National Digital Nagrik Forum (Indian Express)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The forum by the Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and help build the capacities of citizens to engage with innovation via expert sessions and instructional materials.
About the National Digital Nagrik Forum:
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum is an online platform with the primary goal of advancing the rights of traders, consumers, and various sections of society, while also influencing policy to foster the growth of the digital trade economy.
- Through expert sessions and instructional materials, the forum aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and empower citizens to engage with innovation effectively.
- The main objective is to shape policy discourse around the digital economy trade in India, aligning with the Government of India's vision of establishing a trillion-dollar digital economy.
- Simultaneously, it seeks to maintain an open, safe, trusted, and accountable Internet ecosystem.
- The forum will conduct awareness camps, digital and physical dialogues, and training sessions.
- It will also engage in targeted outreach to stakeholders from the government, private sector, and civil society.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum will concentrate on five core themes:
- The first pillar focuses on consumer protection and online safety, with a central emphasis on efficient grievance redressal mechanisms.
- The second pillar addresses the challenges of digital cartelization, advocating for a level-playing field to discourage discriminatory and anti-competitive practices in the online world.
- The third pillar explores the potential of Indian digital technologies to transform retail and industrial trade, while also contributing to employment growth and expanding investment opportunities.
- The fourth pillar advocates for a first principles-based taxation policy that fosters certainty and productivity, especially for sectors with high growth potential. It simultaneously works to prevent illegal activities like tax evasion and money laundering.
- The fifth pillar conducts research on emerging technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence to assess their impact on retail trade and ensure the protection of consumers' interests.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum aims to make significant contributions towards shaping a vibrant digital economy in India, fostering fair trade practices, and safeguarding the interests of both consumers and traders.
Room-temperature Superconductor (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Korean researchers claim to have developed a superconductor that can operate at room temperature and ambient pressure.
What have the researchers developed?
- The researchers assert that they have created a superconductor named LK-99, which operates at room temperature and under ambient pressure.
- LK-99 is a combination of powdered compounds containing lead, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus.
- Upon heating at extremely high temperatures, it transforms into a dark grey solid.
- The potential significance of this discovery is immense, provided other laboratories can replicate these results.
- Nevertheless, some researchers remain skeptical as this study has not undergone peer review, and the results must be independently reproduced by other scientific groups.
What is a Superconductor?
- A superconductor is a material that exhibits superconductivity, a unique state of matter characterized by the absence of electrical resistance and the exclusion of magnetic fields.
- In a superconductor, an electric current can flow indefinitely without any hindrance.
- Superconductors have significant practical applications in our everyday lives.
- In 1933, Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered that superconductors act as perfect diamagnets, repelling magnetic fields, a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect.
- This property makes them ideal for applications like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- However, achieving superconductivity typically requires extremely low temperatures.
- Currently, researchers are actively exploring and developing superconductors that can operate at room temperature, a groundbreaking advancement that would revolutionize various technologies and industries.
How will the room-temperature superconductors help?
- The use of room-temperature superconductors can offer significant benefits in various applications.
- Typically, the critical temperature of conventional superconductors is below 10 Kelvin (-263 degrees Celsius), whereas room temperature is around 20-22°C.
- By having superconductors that function at room temperature, the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, magnets for maglev trains, energy-storage devices, and fusion reactors can be reduced significantly.
- This is achieved through electricity and cost savings on coolants, as the need for extreme cooling methods is eliminated.
- The widespread adoption of room-temperature superconductors holds the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA) (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
During the Man ki Baat program, the Prime Minister announced that India achieved a remarkable feat by destroying 10 lakh kilograms of drugs worth ?12,000 crore in the previous year.
What is Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA)?
- Launched on: The NMBA was launched on 15th August 2020.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment oversees the implementation of NMBA.
- Aim: The primary objective of NMBA is to raise awareness about the harmful consequences of substance abuse, with a special focus on youth, women, and children.
- It aims to reach out to higher education institutes, university campuses, schools, and the broader community, encouraging community involvement and ownership of the initiative.
- Implementation: NMBA is implemented in 372 vulnerable districts, identified based on the findings of the first Comprehensive National Survey and inputs from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Significance:
- NMBA targets and engages various stakeholders directly or indirectly affected by substance abuse, as well as those vulnerable to it.
- The major beneficiaries of NMBA include youth, women, children, educational institutions, civil society, and the community at large.
- This approach emphasizes community involvement rather than just organizational participation in addressing the issue of substance abuse.
Cell-free DNA (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Over the past two decades, as genome sequencing technologies have become increasingly accessible, scientists have made significant strides in understanding the applications of Cell-free DNA.
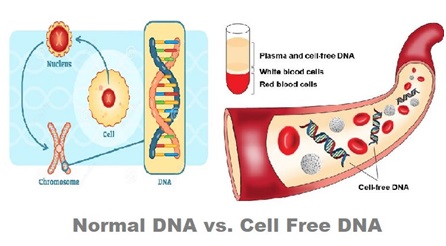
Regarding Cell-free DNA:
- In the human body, a significant portion of the DNA in the genome is safely enclosed within cells, safeguarded by specific proteins to prevent degradation.
- However, in various circumstances, certain DNA fragments are liberated from their confines and can be found outside the cells, circulating in body fluids.
- These minute fragments of nucleic acids are commonly referred to as cell-free DNA (cfDNA).
How Cell-free DNA is generated/released?
- The generation and release of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can occur through various mechanisms.
- One such process is when a cell undergoes cell death, leading to the degradation of nucleic acids and subsequent release of cfDNA.
- The degradation of cfDNA is influenced by a diverse set of processes, resulting in variations in the amount, size, and origin of cfDNA.
- Furthermore, this release of cfDNA can be associated with different biological processes, including those essential for normal development, the progression of certain cancers, and various other diseases.
- The generation and release of cfDNA can be triggered by a range of situations and processes, making it a versatile biomarker with potential implications in various health conditions.
Applications of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA):
- One of the most prevalent uses of cfDNA is in non-invasive prenatal testing, where it aids in screening fetuses for specific chromosomal abnormalities.
- Also, cfDNA serves as a valuable tool for comprehending human diseases and leveraging this knowledge to enhance diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis.
- cfDNA plays a crucial role in understanding the rejection of transplanted organs by the body.
- It shows promise as a potential biomarker for various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, neuronal tumors, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A maritime patrol aircraft from the Indian Navy and a transport aircraft from the Indian Air Force (IAF) made a visit to Australia's Cocos (Keeling) Islands (CKI) recently.
About Cocos (Keeling) Islands:
- Location:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are situated in the eastern Indian Ocean, approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) northwest of the Australian city of Perth.
- Geography:
- Comprising coral atolls and islands, the archipelago includes North Keeling Island and the South Keeling Islands.
- Administrative Headquarters:
- The territory's administrative headquarters are located on West Island, situated in the southern atoll.
- Climate:
- The islands experience a warm and humid climate.
- Vegetation:
- The predominant vegetation consists of coconut palms, which were previously cultivated for copra on plantations.
- On North Keeling and Horsburgh islands, coarse grass serves as the primary ground cover.
- National Park:
- The northern atoll is home to Australia's most remote Commonwealth National Park, known as the Pulu Keeling National Park.
- Inhabitants:
- The population of the islands mainly comprises descendants of the original plantation workers, predominantly of Malay origin.
- Administration:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are governed by an administrator appointed by the Australian governor-general. The islands became an Australian territory under the Cocos (Keeling) Islands Act 1955.
