Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan Now Opens for Safari Tours (TOI)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The forest department started the inaugural jungle safari at the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on Monday, which marks the beginning of organised tiger reserve tours for tourists in four locations across the state.
About Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, also known as Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, spans across four districts – Bundi, Kota, Jhalawar, and Chittorgarh in Rajasthan.
- The reserve is nestled in a valley formed by two parallel mountains, Mukundra and Gargola.
- Establishment: In 2013, the tiger reserve was formed, encompassing Mukandra National Park, Dara Sanctuary, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and a section of Chambal Sanctuary.
- Initially, it served as a hunting preserve for the Maharaja of Kota.
- River: Positioned on the eastern bank of the Chambal River, the reserve is crisscrossed by its tributaries.
- Vegetation: The reserve features a Dry Deciduous Forest.
- Flora: The dominant species is Kala Dhok or Kaladhi (Anogeissus pendula), accompanied by Khair, Ber, Kakan, Raunj, and more.
- On elevated slopes, Anogeissus pendula gives way to Anogeissus latifolia, coexisting with Bel, Salar, Uum, and Shisham.
- Fauna: Noteworthy fauna include Leopard, Sloth bear, Nilgai, Chinkara, Spotted Deer, Small Indian Civet, Toddy Cat, Jackal, Hyena, Jungle Cat, and Common Langur, among others.
- The region is also home to various reptiles and amphibians, such as Pythons, Rat Snake, Buff-striped keelbacks, Green keelbacks, crocodiles, turtles, Gharial and Otters.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Says Unemployment Rate Declined (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) has reported that the unemployment rate in the country has shown a decrease between April and June 2023.
Key Observations of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Improved Work Metrics: Both the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) and Worker-Population Ratio (WPR) showed positive trends in the recent period.
- Urban Employment Trends: In urban areas, LFPR increased from 47.5% (April-June 2022) to 48.8% (April-June 2023) for individuals aged 15 and above.
- The WPR in urban areas rose from 43.9% (April-June 2022) to 45.5% in the corresponding months this year.
- Gender-specific Changes:
- Male LFPR increased from 68.3% to 69.2%.
- Female LFPR showed notable growth from 18.9% to 21.1% during the observed period.
What is the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Conducted by the National Sample Survey (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Launched in April 2017 by the National Statistical Office (NSO) to provide more frequent labour force data.
Objectives:
- Estimate key employment and unemployment indicators every three months for urban areas.
- Annually estimate indicators for both 'Usual Status' and 'Current Weekly Status' in rural and urban areas.
- Key Indicators:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): Percentage of individuals in the population who are part of the labour force (working, seeking, or available for work).
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): Percentage of unemployed persons among those in the labour force.
- Current Weekly Status (CWS): Activity status determined based on the activities in the last 7 days before the survey.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
New Species of Bagworm Moth discovered From Idukki (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from the Zoology Department at St. Thomas College (Autonomous), Thrissur, have discovered a new species of bagworm moth, Wizard Bagworm, from near the Nariyampara Falls in the Idukki district.
What is a Bagworm Moth?
- Belonging to the family of moths in the order Lepidoptera, bagworm moths are recognized for their protective larval cases.
- These moths are distributed globally, with notable populations in North America and Africa.
- In their larval stage, these perennial moths inhabit various evergreen trees and junipers.
- They derive their name from the bag-like cases constructed by the larvae around themselves.
- The larvae can pose a threat to trees, particularly evergreens.
About Eumasia Venefica:
- This recently identified species earned its name due to the unique shape of its bag, resembling a wizard's hat.
- It is the fourth species within this genus to be documented in India.
- Distinctive Features:
- The species exhibits effective camouflage techniques to evade predators.
- Larval cases of Eumasia venefica are discovered attached to rocks adorned with lichens.
- These cases join together, forming a colony covered with lichens.
- The larval bags bear a resemblance to a 'witch's hat,' featuring a disc-like anterior and a tubular posterior part.
- Unlike polyphagous pests, the larvae of this species exclusively feed on algae and mosses present on rocks.
Pontus Tectonic Plate: Geologist Unexpectedly Finds Remnants of a Lost Mega-Plate (Science Daily)
- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Geologists have reconstructed a massive and previously unknown tectonic plate that was once one-quarter the size of the Pacific Ocean.
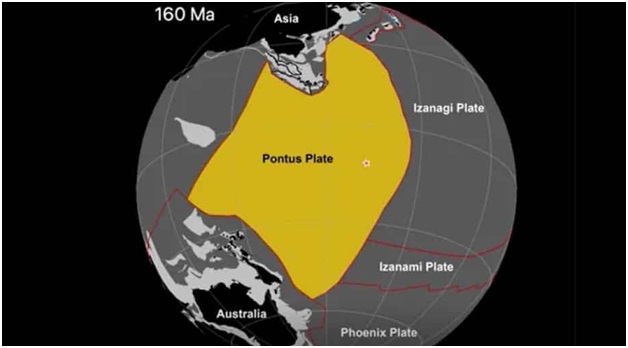
About Pontus Tectonic Plate:
- Recently discovered in the west Pacific Ocean, the Pontus Tectonic Plate is a long-lost geological plate that holds significance in Earth's history.
- Believed to have measured about 15 million square miles at its zenith, roughly equivalent to one-quarter of the Pacific Ocean, this massive tectonic plate dates back as far as 160 million years, with more recent traces extending to approximately 20 million years ago.
- Over millions of years, the Pontus Plate underwent a gradual subduction process, pulled downward beneath a neighbouring plate by the force of gravity.
How was this Discovery Made?
- The subducting process involves the plate sinking into Earth's mantle due to its higher density compared to the surrounding mantle.
- Traces of a subducted plate are discernible in the form of rock fragments concealed in mountain belts.
- During subduction, upper portions of the plate are occasionally scraped off.
- Researchers employed geological data and computer modelling to reconstruct the movements of current plates, revealing a substantial area potentially vacated by the subducted Pontus Plate.
- Utilizing magnetic techniques, scientists identified basalt remnants in Borneo as Pontus relics, suggesting that this fragmentary evidence was left behind during the plate's subduction some 85 million years ago.
What is Plate Tectonics?
- Tectonic plates are large, rigid pieces of Earth's lithosphere, the outer shell comprising the crust and uppermost part of the mantle.
- These plates, which vary in size and shape, constantly move and interact, shaping the Earth's dynamic surface.
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several major plates, such as the Pacific, North American, and Eurasian plates, among others.
- The interactions at plate boundaries result in various geological phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Plate tectonics, the theory explaining these movements, underscores how heat-driven convective currents in the Earth's mantle cause plates to diverge, converge, or slide past each other.
- Tectonic plate movements influence the planet's topography, seismic activity, and the distribution of continents and oceans, playing a fundamental role in Earth's geological evolution.
