamics of the manufacturing sector, covering aspects such as output, value added, employment, and capital formation.
Key Highlights
- Gross Value Added (GVA): Increased by 7.3% in current prices for 2022-23 compared to the previous year.
- Industrial Output: Grew by over 21% in 2022-23 compared to 2021-22.
- Employment: Estimated employment in the sector rose by 7.4% over the previous year, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
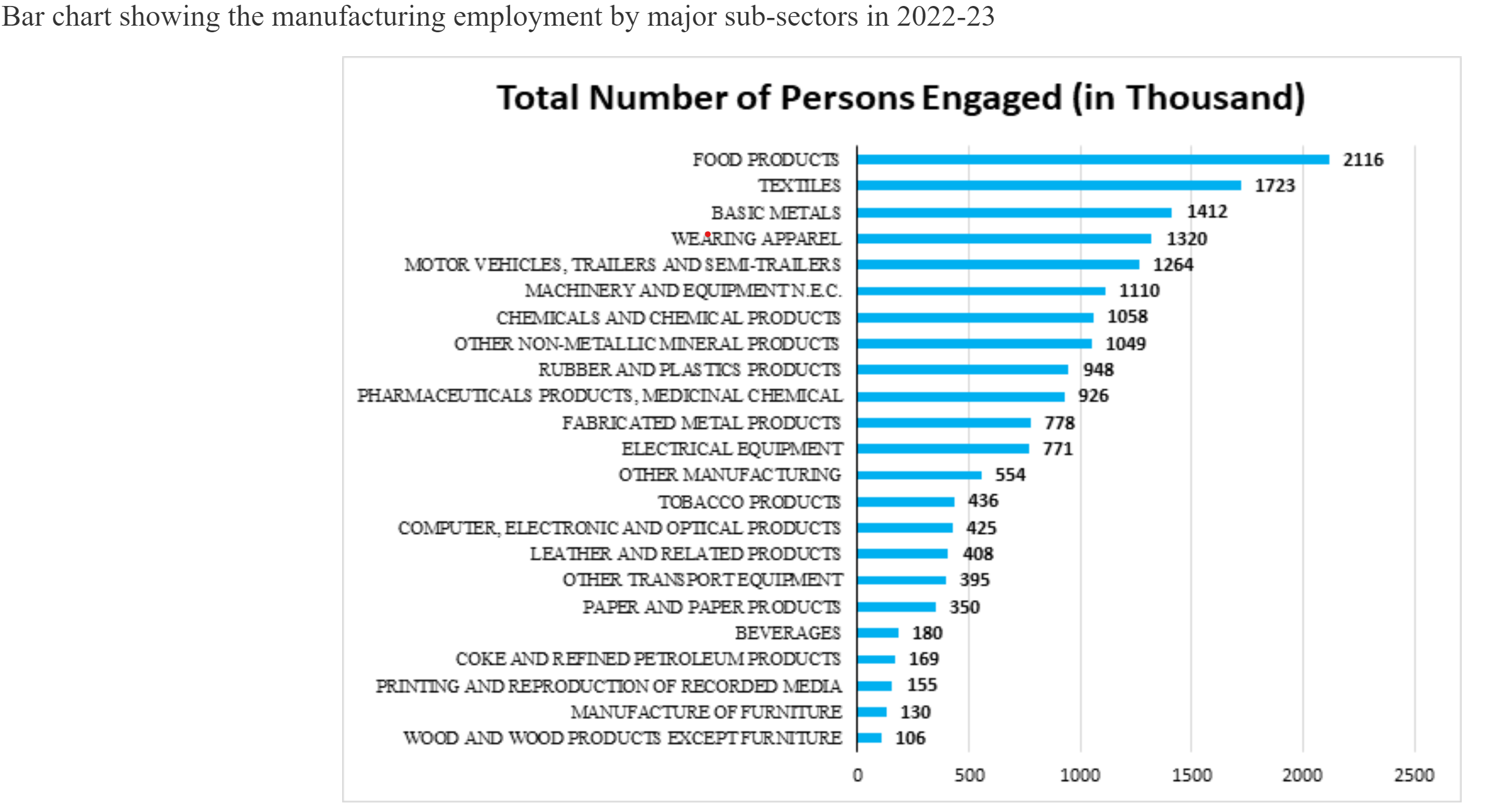
The growth in key economic parameters such as invested capital, input, output, GVA, and wages indicates a robust recovery in the industrial sector. Notably, industries like Basic Metal Manufacturing, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Food Products, Chemicals, and Motor Vehicles were significant contributors, accounting for about 58% of total output and showing a 24.5% increase in output and 2.6% in GVA.
State Contributions
- Top GVA Contributors:
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Uttar Pradesh
Together, these states contributed over 54% of the total manufacturing GVA.
- Highest Employment States:
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Karnataka
Collectively, these states accounted for about 55% of total manufacturing employment in 2022-23.
Survey Details
The ASI encompasses various industrial units, including:
- Factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948.
- Bidi and cigar manufacturing establishments.
- Electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority.
- Units with 100 or more employees registered in the Business Register of Establishments.
The survey employs a comprehensive sampling strategy, dividing units into Central and State Samples to ensure accurate representation. Key components of the data collection include:
- Central Sample: Includes all units in less industrially developed states and specific industrial categories.
- State Sample: Comprises selected units based on employee count and other criteria.
Industrial Classification
Since 1959, the ASI has adopted various classifications to categorize industries. The current classification, NIC 2008, is based on the UN's international standards and has been in use since 2008-09.
Data Collection and Reliability
Data collection is conducted via a dedicated web portal, following the Collection of Statistics Act. Various quality checks ensure reliability, with the Relative Standard Errors (RSE) for important estimates remaining within acceptable limits.
Modified PKC-ERCP project
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
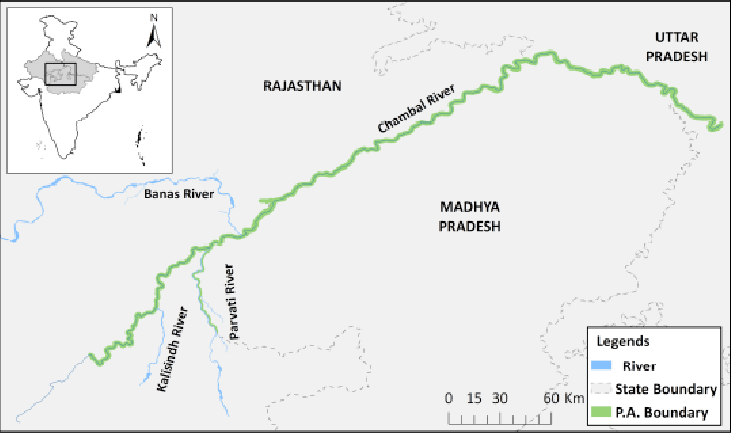
Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan governments signed an agreement for the implementation of the Rs 72,000 crore Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal river linking project.
Modified PKC-ERCP Project Overview
- Signatories: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti signed a MoU for implementation.
- Project Type: Inter-state river linking initiative.
- Integration: Combines the long-standing Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) project with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) under India's National Perspective Plan for interlinking rivers.
Objectives and Benefits
- Water Supply: Aims to provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts in eastern Rajasthan and the Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh.
- Irrigation: Expected to irrigate approximately 5.6 lakh hectares across both states.
- Groundwater Management: Focus on improving groundwater levels and enhancing socio-economic conditions in rural Rajasthan.
Project Components
- Detailed Project Report (DPR): Currently under preparation, will outline water sharing, cost distribution, and implementation strategies.
- Historical Context:
- PKC Project: Proposed in 1980 as part of a national plan, initially focused on diverting water from Kalisindh and Newaj rivers to Chambal.
- ERCP: Proposed by Rajasthan in 2019 to optimize water resources by redistributing surplus monsoon water from various sub-basins to deficit areas.
Geographic Focus
- Beneficiary Districts in Rajasthan: Includes Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, and others.
- River Systems Involved:
- Chambal River: Originates in Madhya Pradesh, flows through Rajasthan, and joins the Yamuna.
- Kalisindh and Parbati Rivers: Serve as sources for water diversion.
Implementation Challenges
- Dependable Yield Issues: The original project proposal was based on a 50% dependable yield, contrary to the 75% norm, which was unacceptable to Madhya Pradesh. This led to discussions and revisions.
- Task Force Recommendations: Integrated discussions led to the proposal of the Modified PKC-ERCP, addressing both states' concerns.
Significance of the Project
- National Perspective Plan (NPP): Part of a larger initiative to manage water resources effectively across India, aiming to address water scarcity and improve irrigation.
- Support for Industrial Development: Enhances water availability for the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor, fostering economic growth.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme

- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) Scheme to promote electric mobility in the country.
Objective:
- Accelerate electric vehicle (EV) adoption
- Establish essential charging infrastructure
- Promote cleaner and sustainable transportation
Key Highlights
- Significant Occasion: Launched on the eve of Mahatma Gandhi's 155th Birth Anniversary, aligning with the vision of ‘Swachh Bharat’ and ‘Swachh Vahan’.
- Financial Commitment: Union Cabinet approved a financial outlay of ?10,900 crore for the scheme over two years (approved on September 11, 2024).
Key Features of the PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Subsidies/Demand Incentives:
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers (e-2Ws)
- 3.16 lakh electric three-wheelers (e-3Ws)
- 14,028 electric buses (e-buses)
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- E-Voucher Introduction:
- Aadhaar-authenticated e-vouchers for EV customers
- Simplifies access to incentives, with real-time generation for dealers.
- E-Ambulances:
- ?500 crore allocated for deployment
- Standards to be developed with relevant ministries.
- E-Buses:
- ?4,391 crore for 14,028 e-buses in nine major cities
- Focus on replacing scrapped state transport unit buses.
- E-Trucks:
- ?500 crore for incentivizing electric trucks
- Scrapping certificates required for incentives.
- Public Charging Stations:
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- 22,100 fast chargers for electric four-wheelers (e-4Ws)
- 1,800 for e-buses
- 48,400 for e-2Ws/3Ws
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- Test Agency Modernization:
- ?780 crore for upgrading Ministry of Heavy Industries test agencies to accommodate new EV technologies.
India’s Oil Imports from Saudi Arabia and Russia

- 03 Oct 2024
Context
- India’s crude oil imports are influenced by refinery maintenance cycles, which affect demand.
- August saw a dip in oil demand due to pre-maintenance preparations, but September recorded a recovery.
September Oil Import Trends
- Saudi Arabia:
- Imports rose 39.8% month-on-month to 0.73 million barrels per day (bpd), the highest since March.
- Saudi market share increased to 15.5% in September from 11.7% in August.
- Riyadh is reducing prices to regain lost market share, as earlier imports had plummeted to a multi-year low (0.42 million bpd in June).
- Russia:
- Remains India’s largest oil supplier with imports increasing by 6.4% from August to 1.88 million bpd.
- Russian crude constituted 40.2% of India’s total crude imports of 4.68 million bpd in September.
- Iraq:
- Supplied 0.87 million bpd, accounting for 18.7% of total imports.
- UAE:
- Oil imports increased by 18.6% month-on-month to 0.49 million bpd, the highest since June 2022.
Market Dynamics
- Price Sensitivity: Indian refiners are highly price-sensitive, which could lead to increased competition among suppliers.
- Potential for Increased Russian Imports: With Indian refiners expected to secure larger long-term contracts for Russian oil, further increases in imports from Russia are anticipated.
Strategic Implications
- Saudi Arabia is concerned about losing market share to Russia, especially as India’s refiners are currently favoring discounted Russian crude.
- Increased competition may benefit Indian refiners through better pricing from various suppliers.
Economic Context
- India, as the world's third-largest oil consumer with over 85% import dependency, is significantly affected by global oil price fluctuations.
- Although discounts on Russian crude have decreased, the overall savings from purchasing large volumes remain significant for Indian refiners.
The evolving landscape of India’s oil imports highlights the competitive dynamics among major suppliers, particularly Saudi Arabia and Russia, and underscores India’s strategic importance as a key market in the global oil sector.
Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Little Prespa Lake on Albanian-Greek border slowly dying.
Overview of Little Prespa Lake's Decline
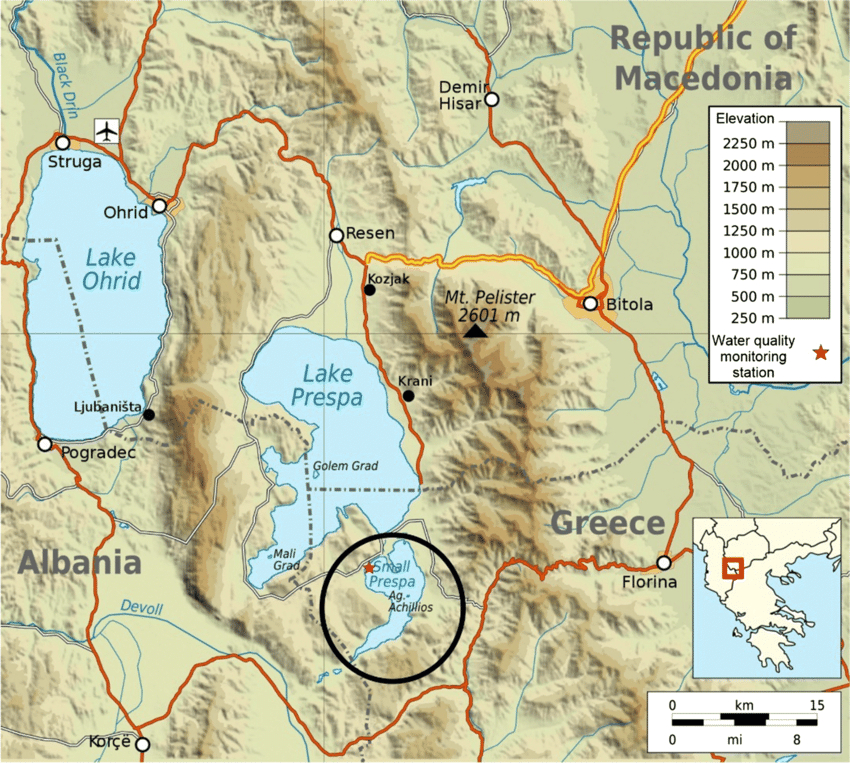
- Location and Geography:
- Little Prespa Lake is situated on the Albanian-Greek border, primarily in Greece with a southern tip extending into Albania.
- It covers approximately 450 hectares in Albania, now largely transformed into swamps or dry land.
- Ecological Changes:
- Once a crystal-clear lake, it has degraded into a marshy area, with about 430 hectares in Albania suffering from significant drying.
- Local wildlife has shifted; cows now roam where fish once thrived.
- Historical Context:
- The lake's decline began in the 1970s when Albanian authorities diverted the Devoll River to irrigate surrounding agricultural lands, severely limiting water inflow.
- Climate Change Impact:
- Rising temperatures, mild winters, and decreased precipitation have intensified the lake’s ecological crisis.
- Local experts warn that continued dry winters and hot summers could lead to irreversible damage.
