‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
Assam-Meghalaya panels for boundary dispute to submit reports by December 31 (The Hindu)
- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
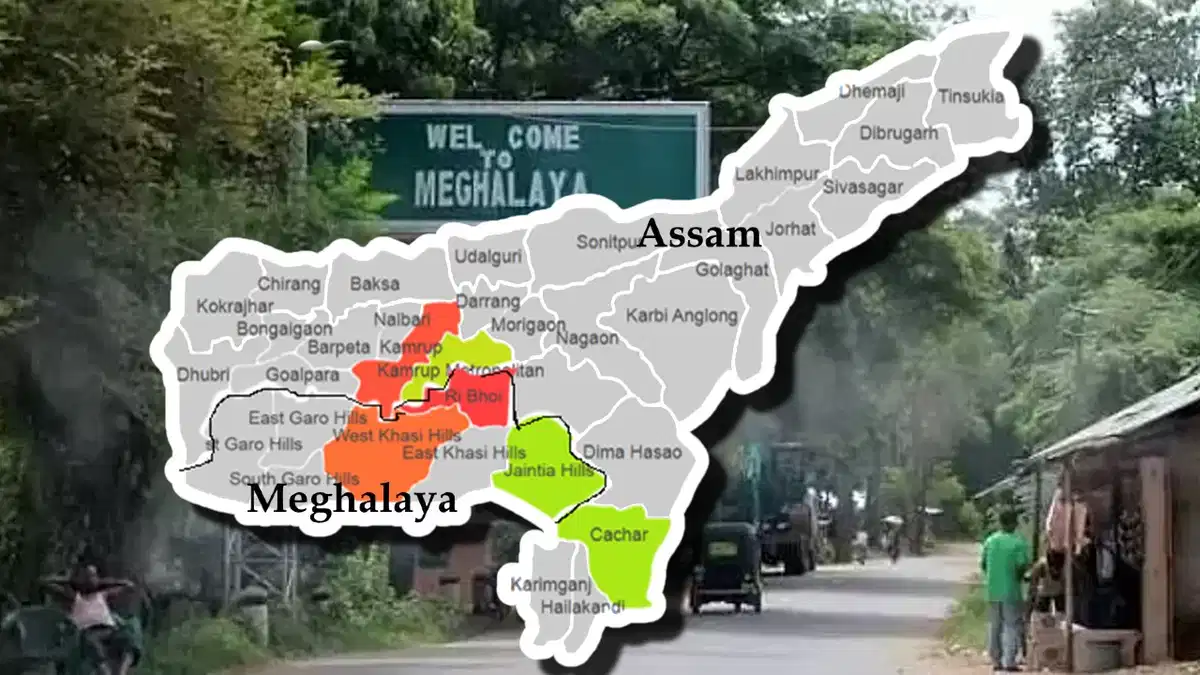
The regional committees on the boundary dispute between Assam and Meghalaya have been asked to submit their reports by December 31, a Meghalaya government official said on Friday, December 22.
What is the Assam-Meghalaya Border Dispute?
- The Assam and Meghalaya have a longstanding dispute in 12 stretches of their 884-km shared border.
- The areas include Upper Tarabari, Gazang Reserve Forest, Hahim, Langpih, Borduar, Boklapara, Nongwah, Matamur, Khanapara-Pilangkata, Deshdemoreah Block I and Block II, Khanduli, and Retacherra.
Historical Context:
- During British rule, undivided Assam encompassed present-day Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Mizoram.
- Meghalaya was delineated in 1972, following the Assam Reorganisation (Meghalaya) Act of 1969, but differing interpretations of the border emerged.
- In 2011, Meghalaya identified 12 disputed areas, covering approximately 2,700 sq km.
Key Point of Contention:
- A focal point of discord is Langpih in West Garo Hills, bordering Kamrup district in Assam.
- Post-Independence, Langpih transitioned from Kamrup district to Garo Hills and Meghalaya.
- Assam contends it's part of the Mikir Hills, while Meghalaya questions the inclusion of Blocks I and II of the Mikir Hills (now Karbi Anglong) in Assam.
Efforts to Resolve Dispute:
- In 1985, an official committee, led by former Chief Justice of India Y V Chandrachud, was formed but didn't yield a resolution.
- Both states identified six out of 12 disputed areas for resolution, resulting in a Memorandum of Understanding in March 2022.
- The second round of discussions for the remaining areas commenced in November 2022.
Potential Solutions:
- Utilizing satellite mapping for precise border demarcation.
- Leveraging constitutional provisions like Article 263 for the Inter-state Council to advise on disputes and coordinate policies.
- Reviving Zonal Councils to address common concerns among states in each zone, including border disputes and economic planning.
- Embracing the spirit of cooperative federalism to strengthen India's unity in diversity.
IIT Guwahati researchers devise mathematical model to help prevent riverbank erosion (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati has developed a new award-winning mathematical model to help prevent erosion of rivers like Brahmaputra.
What is BRAHMA-2D?
- BRAHMA-2D (Braided River Aid: Hydro-Morphological Analyzer) is a sophisticated mathematical model designed for assessing the flow dynamics of expansive braided rivers such as the Brahmaputra.
- Functioning as a quasi-3D river flow model, BRAHMA-2D offers insights into water velocity at various depths within the river and the circulation patterns around structures like spurs, crucial for preventing river bank erosion.
- Developed through collaboration between researchers at IIT Guwahati and the Brahmaputra Board under the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti, this innovative model plays a pivotal role in the design of sustainable hydraulic structures.
- Engineers can leverage BRAHMA-2D to create effective structures like spurs, river bends, and other protective measures to combat river bank erosion.
- The model's successful validation on the Brahmaputra River near Majuli Island in Assam, a region prone to river bank erosion, underscores its practical applicability.
- BRAHMA-2D integrates a two-dimensional water movement model with entropy theory, focusing on disorder or randomness.
- Notably, it identifies a unique dip phenomenon near spurs, where water flows underneath intensifies—a phenomenon absent at points away from these structures.
- Beyond erosion prevention, BRAHMA-2D extends its utility to environmental studies by assessing the habitat suitability of aquatic species, particularly endangered ones.
- This assessment is based on factors such as required depth and flow velocity, showcasing the model's versatility in addressing multifaceted challenges in river ecosystems.
About Brahmaputra River:
- Originating as Siang or Dihang from the Chemayungdung glacier in the Kailash range near Mansarovar Lake, the Brahmaputra enters India to the west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Dibang, Lohit, Siang, Burhi Dihing, Tista, and Dhansari contribute to its flow.
- This perennial river exhibits distinctive features influenced by its geography and prevailing climatic conditions.
- Experiencing biannual flooding, the first occurs from the melting Himalayan snow in summer, and the second is a consequence of monsoon flows.
- Climate change has amplified the frequency and intensity of these floods, posing a threat to populations and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- Known for its dynamism, the Brahmaputra undergoes frequent changes in course, driven by landslides and geological activities.
Three heritage projects in Punjab and Haryana bag UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards 2023 (Business Standard)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resilient urban revitalisation of Rambagh Gate and Ramparts in Punjab, and heritage conservation projects related to Haryana's Church of Epiphany and Delhi's Bikaner House won Unescoawards on Thursday.
About Rambagh Gate & Ramparts:
- A three-story architectural marvel, the Rambagh Gate underwent meticulous restoration employing traditional building techniques.
- Locally sourced materials, including Nanak Shahi bricks set in lime mortar, were integral to the restoration process.
About Pipal Haveli, Gurdaspur:
- Pipal Haveli in Gurdaspur stands as a testament to ecological and traditional building methods, incorporating locally sourced materials and embracing vernacular architectural language.
- Notably, it actively promotes women's empowerment through initiatives like the BaRi Collective, offering programs that enhance women's livelihoods through environmentally conscious craft practices.
What is the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- UNESCO aims to promote private sector engagement and foster collaborations between the public and private sectors to preserve the cultural heritage of the Asia-Pacific region for the benefit of present and future generations.
- Since the year 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation have been acknowledging the accomplishments of private sector entities and public-private initiatives in effectively conserving or restoring structures, places, and properties of significant heritage value in the region.
- Noteworthy, among the recognized sites, five are located in China, six in India, and one in Nepal.
- Highlights of Award-Winning Sites in India:
- Rambagh Gate in Amritsar: Received the prestigious "Award of Excellence," the highest recognition across all categories.
- Pipal Haveli in Punjab: Honored for its sustainable development as a heritage rural homestay.
- Karnikara Mandapam at Kunnamangalam Bhagawati Temple in Kerala: Earned the esteemed "Award of Distinction."
- Epiphany in Haryana, David Sassoon Library and Reading Room in Mumbai, and Bikaner House in New Delhi: Recognized with the "Award of Merit" for their outstanding contributions to cultural heritage conservation.
CISF to take over security of Parliament complex after Lok Sabha breach | What's the plan (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Home Ministry has approved the deployment of the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) in the Parliament complex, according to a government order.
News Summary:
- Following the security breach on December 13, the Union Home Ministry has given the green light for CISF deployment in the Parliament complex.
- Collaborating with Parliament Security Services, CISF will oversee access control for both the new and old Parliament buildings.
What are the Current Security Arrangements in Parliament?
- The Delhi Police currently handles access control, including frisking and baggage scanning.
- In response to the recent incident, eight Delhi Police security personnel responsible for these duties were suspended.
- In the event of armed intervention, the Parliament Duty Group (PDG), an armed unit of the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), is deployed.
- The overall responsibility for security lies with the Parliament Security Service under the Lok Sabha Speaker.
About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF):
- Established under the Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968, CISF is a key Central Armed Police Force (CAPF).
- Initially formed in 1969 with three battalions, it has evolved into a versatile organization boasting a current strength of 1,63,590 personnel.
- Operating under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Home Affairs, CISF's headquarters is situated in New Delhi.
Key Operations:
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Safeguarding 353 establishments nationwide, including Atomic Power Plants, Space Installations, Defence Production Units, Mines, Oil Fields, and Refineries.
- Fire Protection: Maintaining a dedicated Fire Wing catering to 104 establishments for fire safety services.
- VIP Security: Mandated to provide security to VIP protectees categorized as Z+, Z, Y, and X across the country.
- Airport Security: Entrusted with the specialized task of airport security since 2000, following the hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight IC-814 to Kandahar.
- Private Sector Security: Authorized by an amendment to the CISF Act, the force offers security services, on a payment basis, to vital private and joint venture industrial entities contributing to the nation's security and economy.
- Examples include Infosys campuses, Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, and the Reliance refinery.
- Overseas Deployment: Contributing contingents to the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH).
- CISF stands out as the only Central Armed Police Force with a daily public interface, playing a crucial role in securing airports, the Delhi Metro, and iconic monuments.
