India's Akash missile engages four targets at once at 25km, a global first (ET)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
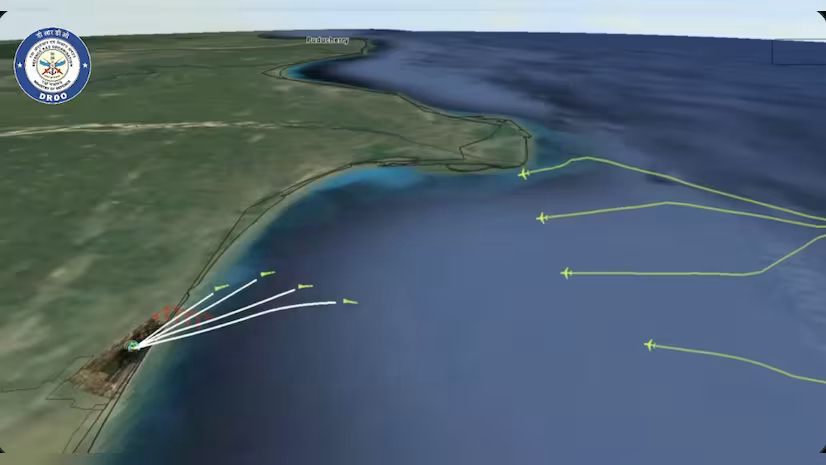
India demonstrated the capability of the Akash missile system to engage four aerial targets simultaneously at a range of 25 kilometres, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) said on Sunday.
Context:
- During the recent Exercise Astrashakti 2023, a solitary unit of the Akash weapon system demonstrated its capability by effectively engaging and eliminating four unmanned targets simultaneously.
- This showcase positions India as the pioneer, being the first country to showcase the proficiency of engaging multiple targets at considerable distances concurrently through command guidance from a single firing unit.
About the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System:
- The Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System is a Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (SRSAM) designed to safeguard vulnerable areas and points from airborne threats.
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), it boasts several notable features:
- Versatility: Capable of simultaneously engaging multiple targets and effectively neutralizing manoeuvring threats, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles, and helicopter-launched missiles.
- Electronic Counter-Counter Measures (ECCM): Equipped with built-in ECCM features, enhancing its resilience against electronic countermeasures.
- Flexible Deployment: The entire system is configured for launch from both static and mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, ensuring adaptable deployment options.
- Transportability: Road and rail transportable, with swift mobilization and deployment capabilities, facilitating rapid response scenarios.
- Range: Capable of engaging aerial targets at a distance of approximately 25 km.
- Altitude of Operation: Ranging from 100 meters up to 20 km.
- Weight: 710 kg.
- Guidance System: Command Guidance.
- Automation: Fully automatic with a quick response time from target detection to neutralization.
- Open-System Architecture: Designed with an open-system architecture, ensuring adaptability to current and future air defence environments.
What is ‘noma’, the latest addition to WHO’s list of neglected tropical diseases (DownToEarth)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) on December 15, 2023, added one of the world’s most under-recognised health challenges, noma, to its official list of neglected tropical diseases (NTD).
About the Noma disease:
- Noma is a severe gangrenous disease of the mouth and face with a mortality rate of approximately 90 per cent.
- It is also known as cancrum oris or gangrenous stomatitis and is often associated with extreme poverty, malnutrition and poor access to sanitation and oral hygiene.
- The name of the disease comes from the Greek word “nom?”, meaning “to devour”, as noma eats away facial tissue and bones if not treated early.
- Noma mainly affects children aged 2-6 years old and is found most commonly among those living in poor communities.
- The illness’s ‘hidden’ or neglected nature is most likely due to the fact that it affects the world’s most marginalised children.
- Noma is associated with a number of risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, weakened immune systems, infections, and extreme poverty.
- While the disease is not contagious, it prefers to attack when the body’s defences are weak.
- The NTD often starts as an ulcer on the mucous membrane lining, commonly after a bout of measles or other diseases, stated another 2003 study.
- “It quickly develops into a massive necrosis, moving from the inside outward, often involving major portions of the face.
- Treatment: “Early treatment with antibiotics, rehydration, correction of electrolytic imbalances, and administering nutritional supplements will halt the disease.
- The patients who survive face many consequences, like significant facial disfigurement, spasms of the jaw muscles, oral incontinence and speech problems.
- The disease is also called the ‘face of poverty’, as effective drugs like sulfonamides and penicillin and adequate surgical treatment for the effects remain inaccessible for many due to extreme poverty.
- “The recognition of noma as an NTD aims to amplify global awareness, catalyse research, stimulate funding, and boost efforts to control the disease through multisectoral and multi-pronged approaches.
Surat Diamond Bourse to create 150,000 jobs! Modi is confident ‘world’s largest office building’ will be a boon for artisans and businessmen (Financial Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
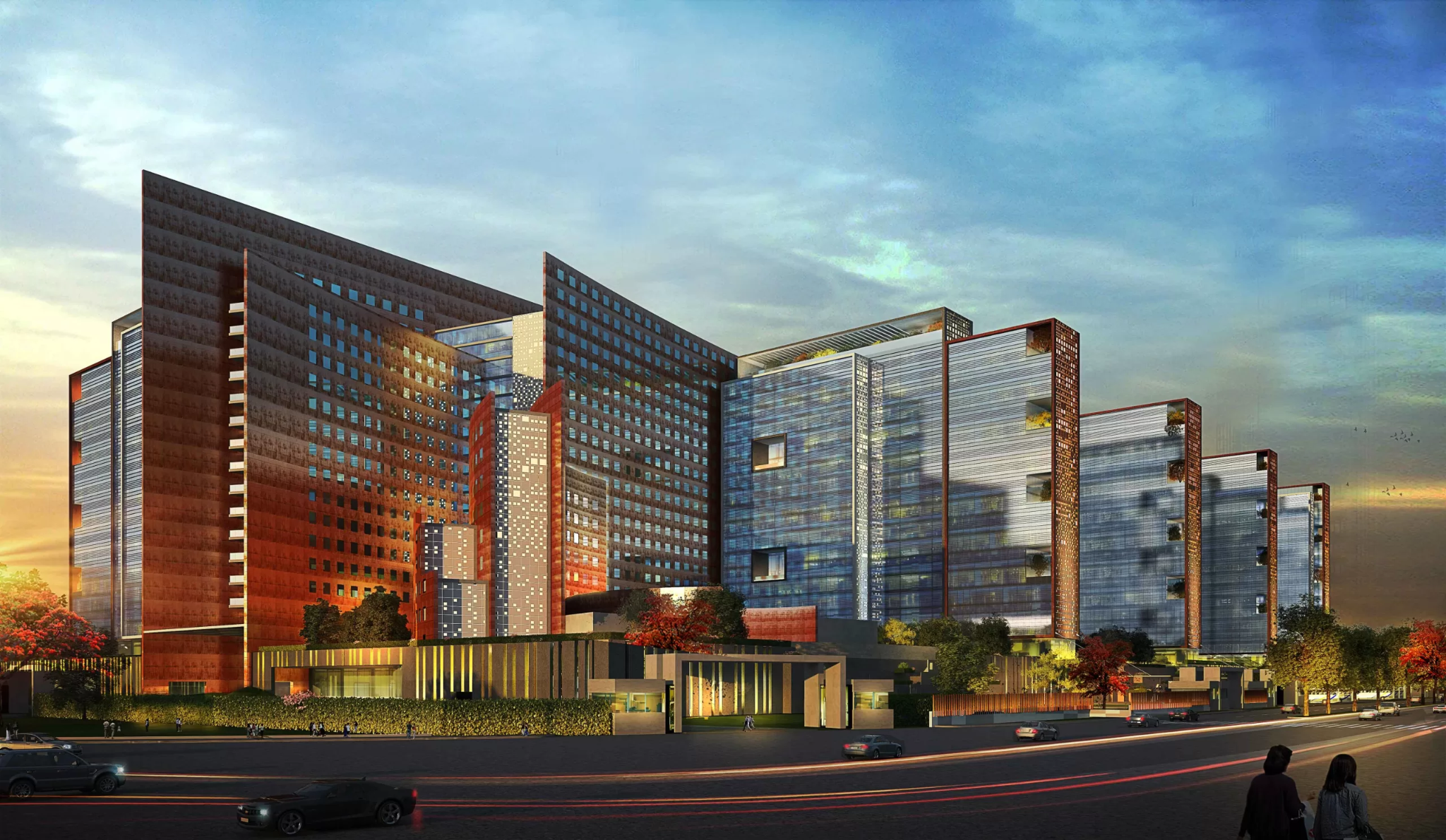
In the inauguration ceremony of the Surat diamond bourse in Gujarat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed plans for the creation of 150,000 new jobs, emphasising the bourse’s role as a “one-stop shop” for artisans and businessmen.
About Surat Diamond Bourse:
- Established in February 2015 by the former Chief Minister of Gujarat, Smt. Anandiben Patel, the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is a prominent diamond trade centre situated in DREAM (Diamond Research and Mercantile) city, Surat, Gujarat.
- Recognized as the "diamond city" due to its diamond industry, which processes 85 to 90% of the world's rough diamonds, the SDB stands as the world's largest diamond trading hub, spanning an expansive floor space of 660,000 square meters and surpassing The Pentagon as the largest office building globally.
- Themed around the 'panch tatva,' symbolizing the five elements of nature – air, water, fire, earth, and sky, the SDB is designed with thematic landscaping.
- As a global centre for both rough and polished diamond and jewellery trading, it unifies various facets of the diamond industry, including cutting, polishing, and trading activities, within its vast expanse.
- The Bourse features a state-of-the-art 'Customs Clearance House' for Import-Export, a Jewelry mall for retail jewellery business, and facilities for International Banking and Safe Vaults.
Importance of the SDB Project:
- The Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is set to accommodate a diverse range of diamond-related enterprises, encompassing the sale of both rough and polished diamonds, diamond manufacturing machinery, diamond planning software, diamond certificate firms, lab-grown diamonds, and more.
- Anticipated to be a major contributor to employment, the SDB is poised to generate substantial job opportunities.
- With an expected direct employment impact on over 1.5 lakh individuals across various roles within the diamond industry, it aims to bolster economic activity and livelihoods.
- Acknowledging its commitment to environmental responsibility, the complex has earned pre-certification as a green building by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
- This recognition is a testament to the SDB's implementation of eco-friendly and sustainable practices in its operations.
What is DREAM City?
- DREAM City, short for Diamond Research and Mercantile City, is an emerging business district located in Surat.
- Encompassing 810 hectares (2,000 acres) of land near Khajod, it follows the model of the Gujarat International Finance Tec (GIFT) City and Dholera Smart City near Ahmedabad.
- Envisioned as a comprehensive urban development, DREAM City is slated to feature office spaces, residential areas, and associated amenities.
- The project is under the purview of a special-purpose vehicle established by the Government of Gujarat.
- With an anticipated opening in 2030, DREAM City is poised to become Gujarat's third smart city, aligning with the state's commitment to fostering modern and sustainable urban environments.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
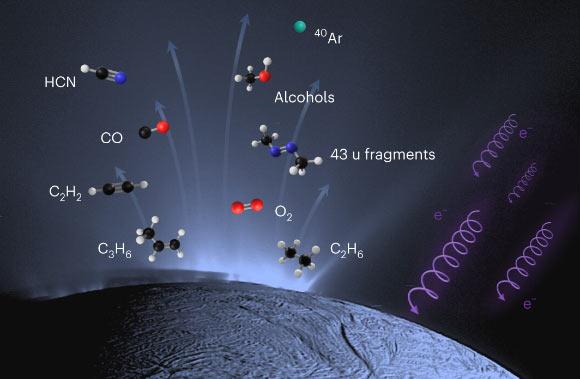
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
How Indian states fare on logistics: What the Centre’s latest survey says (Indian Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) perception survey, released by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry, flags some challenges in logistics and states performance on a regional basis.
Key highlights of the Report:
- Only five states namely Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Telangana continue to make up 70 per cent of exports. Over the years this has caused a widening gap in income and job generation between the landlocked states and coastal states.
- Performance of Landlocked States: Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh have received low perception scores on these counts while user satisfaction in Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab improved.
- Notably, Jharkhand saw below-average scores across all indicators, encompassing infrastructure, services, and operating and regulatory categories.
- Performance of North-East Group: In Manipur, user satisfaction levels for the state are generally lower than the average of the North-East Group for all indicators across pillars.
- The data indicated relatively high stress in the ‘easy of entry’ category.
- While Assam performed better than average on most counts, the user performance assessment was also below the average of North-East Group in the case of Meghalaya.
- Odisha, West Bengal Lag Among Coastal States: Indian coastal states including Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal account for 75 per cent of total exports from the country and have fared well in logistics historically.
- Gujarat accounts for 33% followed by Maharashtra with 16% and Tamil Nadu with 9% share.
- However, the survey showed that Goa, Odisha and West Bengal continue to perform below the average among coastal states.
- In the case of Odisha, the survey said that there has been an improvement in the overall perception of the state’s logistics ecosystem since 2019 but despite this, the indicator averages for this year have remained below the Coastal Group average.
What is Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- Initiated in 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, LEADS draws inspiration from the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Unlike the LPI, which relies solely on perception-based surveys, LEADS incorporates both perception and objectivity, thereby enhancing the robustness and comprehensiveness of its evaluation.
- LEADS focuses on three pivotal pillars:
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services, and
- Operating and Regulatory Environment.
- The recently released 5th edition, LEADS 2023, illuminates the evolving performance of states and union territories across these pillars.
- It provides valuable insights into the enhancement of logistics performance at the State/UT level, emphasizing an augmented stakeholder perception and the impact of various reforms.
- This report not only signals a positive transformation in the performance of states but also empowers State/UT Governments with region-specific insights, facilitating informed decision-making and comprehensive growth.
Importance of the LEADS Initiative:
- The LEADS report serves as a catalyst in fostering healthy competition among States/UTs, driving improvements in logistics performance.
- Notably, 23 States/UTs have aligned their State Logistics Policies with the National Logistics Policy, while 16 have accorded industry status to logistics, collectively contributing to the elevation of India's global positioning in the logistics ecosystem.
- This initiative significantly enhances the overall competitiveness of India's logistics sector, as evidenced by the country's ascent by six places to the 38th position in the 2023 Logistics Performance Index.
- Integral to this success are digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), and GST, which have propelled India's improved global ranking.
- Developed collaboratively and through a consultative approach, the LEADS report introduces objectivity in assessing both infrastructure development and process-related reforms.
