Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
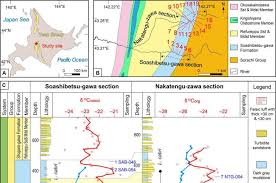
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
