Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
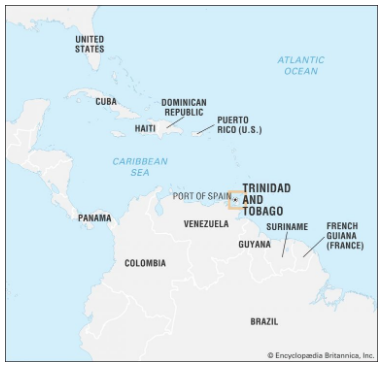
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
