India’s Recalculated Coastline
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
India’s coastline has grown significantly over the past five decades, now extending 11,098 km in 2023-24, compared to 7,516 km in 1970. This marks an increase of 47.6% in just over five decades, attributed to a more precise methodology for measuring coastlines.
Key Factors Behind the Growth:
New Methodology for Measuring Coastlines:
- The old methodology used straight-line distances to measure the coastline, a method that didn't capture the complexity of India’s coastlines.
- The updated approach incorporates bays, estuaries, inlets, and other geomorphological features, offering a more accurate and detailed representation of the coastline.
- Advanced technologies like geospatial mapping have been used to ensure greater precision.
State-wise Recalculated Coastline Changes:
- Gujarat:
- Old coastline (1970): 1,214 km
- New coastline (2023-24): 2,340 km
- Growth: The largest absolute increase in coastline, nearly doubling its size.
- West Bengal:
- Old coastline: 157 km
- New coastline: 721 km
- Growth: A dramatic 357% increase, marking the highest percentage rise.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Old coastline: 906 km
- New coastline: 1,068 km
- Growth: Revised length now exceeds Andhra Pradesh’s coastline, which was 1,053 km.
- Puducherry:
- Old coastline: No major shift, but the updated data shows a contraction of 4.9 km (-10.4%), due to erosion and recalculations.
- Kerala:
- Old coastline: Relatively small increase of 30 km (5%), the smallest among the states.
Notable Observations:
- Andhra Pradesh is developing new ports like Ramayapatnam, Krishnapatnam, and Kakinada Gateway, aiming to boost economic growth and employment by leveraging its expanding coastline.
- The recalculated coastline helps in better maritime planning, focusing on port development, tourism, biodiversity conservation, and coastal erosion.
Impact of Coastline Expansion:
- Economic Growth:
- Coastal states, particularly Gujarat and West Bengal, benefit from an expanded coastline that improves maritime trade, port infrastructure, and tourism.
- The expansion supports industrialization, with growing logistics and transportation activities along the coast.
- Environmental Considerations:
- The new data aids biodiversity conservation, helping to track coastal erosion and accretion (land buildup), especially in areas like the West Coast.
- Understanding these changes is essential for disaster preparedness and sustainable coastal management.
- Coastlines of Emergence and Submergence:
- Emerging Coastlines: Land rising due to uplift or falling sea levels, such as along the Tamil Nadu Coast.
- Submerged Coastlines: Land that has sunk or been submerged due to rising sea levels, particularly noticeable along parts of Kerala’s coast.
Geographical Significance of the Expanded Coastline:
- India’s coast touches three major bodies of water: the Bay of Bengal (east), the Indian Ocean (south), and the Arabian Sea (west).
- The expansion reflects more than just geography—accurate coastline data is crucial for policy planning, maritime security, and resource management.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
Miyawaki Technique
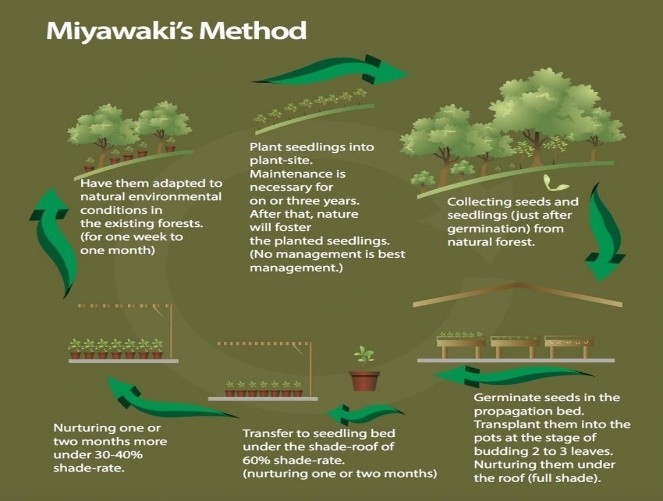
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
AnemiaPhone

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
Key Highlights:
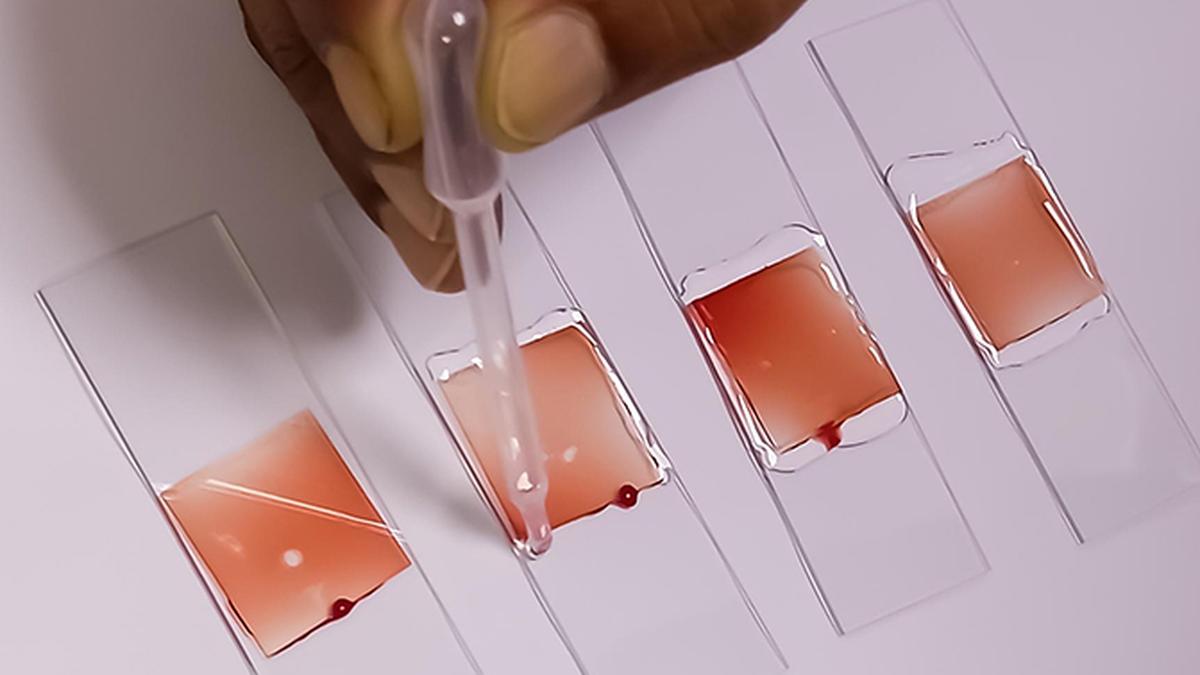
- Technology Features:
- Portable, Rapid, and Affordable: AnemiaPhone is designed to detect iron deficiency efficiently at low cost.
- Requires a fingerstick (small blood sample).
- Results are available within minutes.
- Wireless: Data uploaded to a clinical database via mobile, tablet, or computer.
- Can be used by healthcare workers to assess iron deficiency on the spot and take action (guidance, triage, referral).
- Working Mechanism:
- A drop of blood is placed on a test strip.
- The reader processes the sample.
- Data is uploaded for immediate diagnosis and action.
- Test results assist in on-the-spot intervention by healthcare workers.
Anaemia and Iron Deficiency:
- Prevalence in India:
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anaemia.
- 50%-70% of pregnant women in India suffer from anaemia.
- 59% of women and 47% of children (6-59 months) in India suffer from anaemia (NFHS data).
- Consequences of Anaemia:
- Fatigue, dizziness, organ failure, complications in childbirth, and in severe cases, death.
- Contributes to higher maternal and child mortality rates in India.
- Impact on Health in India:
- India has one of the highest rates of anaemia in the world.
- Iron deficiency is a significant contributor to maternal deaths.
ICMR's Role and Integration into National Programs:
- ICMR and AnemiaPhone:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has integrated AnemiaPhone into its Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-Free India) program.
- The program focuses on eliminating anaemia by 2025 through screening, diagnosis, and treatment in women and children, especially in remote areas.
- Transfer of Technology:
- In November 2024, Cornell University transferred the technology to ICMR for free.
- This collaboration aims to improve health outcomes by sharing innovative health technologies.
Advantages of AnemiaPhone:
- Cost-Effective and Portable:
- Low-cost compared to traditional lab tests.
- Portable and can be used in remote and underserved areas.
- Quick Diagnosis: Results are processed in minutes, allowing healthcare workers to act without delay.
- No Need for Expensive Labs:
- Can be used at primary health centers or in door-to-door health surveys.
- Facilitates healthcare in rural or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Wireless and Easy to Use: The device is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Impact on Healthcare System:
- Improvement in Accessibility:
- Helps reduce the need for people to travel long distances for diagnosis, especially in rural areas.
- Ensures early diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and anaemia.
- Enhancing Maternal and Child Health: AnemiaPhone will contribute to reducing maternal and child mortality rates linked to anaemia.
Technology Testing and Development:
- Testing in India:
- AnemiaPhone has been tested in India and has shown accurate results in diagnosing iron deficiency.
- Single-use test strips help ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
Global Health Context:
- Global Prevalence of Anaemia: More than 2 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia, particularly pregnant women and young children.
- WHO’s Role: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies anaemia as a major global health issue.
