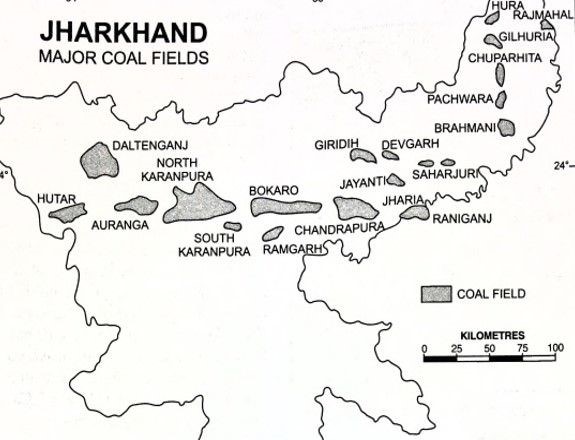
South Karanpura Coalfield
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research has highlighted significant shale gas generation potential in the eastern region of the South Karanpura coalfield, located in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand, India. Evidence from microscopic palynomorphs and organic remains, combined with geochemical assessments, indicates that the eastern Sirka coalfield demonstrates a higher potential for hydrocarbon generation compared to the Giddi coalfield to the north.
Overview of the South Karanpura Coalfield
- Location and Size: The South Karanpura coalfield is situated along the Chingara fault and covers approximately 195 square kilometers, housing an estimated 5,757.85 million tonnes of coal reserves.
- Composition: This region is rich in coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers, making it well-established for its substantial coal deposits.
- Emerging Focus: With increasing energy demands and interest in hydrocarbon exploration, there is a growing emphasis on the potential for coal bed methane and shale gas generation in this area, aligning with national energy strategies for greener energy sources.
Research Methodology
Scientists from the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP) conducted a comprehensive study to evaluate hydrocarbon generation potential. The research involved:
- Sample Collection: Sediments were collected from coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers at the Sirka and Giddi C collieries in Hazaribagh district.
- Analysis Techniques: The study utilized palynological analysis of microscopic remains, alongside Rock-Eval pyrolysis to assess the potential of the rock samples. Key parameters analyzed included:
- Palynofacies
- Free hydrocarbons (S1)
- Heavy hydrocarbons (S2)
- Pyrolyzable carbon (PC)
- Residual hydrocarbon (RC)
The collected samples, which date back to the Permian (Barakar) period, indicate favorable conditions for high hydrocarbon resource potential in the eastern South Karanpura coalfield.
Shale Gas Overview
Shale gas is an unconventional natural resource found at depths of 2,500 to 5,000 meters, deeper than conventional crude oil. Its extraction involves deep vertical drilling followed by horizontal drilling, with hydraulic fracturing (fracking) being the most common method used to access gas trapped in low-permeability rocks.
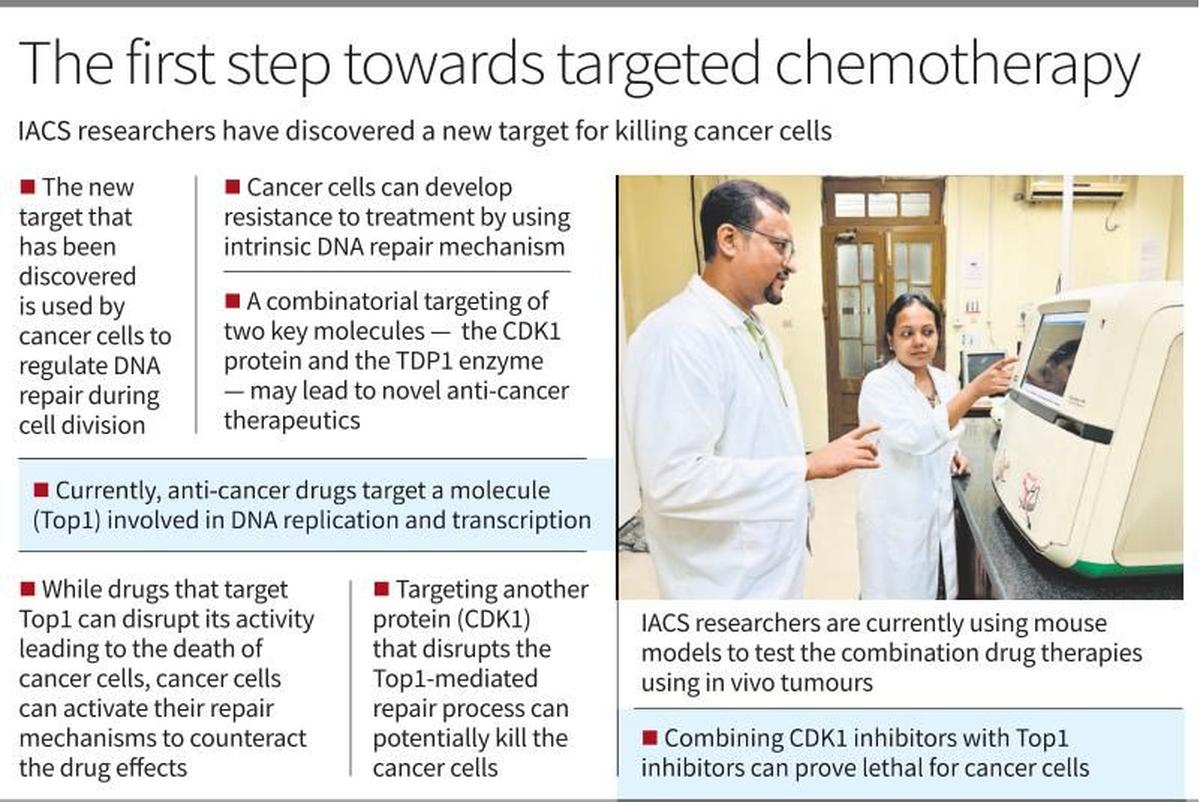
New Cancer Therapy Target
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
NABARD Survey on Rural Financial Inclusion
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
NABARD has published the findings from its second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) for 2021-22, which offers primary data based on a survey of 1 lakh rural households, covering various economic and financial indicators in the post-COVID period.
Survey Overview:
- Inaugural survey conducted for 2016-17, results released in August 2018.
- Aims to analyze changes in rural economic conditions since 2016-17.
- Included all 28 states and Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Insights from NAFIS 2021-22
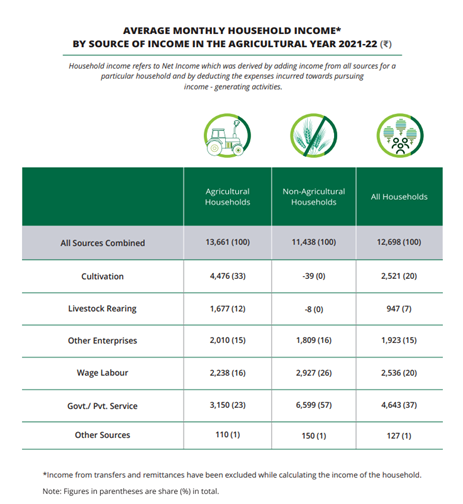
- Increase in Average Monthly Income:
- Average monthly income rose by 57.6% from Rs. 8,059 (2016-17) to Rs. 12,698 (2021-22).
- Nominal CAGR of 9.5%, with annual nominal GDP growth at 9%.
- Agricultural households earned Rs. 13,661; non-agricultural households earned Rs. 11,438.
- Salaried employment contributed 37% to total income; cultivation contributed one-third for agricultural households.
- Rise in Average Monthly Expenditure:
- Average monthly expenditure increased from Rs. 6,646 (2016-17) to Rs. 11,262 (2021-22).
- Agricultural households reported higher consumption (Rs. 11,710) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs. 10,675).
- Expenditure exceeded Rs. 17,000 in states like Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Increase in Financial Savings:
- Annual average financial savings grew to Rs. 13,209 in 2021-22 from Rs. 9,104 in 2016-17.
- 66% of households saved in 2021-22, up from 50.6% in 2016-17.
- 71% of agricultural households reported savings, compared to 58% of non-agricultural households.
- States like Uttarakhand (93%) and Uttar Pradesh (84%) had high saving rates, while Goa (29%) and Kerala (35%) had lower rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Coverage:
- 44% of agricultural households possessed a valid KCC.
- Among larger landholders and those with recent agricultural loans, 77% reported having a KCC.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Households with at least one insured member increased from 25.5% (2016-17) to 80.3% (2021-22).
- Vehicle insurance was most common (55%), followed by life insurance (24%).
- Pension Coverage:
- Households with at least one member receiving any form of pension rose from 18.9% to 23.5%.
- 54% of households with members over 60 years old reported receiving a pension.
- Financial Literacy:
- Good financial literacy increased by 17 percentage points, from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Sound financial behavior improved from 56.4% to 72.8%.
Conclusion
- The NAFIS 2021-22 highlights significant advancements in rural financial inclusion since 2016-17.
- Improvements in income, savings, insurance coverage, and financial literacy are notable.
- Government welfare schemes (e.g., PM Kisan, MGNREGS) have positively impacted rural lives.
- Continued support and investment in rural development are essential for economic empowerment and financial security in India's rural population.
Colombo Security Conclave

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) reached a milestone on August 30, 2024 with India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Mauritius signing a Charter and a memorandum of understanding, for the establishment of the CSC secretariat.
Key Facts:
Background of CSC:
- Originally called the NSA Trilateral on Maritime Security, the CSC was established in 2011 among India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. The initiative aimed to bolster maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
Membership:
- The founding members include India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Mauritius joined in 2022, and Bangladesh became a member in 2024. Seychelles participates as an observer state.
Goals of CSC:
The CSC aims to foster cooperation in five main areas:
- Maritime safety and security
- Counterterrorism and prevention of radicalization
- Combating trafficking and transnational organized crime
- Cybersecurity and safeguarding critical infrastructure
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
Defence Exercises:
- In November 2021, India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives held Exercise Dosti XV in the Maldives, marking their first joint military exercise in the Arabian Sea under the CSC framework.
Nobel Prize in Literature 2024

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Prize in Literature 2024 was awarded to South Korean author Han Kang “for her intense poetic prose that confronts historical traumas and exposes the fragility of human life.”
Key Details:
About South Korean author Han Kang
- Literary Style: Known for her physical empathy and metaphorical style; addresses extreme life stories.
- Career Beginnings:
- Started in 1993 with poetry in Literature and Society.
- Prose debut in 1995 with Love of Yeosu.
- Major Work:
- The Vegetarian (2007; English translation 2015).
- Explores violent consequences of protagonist Yeong-hye's refusal to conform to societal norms regarding food.
- Background:
- Born in 1970 in Gwangju, South Korea; later moved to Seoul.
- Comes from a literary family; father is a noted novelist.
- Engaged in art and music, influencing her writing.
- Significance: First South Korean writer to receive the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Previous Nobel Laureate
- 2023 Awardee: Jon Olav Fosse, Norwegian author.
- Contribution: Recognized for "innovative plays and prose which give voice to the unsayable."
Overview of the Nobel Prize
- Definition: Prestigious awards in six fields for those who have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind.
- Fields: Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace, and Economic Sciences.
- Peace Prize: Awarded for advancing international fellowship and promoting peace.
- Establishment: Founded by Alfred Nobel in his will dated 27 November 1895.
- Nobel's Background:
- Born on 21 October 1833 in Stockholm, Sweden.
- Noted for inventing dynamite; had interests in peace, poetry, and drama.
- Died in 1896; allocated his fortune for the prizes.
- First Award: Presented on 10 December 1901.
Prize Money
- Current award amount: $1.1 million per prize.
Note:
Rabindranath Tagore:
- Awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913 for his profound literary contributions.
- Notable works include Manasi, Gitanjali, and Chitra.
