West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA)

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists utilized a CRISPR-Cas9 tool to restore vision in individuals, including adults and children, afflicted with congenital blindness termed Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA).
What is Leber Congenital Amaurosis?
- Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) is a rare genetic eye disorder where affected infants experience severe vision loss or blindness at birth.
- The condition results from the impaired function of light-gathering cells (rods and cones) in the retina.
Prevalence and Cause:
- LCA affects approximately one in 40,000 people.
- It is caused by a gene mutation that disrupts the proper function of the CEP290 protein, which is critical for vision.
Recent Development:
- Scientists have employed CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to develop a novel therapy called EDIT-101.
- In a clinical trial called "BRILLIANCE," participants received a single dose of EDIT-101.
- The treatment involves cutting out the mutation in the CEP290 gene and replacing it with healthy DNA, restoring the normal function of the CEP290 protein and allowing the retina to detect light.
- This groundbreaking approach offers a promising treatment for individuals affected by LCA.
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence.
- It is currently the simplest, most versatile and precise method of genetic manipulation.
How does CRISPR-Cas9 work?
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system operates through two primary molecules:
- Cas9, an enzyme often likened to "molecular scissors," which can precisely cut both strands of DNA at a designated location in the genome.
- Guide RNA (gRNA), a segment of RNA containing a specific pre-designed sequence (about 20 bases long) within a longer RNA scaffold.
- The scaffold binds to DNA, while the pre-designed sequence guides Cas9 to the intended genomic location, ensuring accurate DNA cleavage.
- The guide RNA is tailored to identify and bind to a particular sequence in the DNA, with RNA bases that complement those of the target DNA sequence.
- This specificity ensures that the guide RNA binds solely to the target sequence and avoids other genomic regions.
- Once bound, Cas9 cuts across both DNA strands at the targeted location.
- Subsequently, the cell's repair mechanisms recognize the DNA damage and attempt to rectify it.
- Scientists exploit this DNA repair process to introduce alterations to one or more genes within the genome of a selected cell.
Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS)

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Political parties are currently reaching out to voters through Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) calls on a daily basis.
What is an Interactive Voice Response System?
- Interactive voice response is a technology that allows telephone users to interact with a computer-operated telephone system through the use of voice and DTMF tones input with a keypad.
- IVR or Interactive Voice Response software accepts caller input, either voice or touch-tone, in response to pre-recorded prompts, and provides programmed responses.
- The responses can range from simple call routing to complex actions involving several external systems and data points depending on the software’s sophistication.
- The name, “interactive voice response” is derived from the caller responding to interactive options, offered by a pre-recorded voice.
Functionality:
- IVRS is powered by pre-recorded messaging or text-to-speech technology.
- It features a dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) interface.
Types:
- Touch-tone replacement: This system prompts callers to use a touch-tone keypad selection to access information.
- Directed dialogue: Provides specific verbal prompts to callers depending on their inquiry.
- Natural language: Employs speech recognition to better understand user requests.
- Industry Application: IVRS technology has been widely used across multiple industries, including banking, customer service, education, healthcare, and travel.
Benefits:
- Increased customer satisfaction by providing a streamlined experience.
- Improved contact centre operations and KPIs through call volume management.
- Reduced hold times during high call volume periods.
- Cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for customer service representatives.
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Nino, could potentially resurface for the second consecutive year during the latter part of 2024.
What is the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)?
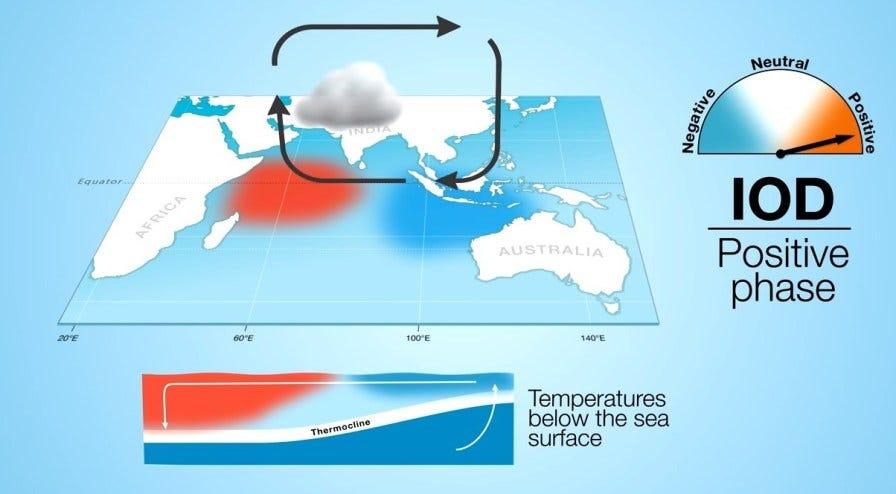
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is defined by the difference in the sea surface temperature between the two equatorial areas of the Indian Ocean – a western pole near the Arabian Sea (in western Indian Ocean) and an eastern pole closer to the Bay of Bengal (in eastern Indian Ocean).
- The IOD affects the climate of Southeast Asia, Australia and other countries that surround the Indian Ocean Basin.
- The Indian Monsoon is invariably influenced by the IOD.
- IOD is simply the periodic oscillation of sea surface temperatures, from ‘positive’ to ‘neutral’ and then ‘negative’ phases.
- If the sea surface temperature of the western end rises above normal (0.4°C) and becomes warmer than the eastern end, it leads to a positive IOD.
- This condition is favourable for the Indian Monsoon as it causes a kind of barrier in the eastern Indian Ocean and all the southwesterly winds blow towards the Indian sub-continent.
- Accordingly, the waters in the eastern Indian Ocean cool down, which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia.
- Conversely, during a negative IOD period, the waters of the tropical eastern Indian Ocean are warmer than water in the tropical western Indian Ocean.
- This results in increased rainfall over parts of southern Australia.
Effects on India:
- A positive IOD can boost India's southwest monsoon performance depending on its development timing.
- Example: In 2019, a strong IOD event improved a 30% rainfall deficit during the late monsoon season.
- Benefits for agriculture through recharging water sources and reservoirs.
- The development of IOD likely benefits India's agricultural sector, particularly in areas with precarious water storage levels.
Difference between El Nino and IOD:
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the El Nino are independent climatic phenomena but often co-occur.
- Both IOD and El Nino result in changes in global wind patterns. To know about the change of wind patterns, click here.
- However, the cycle of IOD is shorter, while El Nino condition could last for even two years.
- IOD commences in the month of May and ends with the withdrawal of the Southwest Monsoon in the Indian sub-continent.
LockBit Ransomware

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The U.S. Department of Justice has indicted Russian national Dimitry Yuryevich Khoroshev, 31, and announced a $10 million reward for any information leading to his apprehension.
What is LockBit Ransomware?
- LockBit is a type of ransomware involving financial payment in return for decryption.
- It mainly targets businesses and government agencies rather than consumers.
- Its potential targets are the institutions that would be hampered by the inconvenience and have sufficient means to pay a large payment.
- It is developed and operated by a cybercriminal group known as LockBit, which offers ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) to other malicious actors.
- Formerly known as ABCD ransomware, has evolved into a distinct danger within the spectrum of extortion tools.
- It carries out its attacks mainly via email attachments.
- The cyber assaults through LockBit ransomware can be traced back to September 2019, when it got its first nickname, “abcd virus.”
- The nickname was derived from the filename used when encrypting a victim’s data.
- They are considered one of the most prolific and aggressive organizations in the industry, and their actions are raising anxiety among security professionals worldwide.
How LockBit Ransomware Operates?
- Exploitation: LockBit ransomware breaches systems through social engineering tactics like phishing or brute force attacks on intranet servers.
- Initial breach probes may take only a few days.
- Infiltration: Once inside a network, LockBit uses post-exploitation techniques to escalate privileges and move laterally to assess targets.
- It disables security programs and infrastructure for recovery, making independent recovery difficult.
- Deployment: LockBit spreads across the network, encrypting system files and leaving ransom notes in each folder.
- Payment of the ransom is often seen as the only viable option for victims to regain access to their systems.
How Does LockBit Ransomware Spread?
- LockBit typically spreads via phishing emails with malicious attachments or through drive-by downloading from infected websites.
- It utilizes common Windows tools like Windows PowerShell or Server Message Block, making it challenging for endpoint security systems to detect.
- Additionally, it disguises its encrypting executable file as a common PNG picture file, further evading system defenses.
Takes ransom in Bitcoins:
- LockBit hackers use so-called ransomware to infiltrate systems and hold them hostage.
- They demand payment to unlock the computers they’ve compromised and often threaten to leak stolen data to pressure victims to pay.
- The group typically demands ransom payments in Bitcoin.
