India's retail inflation moderates to 5.10 per cent in January (The Hindu)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's retail inflation has eased to 5.10% on an annual basis, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
What is Retail Inflation or CPI-based Inflation?
- Retail inflation, also known as Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation tracks the change in retail prices of goods and services which households purchase for their daily consumption.
- CPI is released by The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- To measure inflation, we estimate how much CPI has increased in terms of percentage change over the same period the previous year.
- If prices have fallen, it is known as deflation (negative inflation).
- The Central Bank (RBI) pays very close attention to this figure in its role of maintaining price stability in the economy.
- The CPI monitors retail prices at a certain level for a particular commodity; and price movement of goods and services at rural, urban and all-India levels.
- The change in the price index over a period of time is referred to as CPI-based inflation or retail inflation.
- Generally, CPI is used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation, as a tool by the central bank and government for inflation targeting and for inspecting price stability, and as a deflator in the national accounts.
- CPI also helps understand the real value of salaries, wages, and pensions, the purchasing power of the nation’s currency, and regulating rates.
- CPI, one of the most important statistics to ascertain economic health, is generally based on the weighted average of the prices of commodities.
- It basically gives an idea of the cost of the standard of living.
- CPI specifically identifies periods of deflation or inflation for consumers in their day-to-day living expenses.
- If there is inflation (when goods and services cost more) the CPI will rise over a period of time.
- If the CPI drops, that means there is deflation or a steady reduction in the prices of goods and services.
How is CPI calculated (CPI formula)?
- To calculate CPI, multiply 100 by the fraction of the cost price of the current period and the base period.
- CPI formula: (Price of the basket in current period / Price of the basket in base period) x 100
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
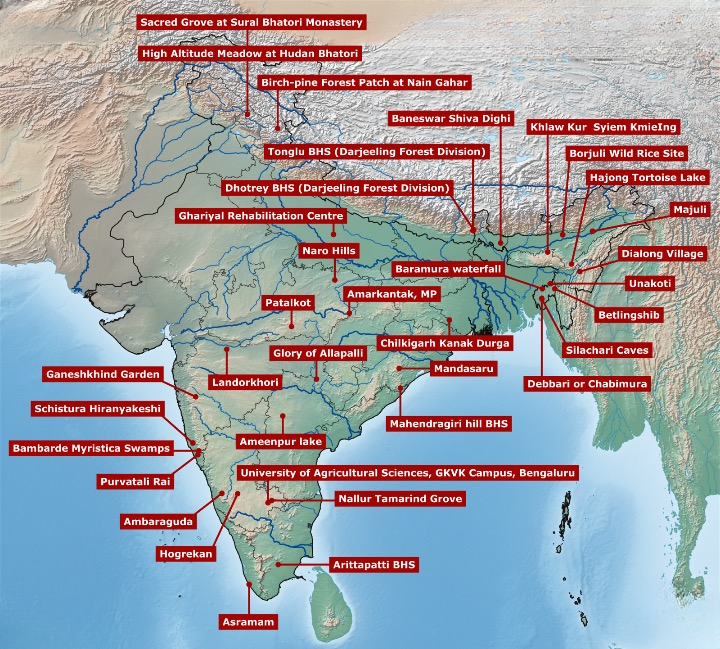
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
Revival of Weimar Triangle (The Hindu)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The governments of Poland, France and Germany vowed Monday to make Europe a security and defence power with a greater ability to back Ukraine, amid concerns that former U.S. President Donald Trump might return to the White House and allow Russia to expand its aggression on the continent.
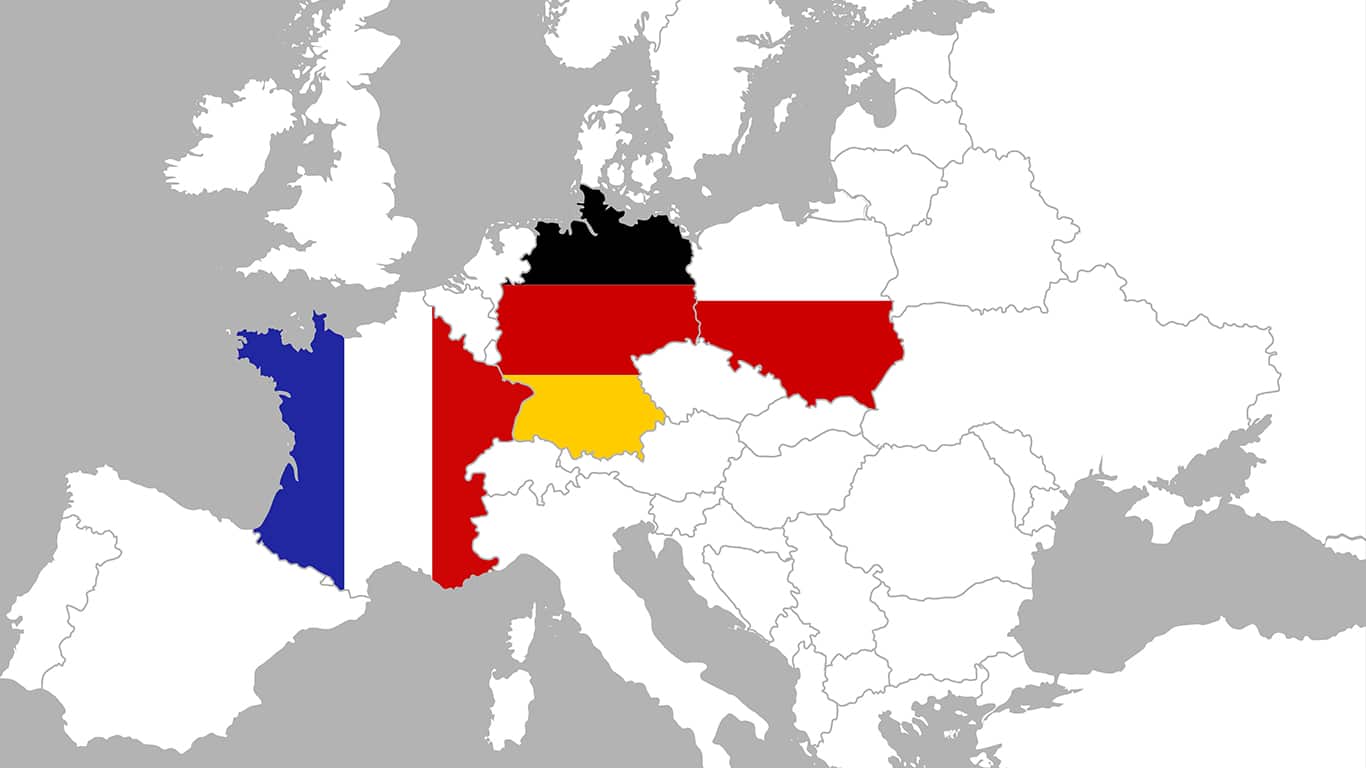
What is the Weimar Triangle?
- The Weimar Triangle is a regional alliance of three European countries:
- France
- Germany
- Poland
- It was established in 1991 in the German city of Weimar, with the aim of promoting cooperation between the three countries on cross-border and European issues.
- The Weimar Triangle is not a formal organization, but rather a platform for dialogue and cooperation.
- The three countries hold regular summits, typically at the level of heads of state or government, and their foreign ministers also meet frequently.
- The Weimar Triangle also includes cooperation between parliaments, militaries, scientists, and cultural institutions.
Significance of the Weimar Triangle:
- The Weimar Triangle has played a significant role in European integration.
- It helped to support Poland's emergence from communism and its accession to the European Union in 2004.
- In recent years, the Weimar Triangle has taken on a renewed importance as Europe has faced a number of challenges, including the Ukraine crisis and the rise of populism.
- The three countries have worked together to promote stability and cooperation in Europe.
Some of the key areas of cooperation between the Weimar Triangle countries:
- Security: The three countries cooperate on a range of security issues, including defence, counterterrorism, and cybersecurity.
- Economy: The Weimar Triangle countries are major trading partners, and they work together to promote economic growth and integration.
- Energy: The three countries are working together to develop a more secure and sustainable energy supply.
- Climate change: The Weimar Triangle countries are committed to combating climate change and have pledged to meet the targets of the Paris Agreement.
- Culture: The three countries have a rich cultural heritage, and they work together to promote cultural exchange and understanding.
Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Report and Portal (DD News)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog recently unveiled the Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW) report and portal, aiming to bolster efforts in environmental conservation and sustainable land use across India.
About the Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Portal:
- The "Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW)-Suitability Mapping" portal offers universal access to state and district-level data.
- Hosted on the Bhuvan website, the GROW initiative aligns with national commitments to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 and create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent.
- Led by NITI Aayog, the initiative involved collaboration from various institutions and utilized advanced technologies like remote sensing and GIS to assess agroforestry suitability across all Indian districts.
- Through thematic datasets, the project developed an Agroforestry Suitability Index (ASI) for national-level prioritization of greening and restoration projects.
- Based on analysis of five remote sensing-derived thematic layers - land use, wasteland, slope, water proximity, and soil organic content - the system provides information on areas suitable for agroforestry across India.
- It classifies areas as highly suitable, moderately suitable, and less suitable for agroforestry.
- Key features include generating district-level information on wasteland areas suitable for agroforestry, area prioritization regimes, live maps, area analysis-statistic reports, and an interactive mode/tool for flexibility in handling weights based on local conditions/needs.
Government Emphasis on Agroforestry in Budget Allocation:
- The Union Budget for the fiscal year 2022-23 has underscored the promotion of agroforestry and private forestry as a priority.
- Recognizing the critical goods and services provided by agroforestry, the budget aligns with the country's commitment to sustainable land use practices.
India's Agroforestry Leadership and Global Alignments:
- As the seventh-largest country globally, India faces challenges such as increased build-up areas, degraded land, and imbalanced resources.
- Approximately 16.96% of the Total Geographical Area (TGA) is a wasteland, necessitating transformation for productive use.
- India's pioneering National Agroforestry Policy, initiated in 2014, aims to enhance productivity, profitability, and sustainability through agroecological land use systems.
- Agroforestry aligns with global commitments, including the Paris Agreement, Bonn Challenge, UN Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations Convention on Combating Desertification (UNCCD), Doubling Farmers Income, Green India Mission, and more.
- India's proactive stance in promoting agroforestry contributes significantly to these international efforts, fostering a sustainable and resilient future.
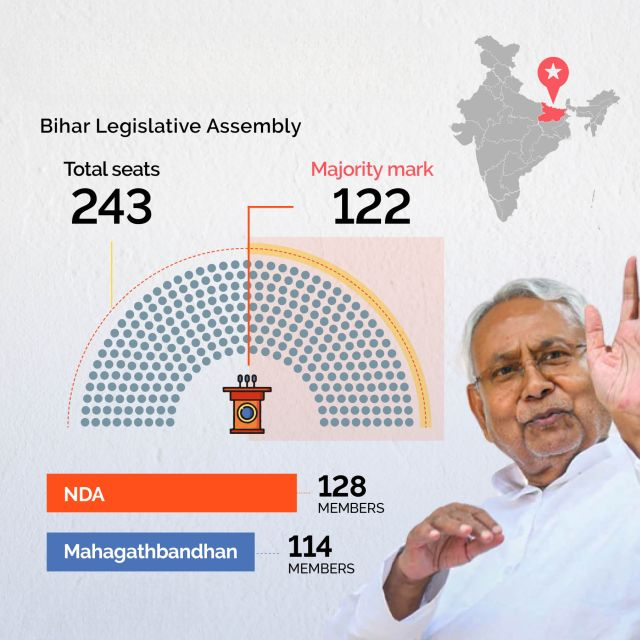
Floor Test in the Bihar Legislative Assembly (Indian Express)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar's coalition government with the Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP) on Monday won a crucial trust vote in the Bihar Assembly.
What is a Floor Test?
- A floor test (also called a ‘trust vote’) is held in legislative bodies, to find out whether the government that is suspected to have lost the majority still retains the confidence of the House.
- This is done through a vote among the members.
- When the House is in session, it is the Speaker who can call for a floor test but when the Assembly is not in session, the Governor’s residuary powers under Article 163 allow him to call for a floor test.”
- Further, “In 2020, the Supreme Court, in Shivraj Singh Chouhan & Ors versus Speaker, Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly & Ors, upheld the powers of the Speaker to call for a floor test if there is a prima facie view that the government has lost its majority.”
What Happens During a Floor Test?
- In case the majority held by the government is questioned, the leader of the party which claims to have the majority has to move a vote of confidence and prove a majority among those present and voting.
- The CM moves a motion seeking a vote of confidence, on which MLAs who are present in the House vote.
- If the majority of members vote in favour, the government survives;
- If the CM loses the vote, the government has to resign.
- This happens both in Parliament and the state Legislative Assemblies.
- Voting can be conducted by either a voice vote, in which MLAs respond to the motion verbally.
- Voting electronically involves the casting of votes by pressing a button, after which the numbers for each side are displayed on a board.
- In a physical division of votes, lawmakers cast votes in a ballot box, which are then counted.
- Also in situations when there are differences within a coalition government, the Governor can ask the Chief Minister to prove majority in the house.
- There is another test, the Composite Floor Test, which is conducted only when more than one person stakes a claim to form the government.
- When the majority is not clear, the governor might call for a special session to see who has the majority.
- The majority is counted based on those present and voting.
- This can also be done through a voice vote where the member can respond orally or through division voting.
- Some legislators may be absent or choose not to vote.
- In division vote, voting can be done through electronic gadgets, ballots or slips.
- The person who has the majority will form the government.
- In case of a tie, the speaker can also cast his vote under Article 100 of the constitution.
