Bathymetry

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) recently conducted a study of the bathymetry, or ocean floor, in the Indian Ocean.
What is Bathymetry?
- Bathymetry is a technique dedicated to mapping the depths of water bodies, that is, it is the measurement and representation of the topography of the bottom of rivers, seas, and oceans.
- In addition to measuring depth, this study also includes identifying underwater relief and creating three-dimensional maps of the sea floor.
- The word “bathymetry” comes from the Greek "bathýs", meaning deep, and "metron", meaning measure.
- Bathymetry allows for obtaining information about the physical characteristics of the sea floor, such as seamounts, mountain ranges, valleys, abyssal plains, and underwater canyons.
How is Bathymetry Performed?
- To carry out bathymetry, specific equipment is used, such as multibeam sonar (MultiBeam Echosounder), IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and high-precision positioning systems (via satellite with RTK correction).
- Multibeam sonar emits sound pulses toward the sea floor and measures the time it takes for the sound to return to the sensor after being reflected by submerged surfaces.
- Based on this sound return time and knowledge of the exact position of the vessel and its attitude (roll, pitch, yaw), it is possible to calculate the depth at a given point.
- The bathymetry service generates charts, blueprints, and digital models (2D and 3D) of the sea floor.
- LiDAR sensors, on the other hand, are used to detect data through beams of light above the waterline, mapping slopes, rockfills, and channel walls.
- The fusion of bathymetry data with Lidar data allows the three-dimensional construction of the environment in very high resolution.
- Allowing the client to plan or verify works and/or assets in the region of interest.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- Established in 1999, the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) under the Ministry of Earth Science, Govt of India.
- It is mandated to provide ocean information and advisory services to a broad spectrum of users through sustained ocean observations and constant improvements through systematic and focused research.
- The activities include data services, consultancy, and capacity development.
- HQ: Hyderabad
- INCOIS is a permanent member of the Indian delegation to the IOC of UNESCO and a founding member of the Indian Ocean Global Ocean Observing System (IOGOOS) and the Partnership for Observing the Oceans (POGO).
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rising incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) across the globe has become a concern for doctors, while early diagnosis is lacking, diagnosis in itself is challenging considering that other conditions could mimic IBD.
What is IBD?
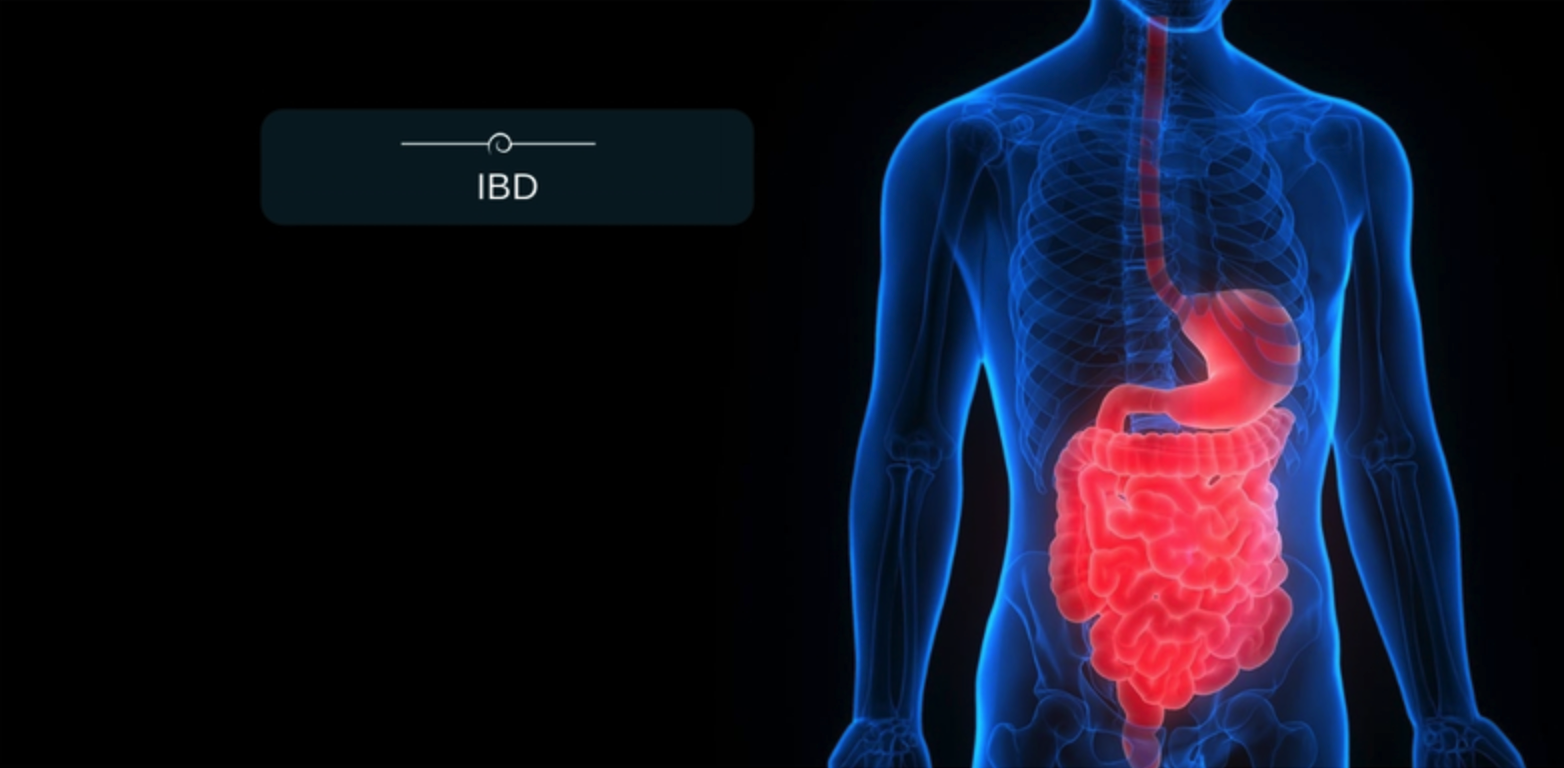
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a recurring and long-term (chronic) condition that affects the digestive tract.
- IBD causes inflammation of the stomach, small intestine, and colon.
- IBD is a progressive disease that can become worse over time and cause other damage if not properly diagnosed and treated.
- There are two types of IBD: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
- Crohn’s disease can also affect the entire thickness or alternating areas of the bowel wall.
- Ulcerative colitis: causes inflammation in the large intestine or colon.
- This form of IBD inflames the innermost lining of the colon and creates tiny open sores (ulcers).
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
What causes IBD?
- The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but IBD is the result of a weakened immune system. Possible causes are:
- The immune system responds incorrectly to environmental triggers, such as a virus or bacteria, which causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- There also appears to be a genetic component.
- Someone with a family history of IBD is more likely to develop this inappropriate immune response.
Symptoms of IBD:
- Although Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are different conditions, IBD conditions have similar symptoms, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
How Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treated?
- While there is no curative treatment for IBD, it is managed through medication, dietary changes, and occasionally surgery.
- The treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, mitigate complications, prevent future flare-ups, and potentially promote the healing of inflamed intestines.
Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto.
About Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC):
- The Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC) is a national forum established in 1919, comprising creators, custodians, and users of records.
- Its primary purpose is to advise the Government of India on matters related to record management and their utilization for historical research.
Secretariat:
- The National Archives of India, New Delhi, serves as the Secretariat for the IHRC, formerly known as the Indian Historical Records Committee since 1911.
Leadership and Membership:
- Led by the Union Minister of Culture, the IHRC consists of 134 members, including government agencies, government-appointed nominees, representatives from State/UT Archives, universities, and learning institutions.
- Over the years, the IHRC has convened 62 sessions.
Committee Structure: The IHRC operates with two adjunct bodies:
- Editorial Committee: Responsible for reviewing and approving papers based on archival sources for presentation at committee sessions.
- Standing Committee: Tasked with reviewing the implementation of committee recommendations and providing input on meeting agendas.
- The Secretary of the Ministry of Culture chairs the Standing Committee of IHRC.
- The Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto recently.
- The logo signifies the theme and uniqueness of IHRC entirely.
- The pages in the shape of lotus petals represent IHRC as the resilient nodal institution for maintaining historical records.
- The Sarnath pillar in the middle represents India's glorious past.
- Brown as the colour theme reinforces the organization's mission of preserving, studying, and honouring India's historical records.
- The motto translates as "Where history is preserved for the future."
- The IHRC plays a vital role in identifying, collecting, cataloging, and maintaining historical documents, manuscripts other sources of historical information.
- By doing so the Commission ensures that valuable historical knowledge is conserved for future generations.
- The motto, therefore, reflects the Commission's commitment to ensuring the safeguarding of historical documents and making these accessible for the benefit of present and future generations.
Nephrotic Syndrome
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the heels of recent news reports on how keratin-based hair-straightening products containing glycolic acid derivatives led to severe kidney injury in women, researchers from Kerala have reported a series of cases wherein, the use of fairness creams has been linked to nephrotic syndrome.
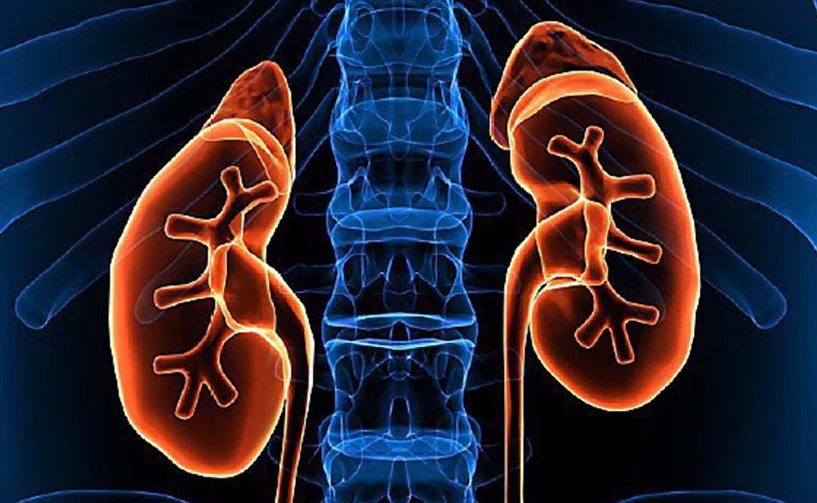
What is Nephrotic Syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome causes scarring or damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomeruli).
- This causes too much protein to be lost from the blood into the urine.
People with nephrotic syndrome often have:
-
- Low levels of protein in the blood (hypoalbuminemia)
- Very high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Swelling (edema), especially around the eyes, feet, and hands
- High cholesterol
What causes nephrotic syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome results from damage to the kidneys' glomeruli.
- These are the tiny blood vessels that filter waste and excess water from the blood and send them to the bladder as urine.
- The glomeruli keep protein in the body. When they are damaged, protein leaks into the urine.
- Healthy kidneys allow less than 1 gram of protein to spill into the urine in a day.
- In nephrotic syndrome, the glomeruli let 3 grams or more of protein leak into the urine during 24 hours.
- Nephrotic syndrome may happen with other health problems, such as kidney disease caused by diabetes and immune disorders.
- It can also develop after damage from viral infections.
- The cause of nephrotic syndrome is not always known.
What are the symptoms of nephrotic syndrome?
- The symptoms of nephrotic syndrome include:
- Swelling or edema, typically in the ankles, feet, or legs
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight gain
- Foamy urine
Treatment:
- The treatment of nephrotic syndrome varies depending on its cause.
- However, it typically includes medications to treat the underlying cause, as well as changes in diet.
- Dietary changes that might help in treating nephrotic syndrome include Source:
- limiting sodium
- eating less protein
- reducing the intake of saturated fat and cholesterol
Complications of nephrotic syndrome:
- Serious complications of nephrotic syndrome include kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Dialysis may be needed if kidney failure develops which can happen in extreme cases.
Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The United States has confirmed providing long-range Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine to aid its war effort against Russia.
What is the ATACMS System?
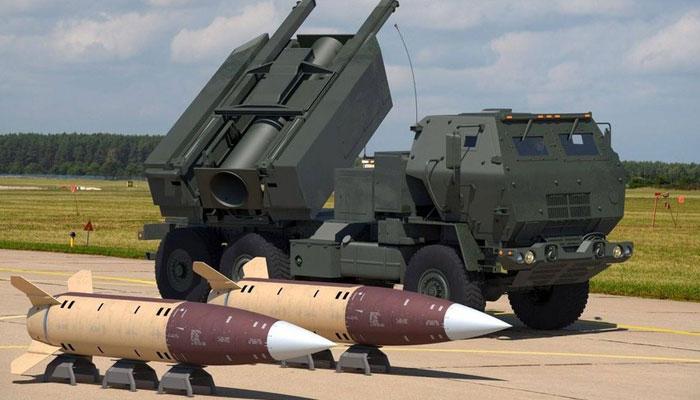
- The Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) is one of the most potent missile systems built by US-based arms manufacturer Lockheed Martin.
- This is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system.
- Its biggest strengths are the long-range of attack, the ability to fire cluster munitions, and the weapon system’s mobility.
- Range: There is a mid-range version of the ATACMS, called Block 1, and a long-range version, Block 1A.
- ATACMS Block 1 has a range of 165 kilometres. Ukraine was provided these systems last year and used them to attack targets in October.
- ATACMS Block 1A, on the other hand, has a maximum range of 300 km. However, this depends on the kind of munition the missile carries.
- With such a range, the long-range ATACMS Block 1A is capable of striking targets well beyond the range of existing Army cannons, rockets, and other missiles.
- Mobility: ATACMS missiles are fired from the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) platforms. Both of these launching systems are highly mobile automatic systems.
Why Ukraine can’t use ATACMS to Target Russian Territories?
- Despite territories deep inside Russia now being within the range of the ATACMS, Ukraine cannot use it to hit targets in these locations.
- Ukraine has committed to only use the weapons inside Ukraine, not in Russia.
- The US administration has made it clear that the weapons cannot be used to hit targets inside Russia.
- The Biden administration is concerned that if Ukraine strikes deep into Russian territory, it will anger Moscow and escalate the conflict.
