Chennai's Pallikaranai Wetlands Welcoming Migratory Bird Flocks (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
With over 150 garganeys, and several other species, including waders and raptors, flocking the Pallikaranai marshland, the curtain for the migratory season has been raised.
About Pallikaranai Marshland:
- Location: Pallikaranai marshland is a freshwater and partly saline wetland, located approximately 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- The eastern border of the marsh is flanked by the Buckingham Canal.
- Rich Ecosystem: The diverse ecosystem of Pallikaranai supports an impressive array of wildlife, including 115 bird species, 10 mammals, 21 reptiles, 10 amphibians, 46 fish, nine molluscs, five crustaceans, and seven butterfly species.
- Notable Species: Among the diverse wildlife are noteworthy species such as the Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis), glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus), and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
- Biodiversity Significance: Beyond its biodiversity, the marshland serves a crucial role in flood prevention for Chennai, absorbing water during wet periods and releasing it during dry spells.
- Environmental Threats: Despite its ecological importance, the site faces threats from invasive non-native species, household sewage, urban wastewater, and periodic droughts.
- Ramsar Designation: Acknowledging its ecological significance, Pallikaranai marshland holds the status of being one of India's Ramsar sites, recognized for its importance in wetland conservation on an international scale.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
Amazon River Hits Lowest Levels in a Century Amid Drought in Brazil (Business Standard)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Amazon River fell to its lowest level in over a century on Monday at the heart of the Brazilian rainforest as a record drought upended the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and damaged the jungle ecosystem.
About the Amazon River:
- The Amazon River holds the distinction of being the world's largest river in terms of both water volume and width.
- Length and Course: Spanning an impressive 6,400 kilometres, it is the second-longest river globally, surpassed only by the Nile.
- Originating high in the Andes Mountains, the river courses its way eastward through vast rainforests and lowlands before reaching its culmination at the northeastern coast of Brazil, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dynamic Width: During the dry season, the Amazon River exhibits a width ranging from 4 to 5 kilometres, expanding significantly to 50 kilometres in certain areas during the wet season.
- Unparalleled Drainage Area: The Amazon boasts the largest drainage area globally, with its watershed spanning across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Approximately two-thirds of the Amazon's mainstream and the majority of its basin lie within the borders of Brazil.
- Water Discharge and Global Impact: With a staggering water discharge of 300,000 cubic meters per second into the Atlantic Ocean, the Amazon contributes one-fifth of the total freshwater volume entering the world's oceans.
- This immense water flow plays a pivotal role in regulating global oxygen and carbon cycles.
- Extensive Tributaries: Featuring over 1,100 tributaries, including seventeen exceeding 1,500 kilometres in length, notable contributors include the Rio Negro, the Madeira River, and the Xingu River.
- Environmental Significance: The Amazon Rainforest, constituting approximately half of the Earth's remaining rainforest, stands as the largest repository of biological resources.
- Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet's oxygen and carbon balance.
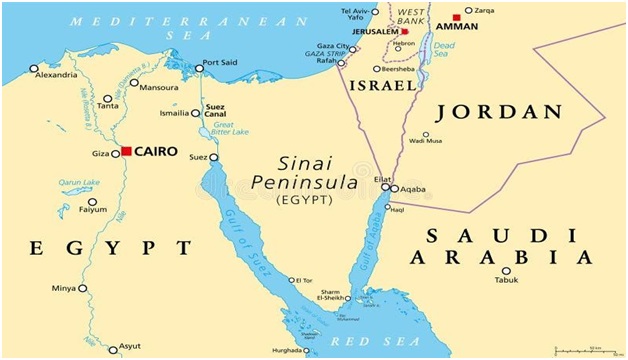
US Says Egypt Border Crossing to Gaza to Reopen (Business Today)
- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Hundreds of tons of aid from multiple countries have been stationed in Egypt's Sinai Peninsula, awaiting an agreement for secure transportation to Gaza for several days.
About the Sinai Peninsula:
- Geographical Location: The Sinai Peninsula is a triangular landmass located in northeastern Egypt, serving as a critical land bridge that connects the continents of Asia and Africa.
- Size and Sovereignty: Encompassing an expansive area of 23,500 square miles (61,000 square km), the Sinai Peninsula is recognized as a sovereign territory within the boundaries of Egypt.
- Geographical Boundaries: It is bordered to the north by the Mediterranean Sea and to the east by Israel and the Gaza Strip.
- The Suez Canal lies to the west, acting as a separation from the African part of Egypt.
- To the southwest, the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea border the peninsula, while the Gulf of Aqaba marks its southeastern boundary.
- Egypt shares maritime borders in the Sinai with Jordan and Saudi Arabia.
- Historical Significance: In the late 19th century, including the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt became part of the British Empire until gaining independence in 1922.
- During the Six-Day War of June 1967, the peninsula was occupied by Israeli forces and returned to Egypt in 1982 as part of the peace treaty signed in 1979.
- Diverse Geography: The Sinai Peninsula is characterized by a diverse landscape, featuring mountain ranges, deserts, plateaus, and coastal regions.
- Population Composition: With a relatively sparse population, the Sinai is home to about 600,000 people, predominantly consisting of Arab Egyptians and Bedouins.
Hailstorms Damage Apple Orchards in Kulgam, Shopian (HT)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A hailstorm in the evening caused massive damage to the crops and fruits in south Kashmir’s Kulgam and Shopian districts. Residents said the hailstorm damaged the apple fruit which was ready for harvesting.
What are Hailstorms?
- Hail, a solid form of rain composed of ice balls or lumps, leads to the formation of hailstorms when they descend to the ground.
- Typically lasting around 15 minutes, these storms can inflict injuries and damage to structures, vehicles, and more, particularly prevalent in midlatitude regions.
- Hailstorms occasionally coincide with other severe weather phenomena such as cyclones and tornadoes.
- The size of hailstones varies widely, ranging from small pellets under 1/4 inch to larger stones measuring several inches in diameter.
- Conditions: Conditions conducive to hailstorm occurrence involve the presence of highly developed Cumulonimbus clouds, massive anvil-shaped formations observed during thunderstorms that can reach heights of up to 65,000 feet.
- Strong updrafts, or ascending air currents within these clouds, and high concentrations of supercooled liquid water are essential elements.
- Formation of Hail: Hail formation begins with a water droplet lifted by an updraft inside a thundercloud.
- As it ascends, supercooled water droplets adhere to its surface, creating layers of ice.
- With continued ascent, the hail embryo grows by accumulating more supercooled particles until gravity pulls it down.
- Large hailstones often display alternating layers of clear and opaque ice due to irregular rates of freezing during their development.
