GARBH-INi-DRISHTI

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
India has made a significant stride in biomedical research and public health with three major developments led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) in Faridabad, Haryana.
Key Highlights:
India’s First Ferret Research Facility
- Inaugurated by: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.
- Location: NCR Biotech Science Cluster, Faridabad.
- Purpose: To bolster India's capacity in:
- Vaccine development
- Therapeutic testing
- Research on emerging infectious diseases like influenza, COVID-19, and tuberculosis.
- Significance:
- Strengthens India’s pandemic preparedness.
- Positions India among the select nations with advanced biosafety labs using ferrets—ideal models due to respiratory systems similar to humans.
Launch of GARBH-INi-DRISHTI Data Repository
- Platform: DBT Data Repository and Information Sharing Hub under the GARBH-INi program.
- Dataset Size: Over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers.
- Developed by: THSTI with collaboration from top Indian research institutions and hospitals.
- Features:
- Comprehensive clinical data, medical images, and biospecimens.
- Secure, controlled access promoting ethical research.
- Facilitates predictive tools for preterm birth and maternal health complications.
- Utility:
- Empowers both national and global researchers.
- Informs maternal and neonatal health interventions.
- Supports evidence-based policymaking in public health.
- Program Genesis:
- GARBH-INi (2014): Interdisciplinary initiative to understand preterm birth risks—biological and non-biological.
- Part of: Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission under the UNaTI initiative.
Technology Transfer Agreement with Industry
- Agreement Between: THSTI and Sundyota Numandis Probioceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
- Technology Transferred:
- Lactobacillus crispatus, a genetically defined synthetic microbial consortium.
- Isolated from reproductive tracts of Indian women enrolled in GARBH-INi.
- Applications:
- Nutraceuticals and probiotics for reproductive health.
- Potential treatments for vaginal infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Significance:
- Promotes microbiome-based interventions.
- Bridges lab-to-market gap, boosting the biomanufacturing ecosystem.
Strategic Implications for India
- Scientific Diplomacy & Global Standing: With cutting-edge facilities and open data-sharing platforms, India emerges as a key player in global biomedical research.
- Public Health Impact: Supports targeted, data-driven maternal health policies and pandemic response frameworks.
- Innovation Ecosystem: Reflects the convergence of academic research, industry collaboration, and translational science.
World Wetlands Day 2025

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2nd February to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
India has been a signatory to the Convention since 1982 and has actively worked towards the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands—critical ecosystems that serve as biodiversity hotspots, natural flood buffers, and carbon sinks.
Theme 2025: "Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future"
The 2025 theme emphasizes collaborative efforts to protect wetlands to ensure ecological sustainability, biodiversity preservation, and long-term human well-being. It highlights the need for integrated management and foresight in conservation strategies.
Key Event: Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organized the national-level celebrations of World Wetlands Day 2025 at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site in Gonda district, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of the Site
- Comprises two rain-fed oxbow lakes—Parvati and Arga—located in the terai region of the Gangetic plains.
- Supports endangered and critically endangered species like the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and Egyptian vulture.
- Attracts migratory birds such as Eurasian coots, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards.
- Threatened by invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- The nearby Tikri Forest is being developed as an eco-tourism site, and a nature-culture tourism corridor is planned between Ayodhya and Devi Patan.
Cultural and Economic Value
- The area includes heritage sites such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, enhancing its potential as a religious and cultural tourism hub.
- A MoU between Amazon and ARGA (UP Government initiative) aims to empower women entrepreneurs through digital training and market access under Amazon’s Saheli programme.
India's Wetland Landscape and New Ramsar Sites (2025 Update)
India’s tally of Ramsar Sites has risen to 89, with four new additions:
- Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Theerthangal – Tamil Nadu
- Sakkarakottai – Tamil Nadu
- Khecheopalri – Sikkim (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar Sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
- Total area under Ramsar protection in India is now approximately 1.358 million hectares.
Amrit Dharohar Initiative
Launched in June 2023, the Amrit Dharohar initiative promotes conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar Sites over three years. It aligns with Budget 2023–24 announcements and focuses on:
- Species and Habitat Conservation
- Nature Tourism
- Wetlands-based Livelihoods
- Wetlands and Carbon Mitigation
The initiative encourages convergence among central ministries, state authorities, and community stakeholders.
Workshops and Public Engagement
A regional workshop for Northern States was organized on 1st February 2025, with participants from nine states and UTs, highlighting collaborative models in wetland management. The main event also included:
- Exhibitions on eco-friendly products, wetland conservation, and green skills.
- Launch of publications like the Integrated Management Plan for Parvati Arga, Factbook of India’s 85 Ramsar Sites, and Development of Van Taungya Villages.
- Felicitation of painting, quiz, and Nukkad Natak competition winners, promoting grassroots awareness.
Significance of Wetlands in India
Wetlands are water-covered ecosystems, either permanently or seasonally flooded. They:
- Support rich biodiversity, including migratory birds and aquatic species.
- Recharge groundwater and regulate floods.
- Provide livelihoods through fisheries and tourism.
- Act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate change mitigation.
Major Threats
- Pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
- Encroachment and urbanization
- Invasive species
PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 has accorded the highest-ever allocation of ?32,646 crore to the Ministry of Labour and Employment, representing an 80% increase over the previous year's Revised Estimates.
The enhanced funding reflects the government's strategic focus on employment generation and strengthening social security mechanisms for unorganised workers and gig economy participants.
Key Budgetary Highlights:
1. Employment Generation Scheme:
- ?20,000 crore has been allocated to the new Employment Generation Scheme, double the previous year’s allocation.
- The scheme is aimed at fostering large-scale employment opportunities and skilling across various sectors.
2. Employees’ Pension Scheme:
- Allocation increased by ?300 crore, strengthening retirement security for formal sector workers.
3. PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM):
- Allocation increased by 37% compared to last year.
- The scheme provides old-age social security to unorganised workers through a voluntary, contributory pension model.
About Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)
Objective:
To provide minimum assured pension and social security to unorganised sector workers, including street vendors, construction workers, agriculture laborers, domestic workers, etc.
Eligibility:
- Indian citizen aged 18–40 years
- Monthly income below ?15,000
- Not a member of EPFO, ESIC, or NPS
Key Features:
- Minimum Assured Pension: ?3,000 per month after 60 years of age.
- Voluntary and Contributory Scheme:
- Contributions made via auto-debit from bank accounts.
- 50:50 matching contribution by the Central Government.
- Pension Fund Management:
- Administered by the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Implemented by LIC and CSC e-Governance Services India Ltd.
- LIC acts as the Pension Fund Manager.
Family Pension Provision:
- In case of subscriber's death:
- Spouse receives 50% of the pension amount as family pension.
- If death occurs before 60 years, the spouse may continue contributions or exit the scheme as per norms.
Exit Provisions:
- Exit before 10 years: Subscriber's share with accrued interest is returned.
- Exit after 10 years but before 60 years: Entire contribution with interest returned to the subscriber.
Social Security for Gig Workers
Recognising the gig economy as a critical pillar of India’s modern workforce, the government has taken key steps to enhance their social security:
- e-Shram registration
- Provision of unique identity cards
- Access to healthcare benefits under PM Jan Arogya Yojana
- Expected to benefit around 1 crore gig workers
Iran’s Missile Advancements
- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant military development, Iran has successfully test-fired the Ghadr-380, an advanced anti-warship cruise missile with a range of 1,000 kilometers (600 miles).
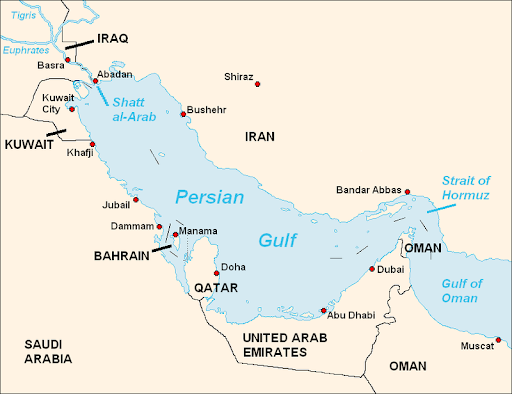
This capability allows it to target U.S. Navy warships deployed in critical maritime regions like the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman. The missile test was launched from an underground missile facility and was broadcast on Iranian state television, underscoring its strategic messaging.
Key Missiles Unveiled by Iran:
1. Ghadr-380 Cruise Missile:
- Type: Anti-warship cruise missile
- Range: Over 1,000 km
- Features:
- Anti-jamming capability
- Quick-launch readiness (operable by one person in less than 5 minutes)
- Launch Details:
- Fired from an underground missile base in central Iran
- Targeted the Sea of Oman
- Specific test timing and warhead specifications were not disclosed
2. Etemad Ballistic Missile:
- Name Meaning: Etemad means "trust" in Persian
- Type: Precision-guided ballistic missile
- Range: 1,700 km (1,056 miles)
- Specifications:
- Length: 16 meters
- Diameter: 1.25 meters
- Equipped with precision-guided warhead
- Built by: Iranian Ministry of Defence
Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles: Understanding the Distinction
Feature Ballistic Missile Cruise Missile
Propulsion Rocket-propelled at launch; unpowered descent Jet engine-powered throughout flight
Flight Path Arched trajectory (leaves and re-enters atmosphere) Straight, low-altitude flight within atmosphere
Detection Easier to track via radar once launched Difficult to detect due to low-altitude flight
Launch Platforms Ground-based, silo, mobile launchers Ground, air, or sea platforms
Warhead Capability Can carry conventional or nuclear warheads Usually conventional, but may carry nuclear in advanced forms
Iran’s Strategic Missile Doctrine
Underground Missile Facilities:
- Iran maintains extensive underground missile bases, especially in southern Iran near the Strait of Hormuz—a chokepoint for global oil trade.
- Such facilities enhance survivability and rapid response capabilities.
Missile Development Drivers:
- Iran's missile program evolved as a strategic deterrent post the Iran-Iraq War (1980–1988), where both countries used missiles to target civilian areas.
- UN arms embargoes led Iran to focus on domestic development of missile systems, including both cruise and ballistic types.
Capabilities:
- Iran now claims to possess missiles with ranges up to 2,000 kilometers, capable of reaching parts of the Middle East, including Israel.
- The Ghadr-380 and Etemad missiles are examples of technological diversification—from ballistic to precision cruise systems.
Implications for Regional and Global Security
- Deterrence Posture: Iran’s missile advancements strengthen its deterrence, especially amid strained relations with the U.S. and its allies.
- Threat to Maritime Security: The Ghadr-380, with its anti-warship focus, poses a direct threat to U.S. naval assets in the Persian Gulf and adjacent waters.
- Escalation Risks: Enhanced missile capabilities could escalate regional tensions, particularly in flashpoints like the Strait of Hormuz.
- Western Concerns: The U.S. and European nations remain wary of Iran’s dual-track approach involving missile and nuclear program developments.
Shubhanshu Shukla

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla of the Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to become the first Indian astronaut to travel to the International Space Station (ISS) on a private mission, marking a significant milestone in India’s space diplomacy and international collaboration in human spaceflight.
Mission Details:
- Mission Name: Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4)
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft
- Launch Site: Kennedy Space Center, Florida, USA
- Tentative Timeline: Spring 2025
- Duration on ISS: Up to 14 days
- Mission Objectives: Conduct scientific experiments, educational outreach, and commercial activities, in collaboration with NASA and ISRO.
International Collaboration:
- The mission includes astronauts from India, Poland, and Hungary—the first such trilateral collaboration in over four decades.
- Marks the return of human spaceflight for Poland and Hungary after a hiatus of more than 40 years.
- Demonstrates Axiom Space’s emerging role in redefining access to low-Earth orbit and supporting national space programs through private missions.
About Shubhanshu Shukla:
- Born: October 10, 1985, in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- Commissioned into IAF: June 2006, Fighter Wing
- Promoted to Group Captain: March 2024
- Current Role: Astronaut-designate for India’s Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission
- Flight Experience: Over 2,000 hours across multiple aircraft including Su-30 MKI, MiG-21, MiG-29, Jaguar, Hawk, Dornier, and An-32
- Astronaut Training: Trained at Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center, Star City, Moscow (1-year program)
Historical Context:
- Rakesh Sharma remains the first Indian to travel to space (1984) aboard Soviet Soyuz T-11, under the Interkosmos program.
- Shukla’s upcoming mission marks a new era of Indian participation in international human space missions, particularly through private partnerships.
