Z-Morh Tunnel Project in Kashmir

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Seven people were killed in Jammu and Kashmir when suspected militants targeted the workers of infrastructure company APCO Infratech, which is constructing the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway. This is the first militant attack on a key infrastructure project in Jammu and Kashmir. In the past, militants have not targeted such infrastructure projects in the region.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- Length: 6.4 kilometers
- Connection: Links Sonamarg (a popular tourist destination) with Kangan town in central Kashmir’s Ganderbal district.
- Construction Site: Located near Gagangir village, ahead of Sonamarg.
- Naming: The tunnel gets its name from the Z-shaped road near the construction site.
Importance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- All-Weather Connectivity: The tunnel is crucial for year-round access to Sonamarg, particularly in the winter when the road is often blocked by snow avalanches.
- Location: Situated at 8,500 feet above sea level, the tunnel provides a safe, all-weather route for tourists and locals, especially during winter months when access to Sonamarg is typically limited.
Strategic Importance
- Part of Zojila Tunnel Project:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is integral to the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh.
- The Zojila Tunnel, under construction at an altitude of around 12,000 feet, will connect Sonamarg (Kashmir) to Drass (Ladakh) and is expected to be completed by December 2026.
- Military and Strategic Significance:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is crucial for rapid military mobilization between Srinagar, Kargil, Leh, and Drass regions.
- It ensures quick access for military personnel to the Ladakh border, particularly in areas of heightened security like Siachen Glacier and the Turtuk sub-sector (on the Pakistan border).
- The tunnel will reduce dependence on air transport for troop and supply movements to forward areas, leading to cost savings and extended aircraft lifespan.
The case for a nature restoration law in India

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), which was enacted by the European Union (EU), is an inspiring model from which India can draw points to tackle its growing environmental crises.
Background of the NRL in the EU
- The Nature Restoration Law (NRL) was enacted by the European Union (EU) to restore ecosystems and combat biodiversity loss.
- Adopted on June 17, 2024, by the EU’s Environmental Council.
- Key objectives:
- Restore 20% of EU’s land and sea areas by 2030.
- Achieve full restoration of all ecosystems by 2050.
- Part of the EU’s Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 and European Green Deal.
- Target Areas:
- Forests, agricultural lands, rivers, urban spaces.
- Restoration measures include:
- 25,000 km of free-flowing rivers.
- Planting 3 billion trees by 2030.
- Global Impact: NRL is a critical tool in reversing Europe’s biodiversity loss, where 80% of habitats are in poor condition.
Environmental Crisis in India
- Land Degradation:
- 29.7% of India’s total geographical area is affected by land degradation (as per ISRO’s Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas, 2018-19).
- 97.85 million hectares of land degraded, with a significant increase since 2003-05.
- Major desertification hotspots in Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
- Desertification: A growing concern, affecting 83.69 million hectares in 2018-19.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- Green India Mission, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, and National Afforestation Programme have had positive effects.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme is the second-largest watershed programme globally.
Need for a Comprehensive Nature Restoration Law in India
- The scale of India’s environmental challenges requires a comprehensive nature restoration law similar to the EU’s NRL.
- The law should have legally binding targets to restore degraded landscapes and ensure ecosystem sustainability.
Key Features of an Indian Nature Restoration Law
- Restoration Targets:
- 20% of degraded land to be restored by 2030.
- Full restoration of ecosystems (forests, wetlands, rivers, agricultural lands, urban spaces) by 2050.
- Wetland Restoration:
- Target restoring 30% of degraded wetlands by 2030.
- Priority wetlands like Sundarbans and Chilika Lake play critical roles in biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity in Agriculture:
- Promote agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices.
- Use biodiversity indicators (e.g., butterfly or bird index) to monitor progress.
- River Restoration:
- Focus on free-flowing rivers such as the Ganga and Yamuna.
- Address pollution, obstructions, and ecosystem damage in major rivers.
- Urban Green Spaces:
- Ensure no net loss of urban green spaces.
- Promote urban forests in cities like Bengaluru and Delhi, where urban heat islands and air quality degradation are prominent.
Economic and Social Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
- Global Economic Impact:
- Nature restoration could generate $10 trillion annually by 2030 (World Economic Forum estimate).
- Benefits for India:
- Agricultural Productivity: Restoring degraded land will enhance farm productivity.
- Water Security: Improved land restoration will contribute to better water availability.
- Job Creation: Millions of rural jobs could be created through ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Contributing to SDGs:
- The law would help India meet SDG 15 (sustainable management of forests, combating desertification).
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- Restoring ecosystems can help India enhance its carbon sinks, which is crucial for meeting Paris Agreement targets.
- Degraded lands lose their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The tiny nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has played an outsized role in scientific discovery, contributing to four Nobel Prizes over the years.
Key Discoveries from C. elegans Research
- C. elegans and Cellular Processes:
- The worm has helped scientists understand programmed cell death (apoptosis), a vital process in development and disease. This work contributed to the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, addressing how cells are instructed to kill themselves and how this process goes awry in conditions like AIDS, strokes, and degenerative diseases.
- Gene Silencing and RNA Interference:
- In 2006, a Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi), a process first explored using C. elegans. This discovery led to the development of a new class of RNA-based drugs.
- Cellular Imaging Techniques:
- In 2008, C. elegans contributed to breakthroughs in cellular imaging, as its use helped invent cellular “lanterns” that allowed scientists to visualize the inner workings of cells, earning a Chemistry Nobel.
- Gary Ruvkun’s 2024 Nobel:
- Gary Ruvkun’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 was the fourth in a series of Nobel recognitions stemming from C. elegans research, reinforcing its role in fundamental biological discoveries.
Key Facts About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
- Size: 1 millimeter long.
- Life Cycle: Completes in 3-5 days.
- Cell Count: 959 cells.
- Genome: First multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced in 1998.
- Sexual Reproduction: Hermaphroditic (self-fertilizing) and male.
- Scientific Role: Used to study genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and cell biology.
- Nobel Prize Contributions: Four Nobel Prizes, including those in Physiology, Medicine, and Chemistry, for advancements in cell death, gene silencing, and imaging.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
Egypt becomes 2nd country in 2024 to be declared ‘malaria-free’
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Egypt was officially declared ‘malaria-free’ by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Key Highlights:
- Egypt became the second country (after Cabo Verde) to be certified malaria-free in 2024.
- It is the fifth African country to achieve this milestone, joining Morocco, UAE, and Cabo Verde in the malaria-free list.
- WHO Certification Criteria:
- A country is certified malaria-free if it can prove the Anopheles mosquito-borne malaria transmission chain has been broken for at least three years.
- The country must also have the capacity to prevent the re-establishment of transmission.
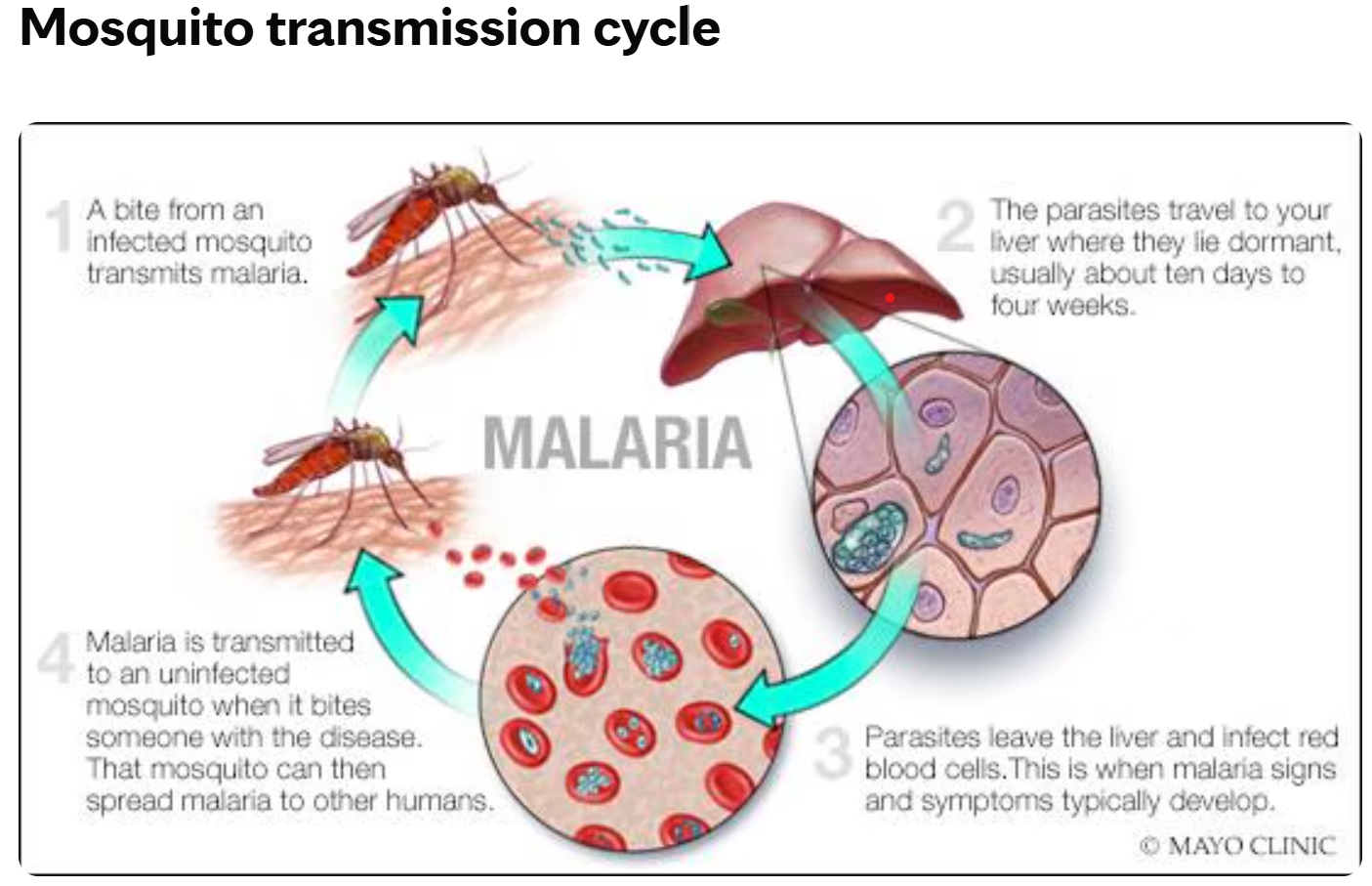
- About Malaria:
- Malaria is an acute febrile illness caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- It is a life-threatening disease primarily found in tropical countries.
- Symptoms include fever, headache, and chills, which can be mild and difficult to diagnose.
- Prevention mainly involves vector control interventions, and treatment involves early diagnosis and use of antimalarial drugs.
