ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
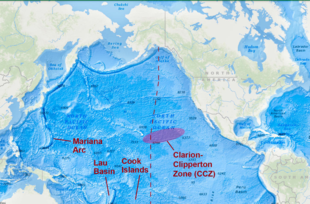
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of India conferred the National Panchayat Awards 2024 on 45 outstanding Panchayats for their contributions to inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and rural development. The event was held on 11th December 2024 (postponed from 24th April due to General Elections).
About the Awards
- Launched to commemorate: 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, which gave constitutional status to Panchayats as institutions of local self-governance.
- Usual celebration date: 24th April — observed as National Panchayati Raj Day.
- Revamped in 2022 to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) via Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
Objectives
- Recognize best practices in rural governance.
- Encourage healthy competition among Panchayats.
- Promote effective implementation of LSDGs and quality service delivery.
Evaluation Structure
- Multi-level assessment: Block → District → State/UT → National level.
- Evaluation based on 9 LSDG themes, including:
- Poverty-Free & Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean & Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just & Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
Award Categories
Award Category Focus Area
Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP) Top 3 GPs under each LSDG theme
Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar Top 3 GPs, Block Panchayats & District Panchayats with highest scores across all themes
Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs promoting renewable energy adoption
Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs achieving net-zero carbon emissions
Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar Institutions providing exemplary support to PRIs in implementing LSDGs
Key Highlights of 2024:
- Total Awards: 45 Panchayats
- Women Leadership: 42% of award-winning Panchayats led by women.
- Participation: 1.94 lakh Gram Panchayats competed.
- Prize Money: ?46 crore transferred digitally to awardees.
- Booklet Released: Best Practices of Awardee Panchayats.
- Film Showcased: Highlighting success stories and capacity-building.
State-wise Recognition
- Notable awardees from: Odisha, Tripura, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, Assam, etc.
- Tripura & Odisha stood out in total recognitions.
- GPs from Maharashtra, Odisha, and Tripura received special awards for energy and carbon neutrality.
Other Key Initiatives for PRIs
Initiative Purpose
SVAMITVA Scheme (2020) Mapping rural property to provide Record of Rights.
e-Gram Swaraj (e-FMS) Work-based accounting to promote transparency.
mActionSoft Geo-tagging Panchayat assets via GPS-enabled photos.
Citizen Charter Portal “Meri Panchayat Mera Adhikaar” – Service delivery assurance to citizens.
India–Singapore Semiconductor Cooperation

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
During his 2025 visit to India, Singapore President Tharman Shanmugaratnam announced plans to collaborate with India on semiconductor manufacturing and the creation of a semiconductor ecosystem, marking the 60th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the two nations.
Singapore’s Semiconductor Landscape
- Contribution to Economy: Accounts for ~8% of Singapore’s GDP.
- Global Standing:
- Produces 10% of global semiconductor output.
- 5% of global wafer fabrication capacity.
- 20% of global semiconductor equipment production.
- Comprehensive Ecosystem: End-to-end capabilities from IC design to packaging and testing.
- Infrastructure: Four wafer fabrication parks with advanced facilities.
- Current Limitation: Focused on mature-node chips (28 nm+); lacks high-end logic chip manufacturing (7 nm or below).
India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Market Size (2024): Valued at USD 52 billion; projected to reach USD 103.4 billion by 2030.
- Import Dependency: ~85% of semiconductor needs met through imports.
- Export-Import Gap (2022): USD 5.36 billion (imports) vs. USD 0.52 billion (exports).
India's Advantages:
- Skilled Talent Pool: Large number of STEM graduates.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower manufacturing and operational costs.
- Geopolitical Opportunity: Global supply chain diversification away from China.
Government Initiatives:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- Semicon India Programme
- Display & Semiconductor Fab Schemes
- SPECS (Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors)
Foreign Collaborations:
- MoUs with US, Japan, and European Commission.
- Tata–Powerchip (Taiwan) collaboration for a fab in Dholera, Gujarat.
How Singapore Can Support India’s Semiconductor Vision
- Manufacturing Partnerships:
- Collaborations with Singaporean firms for assembly and testing services.
- Access to Singapore's advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Talent Development:
- Academic exchanges in microelectronics and semiconductor engineering.
- Joint research and PhD programs.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Replication of Singapore-style wafer fab parks in India.
- Joint ventures to build specialized semiconductor industrial zones.
- Technology Access & Innovation:
- Transfer of advanced technologies and critical semiconductor materials.
- Collaboration on new-generation tech solutions (e.g., AI chips, advanced computing).
Additional Areas of Bilateral Cooperation
- Digital Economy: Exploring data corridor between GIFT City (India) and Singapore.
- Sustainability: Cooperation on green hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable energy.
Strategic Partnership: Upgraded to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2024.
Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building (IGICB) Scheme

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) announced the launch of its Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building Scheme. This program aims to build awareness and develop expertise in internet governance (IG) among Indian citizens.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
To develop awareness and build a skilled pool of professionals in Internet Governance (IG) in India, enabling active Indian participation in global digital policy platforms.
Key Features:
- Internship Format:
- Bi-annual internship with two tracks: 3-month and 6-month durations
- Mentorship by experts from:
- International bodies (e.g., ICANN, APNIC, APTLD)
- Academic institutions and retired officials
- Stipend: ?20,000/month
- Outreach Component: Mandatory awareness programs to be conducted by interns
Focus Areas:
- Engagement with I-Star organizations, such as:
- ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers)
- ISOC (Internet Society)
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
- IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Exposure to global best practices and policy mechanisms in digital governance
- Capacity building for inclusive participation in emerging internet issues
Significance:
- Promotes digital policy leadership among Indian youth
- Enhances India’s representation in global internet governance dialogues
- Fosters a tech-savvy and policy-aware workforce for digital India initiatives
About NIXI (National Internet Exchange of India):
- Established: 19 June 2003
- Type: Not-for-profit (Section 8 company)
- Parent Ministry: MeitY
- Mandate:
- Enhance internet adoption and digital infrastructure in India
- Key Services:
- Internet Exchange Points (IXPs): Facilitate domestic internet traffic exchange
- .IN Registry: Manage India’s country code top-level domain (.in)
- IRINN: Allocate IPv4 and IPv6 resources within India
Capacity Building & Training: Promote internet-related knowledge and skills
