BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Hornbill Festival

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The Hornbill Festival, a vibrant celebration of Nagaland's culture and tourism, is an annual event that takes place from December 1 to 10.
About the Hornbill Festival:
- Origin: First held in the year 2000.
- Purpose: The festival aims to foster inter-tribal communication, preserve the cultural heritage of Nagaland, and showcase the harmonious blending of traditional and modern elements.
- Significance: Referred to as the “festival of festivals,” it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural calendar.
- Organizers: It is organized by the Tourism and Art & Culture Departments of the Government of Nagaland.
- Location: The festival takes place annually at the Naga Heritage Village in Kisama, located about 12 kilometers from Kohima.
- Cultural Showcase: Over the years, it has evolved into a significant celebration that highlights the vibrant and diverse cultural traditions of the various tribes in Nagaland.
- Name Origin: The festival is named after the Hornbill bird, which holds cultural importance among the Naga tribes.
- Theme of the 2024 Hornbill Festival:The 2024 edition is themed “Cultural Connect,” celebrating the rich heritage and cultural diversity of Nagaland. The festival continues to merge modernity and tradition through a variety of activities, including Naga wrestling, traditional archery, food stalls, fashion shows, beauty contests, and musical performances. Additionally, the Archives Branch is presenting a special exhibition titled “Naga-Land & People in Archival Mirror” in partnership with the National Archives of India, offering a deeper look at the region's history and cultural practices.
- Recent Milestone:This year marks the 25th anniversary of the Hornbill Festival.
Festival Highlights:
- Annual Event: Held each year since its inception in 2000, it serves as a major cultural event for Nagaland.
- Symbolism: Named after the Hornbill bird, which represents boldness and grandeur in Naga folklore.
- Location: The festival is hosted at Kisama Heritage Village, a cultural center that preserves Naga traditions with 17 indigenous houses (Morungs) that represent each of the tribes.
- Cultural Diversity: Nagaland, known as the “Land of Festivals,” is home to 17 major tribes, each with its distinct festivals and cultural practices. The Hornbill Festival promotes inter-tribal interaction and celebrates the state’s rich heritage.
- National Significance: Reflecting India’s unity in diversity, the festival serves as a platform for different cultural practices to coexist, strengthening the nation’s collective identity.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
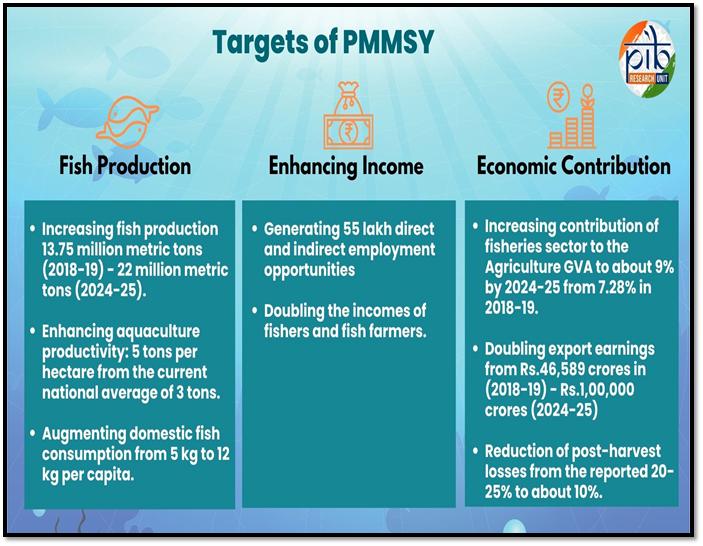
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
