Tenkana

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- A team of arachnologists has discovered a new genus of jumping spiders, Tenkana, found across southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The discovery includes two previously known species, Tenkanamanu and Tenkanaarkavathi, and introduces a new species, Tenkanajayamangali, from Karnataka.
Name and Origin:
- The name Tenkana comes from the Kannada word for "south," reflecting the geographical region where all known species of this genus are found—southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The genus belongs to the Plexippina subtribe of jumping spiders, which is distinct from related genera like Hyllus and Telamonia.
Key Findings:
- Tenkanajayamangali was first discovered in Devarayanadurga reserve forest, Tumakuru district, Karnataka, at the origin of the Jayamangali river.
- The new species was identified through genetic analysis and physical examination, showing it did not match any known species.
Physical Characteristics:
- The male and female Tenkanajayamangali exhibit distinct physical differences.
- The male has pale hairs covering most of its carapace, while the female is grey with a pattern.
- The ocular area of T. jayamangali is uniformly covered with white hairs, in contrast to T. arkavathi and T. manu, which have distinctive markings.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Tenkana spiders are typically ground-dwelling and prefer dry, open habitats like short grasses, leaf litter, and rocky outcrops.
- These spiders have been observed in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and some areas in Sri Lanka.
- The male and female spiders of T. jayamangali were discovered in different regions, 2 km apart, at the hilltop and foothills of the same forest.
Ecological and Behavioral Insights:
- The Tenkana genus is considered endemic to India, with species observed in diverse regions such as Bengaluru, Yercaud (Tamil Nadu), and Bannerghatta (Karnataka).
- These spiders are found in complex microhabitats, like shaded short grasses with dry leaf litter or rocky outcrops in relatively dry habitats.
- The movement of Tenkana spiders resembles that of Stenaelurillus, another ground-dwelling spider species.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
India's Mission Mausam and the Cloud Chamber

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
Mission Mausamaims to not just improve weather forecasting in the country but also ‘manage’ certain weather events, and on demand, enhance or suppress rainfall, hail, fog and, later, lightning strikes.
- Focus Areas:
- Enhancing or suppressing rainfall, hail, fog, and later, lightning strikes on demand.
- Strengthening cloud physics research to better understand and modify weather conditions.
- Establishment of Cloud Chamber:
- Location: The cloud chamber is being built at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune.
- Purpose: To study cloud physics in detail and develop methods for weather modification.
- Key Feature: It will be a convective cloud chamber, capable of simulating conditions specific to Indian monsoon clouds.
What is a Cloud Chamber?
- A scientific apparatus that mimics the conditions required for cloud formation.
- Function: Water vapour, aerosols, and other particles are injected into the chamber, and under controlled temperature and humidity conditions, clouds can be formed.
- Global Context: While many countries have cloud chambers, India is building one with convection properties, which are essential for studying monsoon clouds. Only a few such chambers exist globally.
Why India Needs a Convective Cloud Chamber?
- Cloud Physics: The chamber will allow scientists to study various phenomena such as:
- Cloud behaviour under normal and extreme conditions.
- Formation of rain droplets and ice particles.
- Influence of moisture from cyclones or low-pressure systems.
- Interactions between different cloud layers.
- Objective: To gain insights into cloud formation specific to the Indian monsoon and develop strategies for weather modification.
Applications for Weather Modification:
- The cloud chamber will help scientists simulate and understand how to influence weather events like rain and fog, particularly in monsoon systems.
- It will allow testing of new ideas and theories under controlled conditions, adjusting temperature, humidity, and convection parameters to suit Indian weather conditions.
India’s Experience with Cloud Seeding:
- Cloud Seeding: A technique tested in India to enhance rainfall by introducing particles (seeds) into clouds.
- CAIPEEX Program: India conducted the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX) over a decade to study cloud seeding's effectiveness.
- Findings: Cloud seeding increased rainfall by up to 46% in some regions, showing its potential under specific conditions.
- Limitations: Cloud seeding is not a one-size-fits-all solution and is effective only under certain conditions.
Significance for India’s Weather Forecasting:
- Improved Weather Modification: The cloud chamber and insights from it could lead to better management of weather events, especially in regions affected by monsoon rains, cyclones, and droughts.
- Tailored Strategies: India will be able to implement targeted weather interventions, especially in agricultural regions, to reduce the negative impacts of extreme weather.
???????Global and Regional Relevance:
- Cloud Chamber: The Pune facility will be one of the few globally with the specific focus on convective properties needed to study Indian monsoon systems.
- Role in Climate Science: India’s investment in cloud physics research positions it at the forefront of developing technologies to manage climate variability and extreme weather events.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
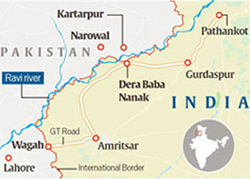
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
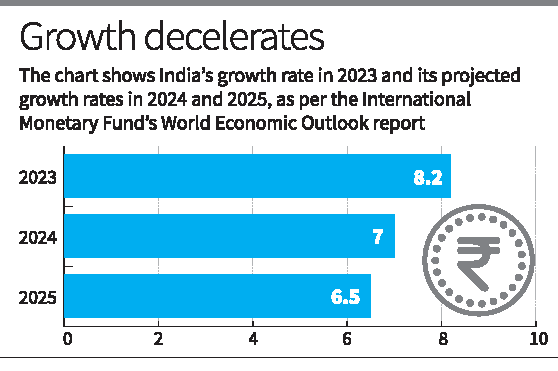
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
