UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Kingdom said it would cede sovereignty of the strategically important Chagos Islands to Mauritius, calling it a “historic political agreement”. The UK has long controlled Chagos and the Diego Garcia military base located there, jointly operating it with the United States.
Background of the Chagos Archipelago
Historical Context
- The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located about 500 km south of the Maldives.
- Initially uninhabited, the islands were populated in the late 18th century through the importation of slave labor.
- The islands were ceded to Britain from France in 1814, and in 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which includes Chagos.
Controversy Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius, a former British colony, claims that the detachment of Chagos from its territory during its independence in 1968 was illegal.
- The UK compensated Mauritius with a grant but retained control, establishing a military base on Diego Garcia.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
Military Significance
- Diego Garcia has been a crucial U.S. military base since its operational status began in 1986.
- It played a key role in U.S. military operations during conflicts in the Gulf, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The base enables rapid response to crises and supports regional security, especially in light of U.S. interests in monitoring key trade routes like the Malacca Strait.
Geopolitical Implications
- The presence of the U.S. military in the Indian Ocean is vital for countering security threats, particularly regarding China's growing influence.
Recent Developments: The UK-Mauritius Agreement
Key Features of the Treaty
- On October 3, 2023, the UK agreed to cede sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, marking a significant political shift.
- The treaty allows Mauritius to resettle Chagossians (excluding Diego Garcia) and establishes a trust fund for their benefit.
- Despite this, the UK retains control over Diego Garcia for an initial period of 99 years.
Implications of the Agreement
- The resolution of the sovereignty issue may strengthen Western commitments to a stable and free Indo-Pacific region.
- If unresolved, tensions could push Mauritius toward seeking alliances with alternative powers like China.
India’s Position and Interests
Support for Mauritius
- India has historically supported Mauritius in its claims over Chagos, reflecting its stance against colonial legacies.
- In 2019, India voted in favor of Mauritius at the UN General Assembly regarding the Chagos dispute.
Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Indian Ocean, India has been strengthening its ties with Mauritius.
- Recent initiatives include the inauguration of an India-built airstrip and jetty in Agaléga, enhancing connectivity and support for Mauritius.
Conclusion
The UK-Mauritius treaty over the Chagos Archipelago marks a significant turning point in colonial legacies and geopolitical alliances in the Indian Ocean. For India, supporting Mauritius aligns with its broader strategic interests and enhances its influence in a region marked by competing global powers. As the dynamics evolve, India's role in fostering regional stability and partnerships will be crucial.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Marburg Virus
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
- Definition:
- Marburg virus is one of the deadliest pathogens known to infect humans, causing severe hemorrhagic fever.
- Current Situation in Rwanda:
- Rwanda reported its first Marburg case late last month.
- At least 46 individuals have been infected, with 12 reported deaths.
- Approximately 80% of infections are among medical workers.
- The outbreak poses a significant threat to Rwanda’s fragile healthcare system, which has only 1,500 doctors for over 13 million people.
Characteristics of Marburg Virus
- Deadliness:
- Marburg virus disease (MVD) has case fatality rates ranging from 24% to 88%, depending on the strain and case management.
- The first outbreak occurred in Marburg, Germany, in 1967, with subsequent outbreaks primarily in Africa.
- Family:
- Marburg belongs to the filovirus family, which includes Ebola.
- Both viruses are clinically similar and can cause high-fatality outbreaks.
Transmission
- Initial Infection:
- Human infections initially occurred through prolonged exposure to mines or caves inhabited by Rousettus bats (notably the Egyptian fruit bat).
- Human-to-Human Transmission:
- MVD spreads directly through contact with blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
- Indirect transmission can occur via contaminated surfaces and materials (bedding, clothing).
- Risk for Medical Workers:
- Medical workers treating MVD cases are frequently infected, especially when infection control measures are inadequate.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)
- Incubation Period: Symptoms can appear 2 to 21 days after infection.
- Initial Symptoms: High fever, Severe headache, Muscle ache, Watery diarrhea, Abdominal pain and cramping, Vomiting
- Hemorrhagic Symptoms:
- Many patients develop bleeding from various sites, including the digestive system (fresh blood in feces and vomit), nose, gums, and vagina.
- Fatalities often occur due to severe blood loss and shock, typically 8 to 9 days after symptom onset.
Prevention and Treatment
- Current Status:
- No approved vaccines or specific treatments exist for MVD.
- Supportive Care:
- Rehydration (oral or intravenous fluids) and symptom management improve survival rates.
- Experimental Treatments:
- Rwanda is seeking experimental vaccines and treatments to address the outbreak.
- The US-based Sabin Vaccine Institute provided 700 doses of an experimental Marburg vaccine for healthcare professionals on the frontlines.
Genome Editing and Hereditary Cancers
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Agency for Research on Cancer’s estimates of the burden of 36 cancers in 185 countries suggest one in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer.
- Impact of CRISPR on Cancer Research:
- CRISPR screens have revolutionized the study of BRCA genes through high-throughput functional genetic analysis.
- Researchers use CRISPR-Cas9 to create specific mutations in BRCA genes, studying their effects on DNA repair and cancer development.
- Cancer Statistics:
- One in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer (International Agency for Research on Cancer).
- In 2022, there were approximately 20 million new cancer cases and 9.74 million cancer-related deaths; projections suggest these could rise to 32 million new cases and 16 million deaths by 2045, with Asia potentially accounting for half of the cases.
- Genetic Mutations and Inheritance:
- All cancers stem from genetic mutations; about 10% of cancer cases may involve inherited mutations.
- Specific inherited mutation prevalence:
- 20% in ovarian cancer patients.
- 10% in breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers.
- 6% in cervical cancer.
- BRCA Genes Overview:
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, discovered in 1994 and 1995, are crucial for understanding hereditary cancer syndromes.
- Mutations in BRCA genes significantly increase the risk of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers.
- BRCA mutations are estimated to occur in 1 in 400 individuals, with higher prevalence (1 in 40) among Ashkenazi Jews due to genetic bottlenecks and founder effects.
- Importance of Genetic Testing:
- Testing for BRCA mutations helps identify individuals at higher risk, enabling personalized prevention strategies such as increased surveillance or preventive surgery.
- The American Society of Clinical Oncology recommends testing for 15 genes related to breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Targeted Therapies:
- PARP inhibitors represent a new class of chemotherapy drugs effective for cancers with BRCA mutations.
- Clinical trials show promising results, especially when combined with platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Advancements in Understanding Cancer Genes:
- CRISPR technology has improved our understanding of cancer-related genes, enabling researchers to study the effects of specific mutations.
- Studies have identified how different mutations influence responses to therapies like PARP inhibitors.
- Recent Research Findings:
- Research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute identified over 3,000 genetic changes in the RAD51C gene that could significantly increase breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Variants disrupting RAD51C function can increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and aggressive breast cancer risk four-fold.
- Risk Spectrum:
- Genetic risk is a spectrum based on how mutations affect protein function.
- Large-scale variant analysis is vital for personalized medicine and cancer prevention.
- Role of Population Studies:
- Population prevalence studies help identify hereditary cancer risks and inform genetic screening for at-risk individuals.
- Early cancer detection allows for better healthcare decisions and potential preventive therapies.
- Goals for Cancer Management:
- The ultimate aim is to reduce cancer morbidity and mortality, leading to healthier lives for individuals and families.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
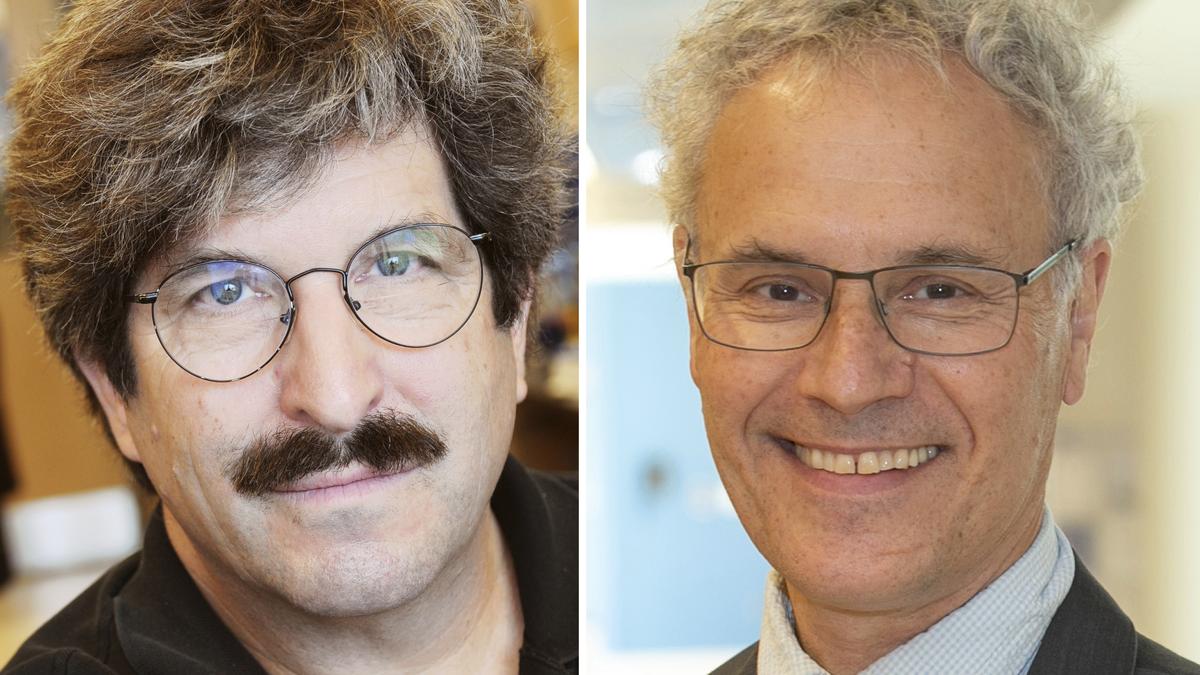
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
