STARFIRE Algorithm (PIB)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers at Raman Research Institute (RRI) have recently successfully created an algorithm named STARFIRE.
Facts About STARFIRE Algorithm:
- The STARFIRE Algorithm, also referred to as the Simulation of TerrestriAl Radio Frequency Interference in oRbits around Earth (STARFIRE) algorithm, is designed for its specific application in modeling and analyzing terrestrial radio frequency interference within Earth's orbits.
- The model possesses several advantages, including its capability to estimate Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) emitted by various sources such as FM radio stations, Wi-Fi networks, mobile towers, radar, satellites, and communication devices.
This estimation aids in designing and fine-tuning antennas for optimal performance.
- The algorithm can effectively estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in space, providing valuable insights for enhancing data quality from future space-based Astronomy missions.
- By facilitating the design of instruments capable of operating optimally in the presence of RFI, the algorithm significantly enriches the data obtained from future space missions.
- Another noteworthy advantage of the STARFIRE Algorithm is its usefulness in orbit selection for upcoming missions, contributing to better planning and execution.
- To develop this model, scientists utilized data from FM transmitter stations in six countries worldwide, including Canada (8,443 stations), USA (28,072 stations), Japan (Tokyo - 21 stations), Australia (2,664 stations), Germany (2,500 stations), and South Africa (1,731 stations), making the model comprehensive and robust.
Biological Diversity Amendment Bill (The Hindu)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021, aimed at modifying the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
About Biological Diversity Act, 2002:
The act was enacted in 2002, it aims at the conservation of biological resources, managing its sustainable use and enabling fair and equitable sharing benefits arising out of the use and knowledge of biological resources with the local communities.
Regulatory Structure: The act envisaged a three-tier structure to regulate the access to biological resources:
- The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at the national level.
- State Biodiversity Boards(SBB) at the state level.
- Biodiversity Management Committees at the local body level.
- Under the Biological Diversity Act of 2002, provisions are made to share benefits with biodiversity conservers, holders, and creators of associated knowledge. These benefits encompass monetary compensation, sharing of Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs), and technology transfer.
Amendments Made in Biodiversity Bill 2021:
- Regarding Access to biological resources and associated knowledge, It amends the classification of entities, list of activities requiring intimation, and adds exemptions.
- Approval for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) will be required before the grant of IPR instead of before the application itself.
- SBB will determine benefit sharing while granting approvals to domestic entities as per the regulations by NBA.
- The Bill decriminalises the offences and makes offences punishable with a penalty between one lakh rupees and Rs 50 lakh.
Significance of the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021:
The Bill seeks to amend the 2002 Act to:
- Simplify compliance requirements for domestic companies.
- Encourage the Indian system of medicine and cultivation of wild medicinal plants,
- Facilitate fast-tracking of processes for research, patent application, and transfer of research results,
- Decriminalise offences, and
- Encourage foreign investment in the sector.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam (The Hindu)
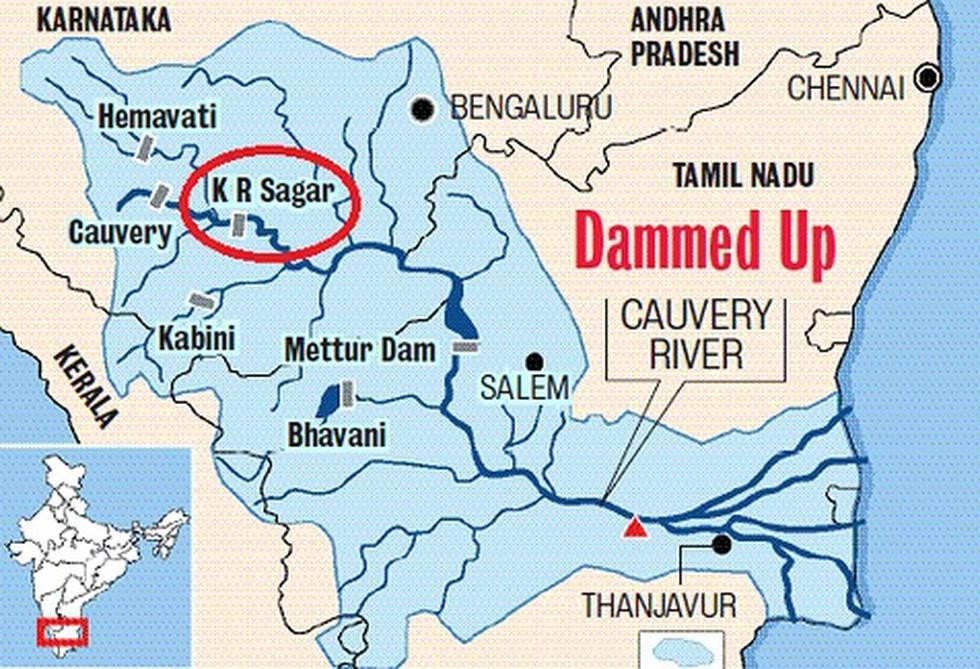
- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Due to heavy rainfall in the river's catchment area, the water level in the Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) across the Cauvery recently surpassed the 100-ft mark, although its capacity reaches 124.80 feet.
About Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- Situated in Karnataka's Mandya district, it lies beneath the merging point of the Kaveri river with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha.
- It is a type of gravity dam.
- The dam is named for the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV.
- The dam was designed by Sir M. Visvesvaraya, a famous Indian engineer.
- The reservoir is also the main source of drinking water for all of Mysore city and almost the whole of Bangalore.
- The water released from this dam is further used as an important source of water in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- An ornamental garden named “Brindavan Gardens” is attached to the dam.
Kaveri River:
- Kaveri or Cauvery is a sacred river of southern India. It is known as the Ganga of South India.
- It rises on Brahmagiri Hill of the Western Ghats in southwestern Karnataka state.
Drainage Basin:
- It flows in a southeasterly direction through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, and descends the Eastern Ghats in a series of great falls.
- Before emptying into the Bay of Bengal south of Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu, the river breaks into a large number of distributaries forming a wide delta called the “garden of southern India.”
Tributaries of Kaveri:
- Arkavathi, Hemavathi, Lakshmana Theertha, Shimsa, Kabini and Harangi.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
