Rapid Chess Championship

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In a monumental achievement, Koneru Humpy from Vijayawada, India, claimed the 2024 FIDE Women’s World Rapid Chess Championship in New York. This victory marks her second World Rapid Chess title, five years after her first win in 2019 in Georgia, making her the first Indian and only the second player after China’s Ju Wenjun to win the title multiple times.
Key Highlights of Humpy’s Victory:
- Final Score: Humpy finished with an impressive 8.5 points from 11 rounds, securing the top spot by defeating Irene Sukandar of Indonesia in the final round.
- Strong Finish: Humpy surged ahead of the other joint leaders to clinch the title, with D. Harika, another Indian chess star, securing 5th place with 8 points.
World Rapid Chess Championship
- The World Rapid Chess Championship is a chess tournament that determines the world's top rapid chess player. The tournament is held annually by FIDE, the International Chess Federation.
- How it works
- The tournament uses a Swiss system, where players are paired with opponents of similar scores in each round.
- Players are not eliminated after losses.
- The player with the highest score at the end of the tournament wins.
- Time controls
- Players are given a set amount of time per move, plus an increment for each move.
- In the World Rapid Championship, players have 15 minutes per move, plus a 10-second increment for each move.
A Historic Year for Indian Chess:
- 2024 has been a remarkable year for Indian chess, with D. Gukesh becoming the youngest-ever World Chess Champion after his victory over Ding Liren (China) at the World Chess Championship in Singapore.
- India also made history by winning both the open and women’s sections at the 2024 Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
H-1B Visa
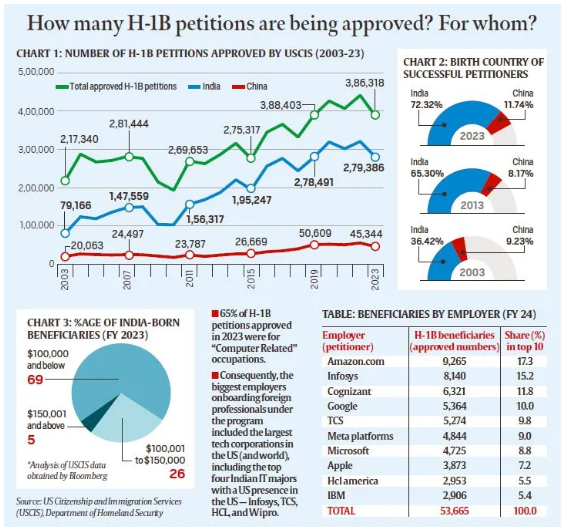
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
Business Ready (B-READY) Report 2024

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The B-READY report, launched by the World Bank in 2024, replaces the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index.
- Focus: It evaluates the global business environment to foster inclusive private sector growth, assessing 10 core topics covering a firm's lifecycle, such as business entry, taxation, labor, and international trade.
India’s Potential Challenges
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, making it slower compared to benchmarks like Singapore, which achieves one-day registration at minimal cost.
- Labor Regulations: While India has introduced four labor codes, the implementation remains slow and inconsistent, affecting labor flexibility and compliance.
- International Trade: India struggles with customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs, unlike countries like Germany and Singapore, which promote trade efficiently.
- Business Location: Regulatory delays and inconsistent approvals hinder the establishment of business facilities, affecting investment decisions.
- Public Services Gap: While regulations may be strong, there is often a gap in the provision of public services that support their effective implementation, leading to inefficiencies.
Key Strengths for India
- India is expected to score well in the areas of Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- The country shows promise in promoting digital adoption and aligning with global environmental sustainability practices, though gender-sensitive regulations need more emphasis.
Significance
- The B-READY report serves as an essential benchmark for assessing India's business environment, offering insights into regulatory reforms and operational efficiency.
- Key policy implications for India include the need to:
- Streamline business operations by digitizing registration and regulatory approval processes.
- Improve logistics and trade efficiency by reducing customs delays.
- Address labor market inefficiencies through better implementation of labor codes.
- Invest in public services and promote digital transformation for better compliance and operational ease.
- Focus on sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring gender-sensitive policies and fostering green business practices.
Global Findings from the B-READY Report
- Economies with strong regulatory frameworks and digital tools (e.g., Rwanda, Georgia) show that even countries with varying income levels can achieve high scores.
- High-income countries like Estonia and Singapore still have room for improvement, especially in areas like taxation and dispute resolution.
Comparison of B-READY with Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Scope: B-READY is broader, covering a firm’s lifecycle and social benefits, while EoDB focused mainly on regulatory burdens.
- Indicators: B-READY uses 1,200 indicators from expert consultations and firm-level surveys, offering more comprehensive insights compared to the EoDB's limited metrics.
- Focus on Public Services: Unlike EoDB, which provided limited attention to public services, B-READY explicitly evaluates public service efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Policy Recommendations
- Streamline Business Operations: Inspired by countries like Singapore, India should simplify business registration and reduce delays in customs and regulatory approvals.
- Strengthen Public Services: Focus on improving tax portals, utility access, and dispute resolution systems through digital tools.
- Promote Sustainability: Encourage environmentally sustainable business practices and adopt gender-sensitive regulations to ensure inclusive growth.
- Peer Learning and Global Collaboration: Encourage India to learn from best practices in countries like Singapore and Estonia for effective reforms.
- Tailored Reforms: India must design policies addressing unique local challenges while adhering to global standards.
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
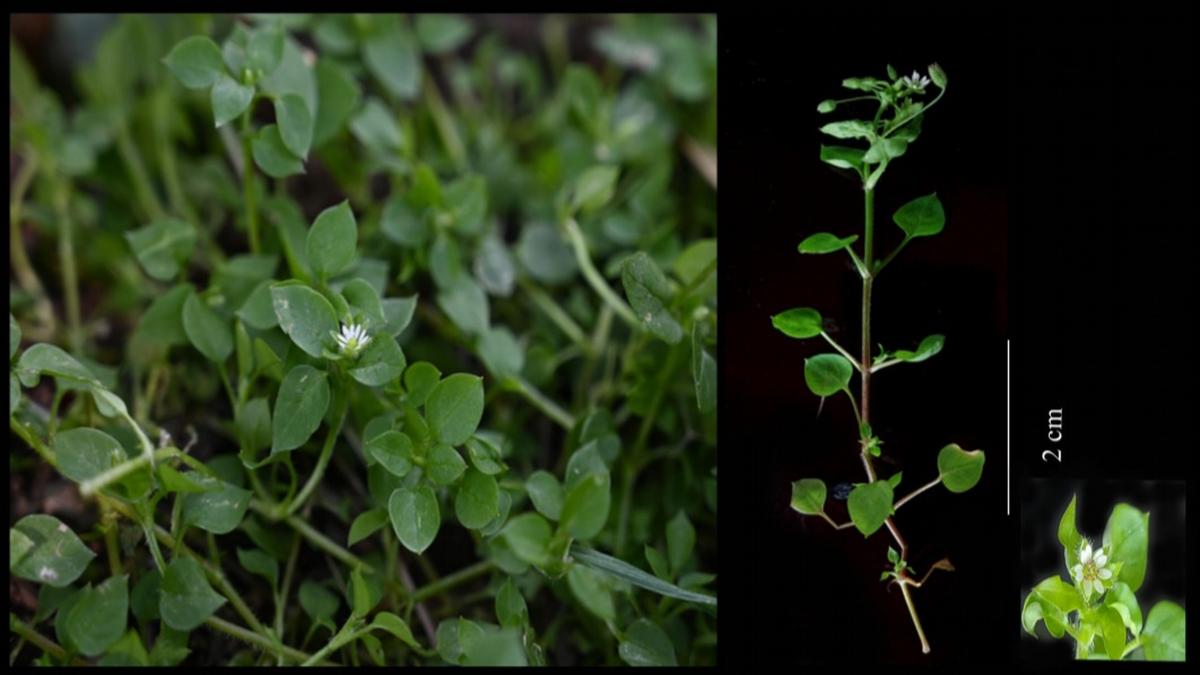
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
