Indian Military Heritage Festival 2024

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan inaugurated the 2nd edition of the Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) on November 8, 2024, in New Delhi.
- The two-day festival engages global and Indian experts, corporations, academicians, and non-profits focusing on India’s national security, foreign policy, military history, and military heritage.
Launch of Project Shaurya Gatha:
- Project ‘Shaurya Gatha’ was launched to conserve and promote India’s military heritage.
- The initiative, spearheaded by the Department of Military Affairs and USI of India, focuses on education and tourism to highlight India’s military history and valor.
- Publications Released:
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- "Because of this: A History of the Indo-Pak Air War December 1971" by Air Marshal Vikram Singh (Retd).
- "Valour and Honour", a joint publication by the Indian Army and USI of India.
- "War-wounded, Disabled Soldiers, and Cadets", a joint publication by USI and the War Wounded Federation.
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- Festival's Significance:
- The festival addresses the gap in public awareness regarding India’s military heritage and security concerns.
- It aims to enhance understanding of India’s military traditions, security issues, and the country’s efforts toward self-reliance in military capabilities under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Zhurong Rover

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
QS World University Rankings
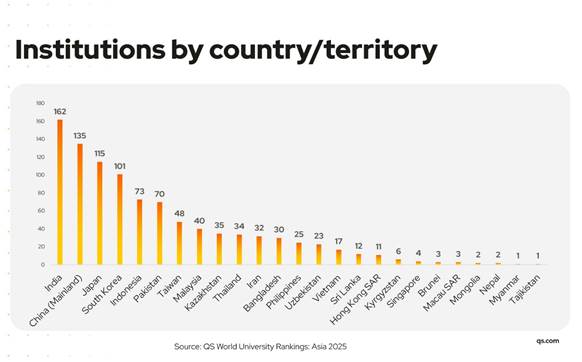
- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
The QS World University Rankings: Asia 2025 spotlights the top institutions in Eastern, Southern, South-Eastern, and Central Asia, emphasizing academic excellence, research, innovation, and internationalization.
India's Performance:
India has shown a remarkable upward trajectory, featuring:
- Two institutions in the Top 50:
- IIT Delhi ranked 44th (up from 46th), with a 99% employer reputation score.
- IIT Bombay ranked 48th, excelling with a 99.5% employer reputation score and 96.6% academic reputation score.
- Top 100 Institutions:
- IIT Madras (56th), IIT Kharagpur (60th), Indian Institute of Science (62nd), IIT Kanpur (67th), and University of Delhi (81st).
- Top 150 Institutions:
- IIT Guwahati, IIT Roorkee, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Chandigarh University (120th), UPES (148th), and VIT (150th).
Key Indicators for India:
- International Research Network and Citations per Paper contribute to India's growing global academic reputation.
- Papers per Faculty and Staff with PhD are India’s strongest indicators, reflecting robust research output and high teaching standards.
- Anna University achieved a perfect score of 100 in the Papers Per Faculty indicator, emphasizing high research output.
- North Eastern Hill University and University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore received a perfect score of 100 in the Faculty-Student Indicator.
Growth of Indian Institutions:
- India now has 46 institutions in the 2025 rankings, up from just 11 in 2015, marking a 318% increase over the past decade.
- India dominates Southern Asia with seven institutions in the top 10, showcasing the country's strengthening educational landscape.
India's Growing Global Influence:
- India's achievements underscore its commitment to academic excellence, competitiveness, and resilience in global higher education.
- Institutions like IIT Delhi and IIT Bombay highlight India’s ability to balance research productivity with high-quality teaching, enhancing its reputation as a global education hub.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
