Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ONDC Startup Mahotsav was held in New Delhi recently in collaboration between the Startup India initiative and the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC).
About the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is a network based on open protocol and will enable local commerce across segments, such as mobility, grocery, food order and delivery, hotel booking and travel, among others, to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled application.
- The platform aims to create new opportunities, curb digital monopolies support micro, small and medium enterprises and small traders and help them get on online platforms.
- It is an initiative of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Features of ONDC:
- ONDC, a UPI of e-commerce, seeks to democratise digital or electronic commerce, moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network.
- Through ONDC, merchants will be able to save their data to build credit history and reach consumers.
- The proposed government-backed platform aims to create a level playing field for e-commerce behemoths such as Amazon, Flipkart, and offline traders who have been crying foul at the unfair trade practices of these e-tailers.
- The platform will also be compliant with the Information Technology Act, 2000 and designed for compliance with the emerging Personal Data Protection Bill.
- In this system, ONDC plans to enable sellers and buyers to be digitally visible and transact through an open network, regardless of what platform or application they use.
- It will also empower merchants and consumers by breaking silos to form a single network to drive innovation and scale, transforming all businesses from retail goods, food to mobility.
- The new framework aims at promoting open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols independent of any specific platform.
- It is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiencies in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- According to the government's official statement, ONDC shall take all measures to ensure confidentiality and privacy of data in the network.
- ONDC shall not mandate the sharing of any transaction-level data by participants with ONDC.
- It will work with its participants to publish anonymised aggregate metrics on network performance without compromising on confidentiality and privacy.
- Presently, ONDC is in its pilot stage and the government has set up a nine-member advisory council, including Nandan Nilekani from Infosys and National Health Authority CEO R S Sharma, on measures needed to design and accelerate the adoption of ONDC.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
World Telecommunication and Information Society Day

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To commemorate the World Telecommunication and Information Society Day, C-DOT, the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) celebrates and announces special Initiatives “NIDHI” & “STAR Program” for the development of indigenous telecom solutions & technologies.
What is World Telecommunication and Information Society Day?
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is celebrated every year in May to honour the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) on May 17, 1969.
- The day can be traced back to commemoration of the two significant events in the history of global communication.
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) commemorates two significant events in the history of global communication.
- Firstly, it marks the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1865, when the first International Telegraph Convention was signed.
- Followed by, in November 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) called upon the United Nations General Assembly to also declare May 17th as World Information Society Day.
- And then in 2006, the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference in Antalya, Turkey, agreed to combine the two events as World Telecommunication and Information Society Day.
- This year’s World Telecommunications and Information Society Day 2024 focuses on the theme, “Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development,” underlying how digital innovation may help link everyone and create sustainable prosperity for all.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Established in 1865, it is the oldest among the UN’s 15 specialized agencies.
- ITU is responsible for allocating global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, developing technical standards to ensure network interconnectivity, and improving ICT access for underserved communities.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, ITU is part of the UN Development Group and operates 12 regional offices worldwide.
- It functions as an intergovernmental public-private partnership with 193 member states and around 800 sector members. India, a member since 1952, was re-elected to the ITU Council for the 2019-2022 term.
Mitogenome
- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found South African leopards originated from two unique clades in southern and central Africa approximately 0.8 million years ago.
What is a Mitogenome?
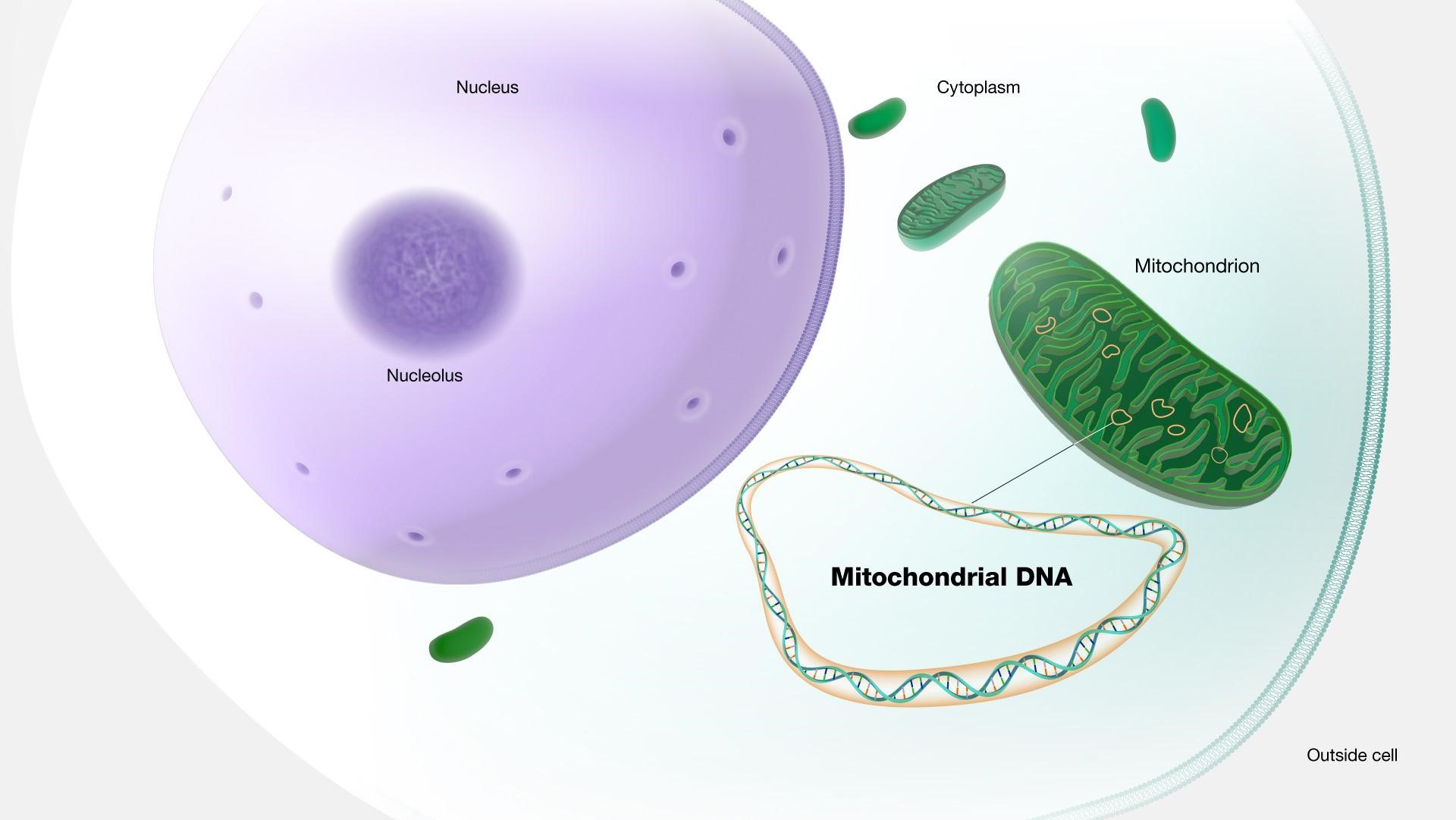
- DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and also in the mitochondrial genome, or mitogenome.
- Mitogenomes are DNA molecules that float around outside the nucleus of a cell.
- They store their own set of genetic information and are maternally inherited, which means they are only passed on from mother to offspring.
- Mitogenomes are a “genomic by-catch” when sequencing the whole genome.
- They are so abundant in cells that it is very easy to extract them.
- Studying mitogenomes is a reliable way to track the ancestry of a species.
- This is because genes mutate (change) at a regular rate over time.
- The changes in the mitogenome provide a picture of any species' evolution over hundreds of thousands of years.
What is DNA?
- DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material that codes the information for all the different processes that make an organism living like growth, replication, metabolism, etc.
- DNA is present in each cell (except for some viral species, RBCs, sieve cells, etc.) and is passed down from parents to their offspring. DNA is comprised of units called nucleotides.
- DNA is self-replicating, a long stretch of nucleotides.
- DNA is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four major macromolecules that make up the living system.
- In eukaryotic cells, it is found in the nucleus of the cell whereas in prokaryotes it is found free-floating in the cell cytoplasm.
- Other than the nucleus DNA is also found in mitochondria, chloroplast, and in smaller forms called plasmid in certain bacterial species.
Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The DCGI recently issued a directive to all medical device license holders and manufacturers, instructing them to report any adverse events associated with life-saving medical equipment on the government's Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI) platform.
What is the Materiovigilance Programme of India?
- The Materiovigilance Programme of India was launched on July 6, 2015, that monitors and evaluates the safety of medical devices across the country.
- It aims to systematically collect and scientifically analyze data on adverse events related to medical devices, offering guidance on their safe usage and supporting regulatory decision-making processes.
Objectives and Importance:
- The primary goal of the Materiovigilance Programme is to enhance patient safety in India by carefully recording, assessing, and determining the root causes of adverse events or risks associated with medical devices, including in-vitro diagnostics.
- By coordinating the reporting and analysis of such events, the programme seeks to inform regulatory bodies and healthcare professionals, promoting the appropriate use of medical devices and ultimately improving patient safety.
Governance and Regulation:
- Since 2018, the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has served as the National Coordination Centre (NCC) for the programme.
- The Materiovigilance Programme is regulated by the Central Drugs Standards Control Organization (CDSCO), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, and Medical Device Rule, 2017, currently govern all medical devices in India.
- Given that the country is 80% dependent on imports for medical devices, the programme's role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these essential healthcare tools is crucial.
About Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI):
- The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) leads the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), ensuring the quality of drug supply nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
Functions:
- Approving new drugs and overseeing clinical trials.
- Establishing standards for drug manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution in India.
- Granting licenses for specific drug categories such as blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- Ensuring uniform implementation of the Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940, and its associated rules to safeguard patient safety, rights, and well-being.
