18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD)
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) Convention will be held from January 8-10, 2025, in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
Key Highlights:
- Theme 2025:
- The theme is "Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat", highlighting the vital role of the Indian diaspora in India's development into a prosperous and developed nation.
- Exhibitions:
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Vishwaroop Ram – The Universal Legacy of Ramayana: Showcasing the Ramayana’s influence through traditional and contemporary art forms.
- Diaspora’s Contribution to Technology and Viksit Bharat: Highlighting the global technological impact of the Indian diaspora.
- Spread and Evolution of the Indian Diaspora: Focused on the migration of Indians from Mandvi (Gujarat) to Muscat (Oman).
- Heritage and Culture of Odisha: A look into Odisha’s rich cultural traditions.
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Key Initiatives:
- Pravasi Bharatiya Express: PM Modi will flag off this special tourist train for the diaspora, covering key religious and tourist sites in India under the Pravasi Teertha Darshan Yojana.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards (PBSA): Recognizing significant contributions by members of the Indian diaspora in various fields.
About Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD):
- Origins:
- Celebrated on January 9 each year, marking Mahatma Gandhi's return to India from South Africa in 1915, symbolizing the contributions of migrants.
- First held in 2003, the event became biennial in 2015.
- Objectives:
- Recognizes the contributions of the Indian diaspora to India’s growth.
- Fosters engagement between India and its global diaspora.
- Strengthens India’s relations with host countries and promotes understanding of India’s culture and achievements.
Contributions of the Indian Diaspora to a Viksit Bharat:
- Economic Growth:
- The diaspora plays a pivotal role through remittances, investments, and connecting Indian businesses to global markets.
- Example: The development of a thorium-based fuel by a U.S.-based NRI is a significant step toward clean nuclear energy in India.
- Global Trade Linkages:
- Facilitating partnerships, investments, and knowledge exchange to expand India’s trade base and global market presence.
- Supporting Innovation: Diaspora-driven collaborations in emerging markets boost India’s entry into high-growth sectors, enhancing the country's development prospects.
- Cultural Contributions: Indian diaspora members serve as cultural ambassadors, promoting Indian traditions, art, and heritage globally (e.g., Diwali recognized as a public holiday in several U.S. states).
Challenges Faced by the Indian Diaspora:
- Cultural Integration: Struggles with balancing cultural identity and integrating into host societies can lead to alienation.
- Political and Religious Issues: Increasing politicization and religious biases, especially against Hindus and Sikhs, in countries like the USA and Europe.
- Legal and Citizenship Issues: Complicated visa statuses, restrictive immigration laws, and issues like the H-1B visa challenge the diaspora, despite their significant contributions.
- Remittance Challenges: Economic instability, exchange rate fluctuations, and banking hurdles affect the regular flow of remittances to India, impacting families dependent on them.
Government Initiatives for the Diaspora:
- National Pension Scheme for NRIs
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Card Scheme
- Pravasi Bhartiya Kendra
- Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF)
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
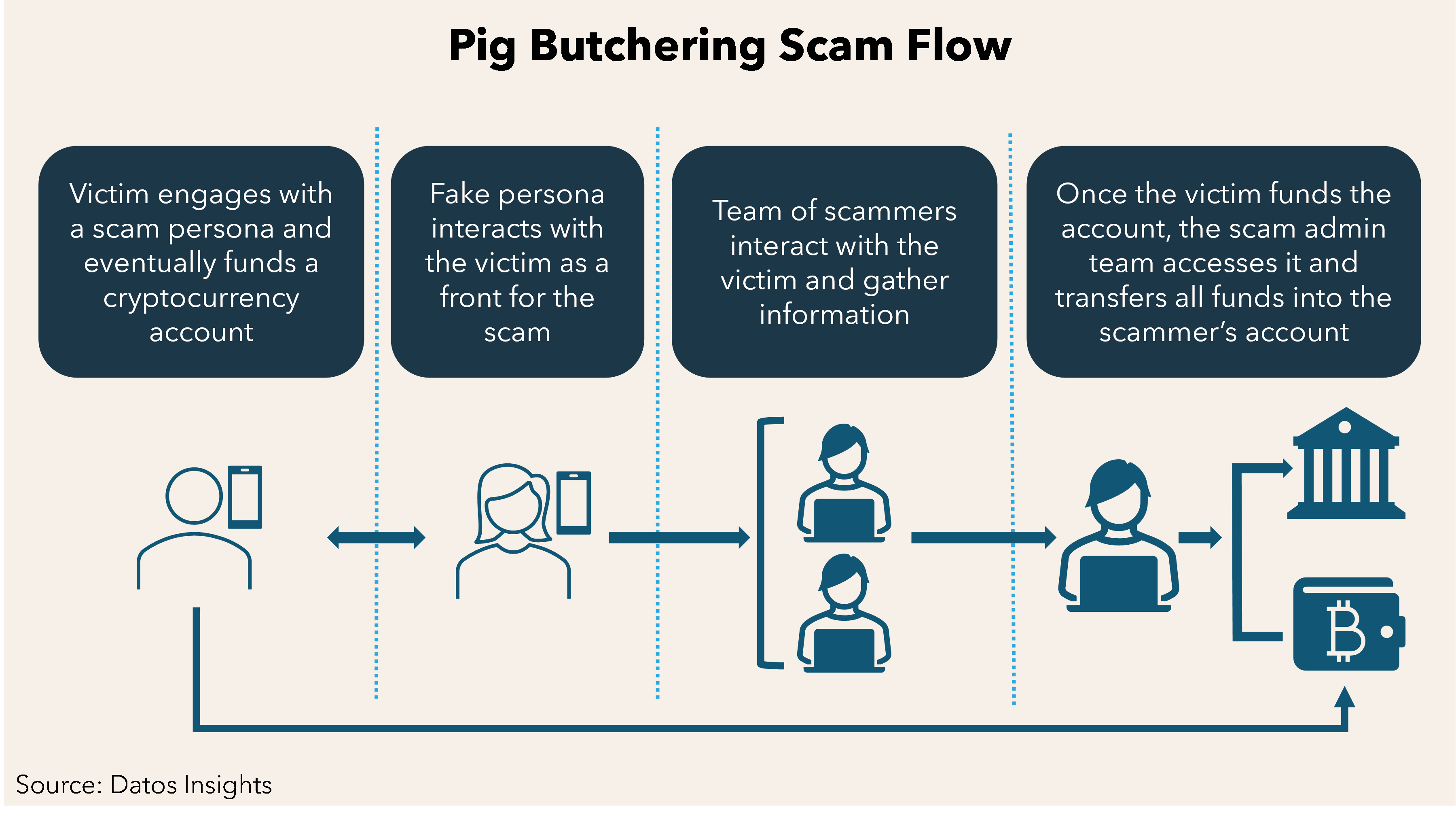
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
