Global Stocktake should account for failures of developed nations: BASIC nations at COP28 (The Hindu)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The BASIC grouping, comprising Brazil, South Africa, India and China, has pushed during annual climate talks here that the Global Stocktake should also account for the failures of the developed nations.
About Global Stocktake:
- The global stocktake serves as a mechanism for nations and stakeholders to collectively assess their progress in achieving the objectives outlined in the Paris Climate Change Agreement, highlighting areas of success and areas needing improvement.
- In essence, it is akin to taking inventory on a global scale.
- Essentially, the global stocktake involves a comprehensive examination of everything related to the world's status regarding climate action and support.
- It entails identifying gaps and collaboratively strategizing to steer a more effective course towards accelerating climate action.
- This evaluation occurs every five years, with the inaugural stocktake scheduled to conclude at COP28.
- Background: In 2015, during COP21 in Paris, it became obligatory for all countries to establish emissions reduction targets and adapt to climate change impacts, known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- The agreement mandated that countries evaluate their progress, starting in 2023 and subsequently every five years.
- Initial Assessment: The UN released a technical report on the first Global Stocktake in September 2023.
- According to this report, while the global community demonstrated some progress, it fell short of the necessary scale.
- The report emphasizes the need to expedite implementation, adopting an all-of-society approach to enhance ambition across all aspects, aligning with the goals of the Paris Agreement and addressing the climate crisis.
- The report acknowledges existing progress but underscores the urgency for more concerted efforts.
- Recognizing well-known gaps, the technical findings also spotlight opportunities and creative solutions, addressing both current challenges and those emerging.
- Additionally, the report notes that the average global temperature has risen by nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times.
INCOIS wave rider buoy washes ashore in Gopalpur (New Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A wave rider buoy, equipped belonging to the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), with GPS and various weather-related instruments, was found ashore at the Gopalpur Military Station in Ganjam district on Saturday.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi.
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- The ESSO operates as an executive arm of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for its policies and programmes.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
What is the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO)?
- Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO) is a virtual organisation set up by the Ministry of Earth Sciences GOI in 2007 and it is the executive arm of MoES.
- It has three major branches of earth sciences viz.,
- Ocean Science & Technology
- Atmospheric Science & Technology
- Geosciences and Technology.
- The overall vision of the ESSO is to excel in knowledge and technology enterprise for the earth system science realm towards the socio-economic benefit of the Indian sub-continent and in the Indian Ocean region.
- The ESSO contributes to the areas of Weather (General) and Weather advisories specific to agriculture, aviation, shipping, sports, etc. Monsoon, Disasters (cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, sea level rise), Living and non-living resources (fishery advisory, poly-metallic nodules, gas hydrates, freshwater etc), Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Climate Change, Underwater Technology.
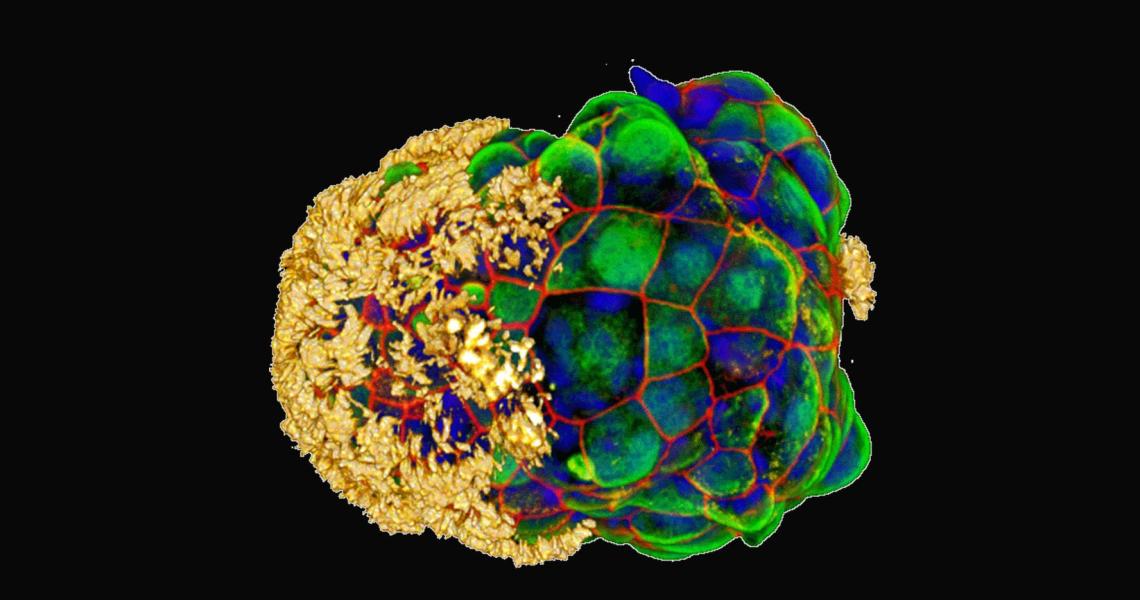
Scientists Create Tiny Robots Called 'Anthrobots' From Human Cells (India Times)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have created 'Anthrobots' , tiny living robots from human cells and the robots are able to move around in a lab dish and one day may be helpful in healing wounds or damaged tissue.
What is an Anthrobots?
- Anthrobots are self-assembling biological robots made from human tracheal cells, capable of movement and encouraging neuron growth.
- They can be created from adult human cells without genetic modifications, making them a potential patient-specific therapeutic tool.
- Anthrobots represent a significant advancement in regenerative medicine, potentially aiding in treating a variety of diseases and injuries.
- The multicellular robots, ranging in size from the width of a human hair to the point of a sharpened pencil, were made to self-assemble and shown to have a remarkable healing effect on other cells.
- The discovery is a starting point for the researchers’ vision to use patient-derived biobots as new therapeutic tools for regeneration, healing, and treatment of disease.
What are Tracheal cells?
- Tracheal cells come from the lining of the bronchi and trachea, forming the network of tubes that transport air to the lungs.
- These cells, a type of epithelial cell, are crucial for producing lubricating mucus to maintain the functionality of the airways.
- They are responsible for generating not only mucus but also various other compounds, all of which play a vital role in the process of respiration.
Is White Lung Syndrome caused by a new pathogen? Here is what you need to know (Indian Express)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
An outbreak of a respiratory illness in northern China and Ohio in the US — the White Lung Syndrome as people are calling it — has sparked speculation online of a new pandemic threat after COVID-19.
About White Lung Syndrome:
- “White lung syndrome” is a term used to describe a severe form of pneumonia characterized by the appearance of white patches on chest X-rays.
- While the term suggests a specific disease, it is actually used to describe a variety of conditions that cause similar symptoms.
- Symptoms: The specific symptoms of white lung syndrome can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Cough, feThere is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- ver, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, loss of appetite and wheezing
- In severe cases, white lung syndrome can lead to respiratory failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Causes: There are many different causes of white lung syndrome, including:
- Viral infections: These are the most common cause of white lung syndrome, including viruses like influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19.
- Bacterial infections: These are less common than viral infections, but can still cause white lung syndrome.
- Fungal infections: These are rare, but can occur in people with weakened immune systems.
- Inhalation of harmful substances: This can include inhaling dust, fumes, or chemicals.
- Autoimmune diseases: These are diseases in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues.
- Prevention: There is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- However, there are vaccines available for some of the viruses that can cause white lung syndrome, such as influenza and COVID-19.
- Treatment: The treatment for white lung syndrome depends on the underlying cause.
- In some cases, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- In more severe cases, oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
11 bodies recovered after the volcanic eruption in Indonesia, and 12 climbers are still missing (Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The bodies of 11 climbers were recovered on Monday a day after a furious eruption of the Mount Marapi volcano as Indonesian rescuers searched for 12 apparently still missing.
About Mount Marapi:
Don't confuse it with Mount Merapi, which is located on Java Island.
- ‘Mount Marapi’ located is a volcanic mountain located in West Sumatra of Indonesia.
- It also known as Marapi or Gunuang Marapi in Minangkabau.
- According to legend, the mountain is the site first settled by the Minangkabau people after their ship landed on the mountain when it was the size of an egg and surrounded by water.
- There are large numbers of upright burial stones in the region which are oriented in the direction of the mountain, indicating its cultural significance.
- A significant eruption occurred in 1979, and in April-May 2018, ashfalls to the southeast were recorded.
About Mount Merapi:
- Mount Merapi is a volcanic mountain on the island of Java in Indonesia and is the most active volcano in Indonesia (out of a total of 30 active volcanoes).
- Although Mount Merapi was discovered by humans in 1754, geologists have estimated that the volcanic mountain is over 400,000 years old.
- The last major eruption of Mount Merapi back in 2010. This eruption took the lives of 347 people, and a further 20,000 locals were forced to evacuate the area.
- The local name for Mount Merapi is Gunung Merapi which can be translated to Fire Mountain or Mountain of Fire.
- Mount Merapi is considered sacred by local people. They believe that a supernatural kingdom exists there.
- Mount Merapi has erupted countless times, which haven't been recorded in modern history.
- However, we do know that Merapi has erupted over 68 since 1548.
- Merapi has now been active for approximately 10,000 years.
