FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE (FATF) (Business Standard)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body that sets anti-money laundering standards, has removed the offshore tax haven Cayman Islands from its ‘grey list’.
Facts About:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1989 as part of the G7's effort to develop laws to combat money laundering.
- Its directive was extended to cover financing of terrorism in 2001.
- Only a few nations are listed in the grey and black lists that the FATF releases.
- To monitor the country's progress in combating money laundering and terrorism financing, a grey list is established.
- Non-cooperative nations are included on a blacklist in an effort to combat money laundering and financing of terrorism.
About the Cayman Islands:
- The Cayman Islands are situated in the Western Caribbean Sea and are a British Overseas Territory.
- Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman are the three islands that make up the territory; they are situated northwest of Jamaica and south of Cuba.
- Its topography is low-lying, with coral reefs.
- Economy: The islands are a thriving offshore financial hub, with a mixed economic system.
ARALAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, individuals suspected to be associated with Maoist groups allegedly engaged in a gunfire exchange with Forest Department watchers in the Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary located in Kannur, Kerala.
Facts About:
- It's situated on the Western Ghats' western slopes.
- Founded in 1984, it is the northernmost wildlife sanctuary in Kerala.
- It shares borders with Wayanad-Brahmagiri, the northern slopes of Wayanad, and the Karnataka State Protected Areas, which include the Coorg forests and the Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Katti Betta is the sanctuary's highest peak.
- In terms of vegetation, West Coast semievergreen forests and tropical evergreen forests predominate here.
It is the only protected area of the West Coast Tropical Evergreen Forest of Dipterocarpus-Mesua- Palaquium type.
- This wildlife sanctuary is traversed by the Cheenkani River.
- Flora: Cinnamomum Zeylanicum, Hopea parviflora, Largestroemia lanceolata, Xyliaxylocarpa, Mallotus, and Philippinensis are common trees in the semievergreen regions.
- Fauna: Bison, deer, boar, and elephants are fairly common. Here, one can see leopards, jungle cats, and a variety of squirrel species.
CRAB PLOVER (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, for the first time, breeding nests of crab plovers were spotted at Great Vedaranyam Swamp near Point Calimere, Tamil Nadu.
Facts About:
The Crab-Plover is a distinctive bird found along the coasts of the Indian Ocean.
- It stands out with its long legs and striking black-and-white colouration.
This bird belongs to the plover family and is closely related to other shorebird species.
Unlike most shorebirds, the Crab-Plover lays white eggs.
- Their chicks stay inside burrows until they are ready to fledge, which sets them apart from other shorebirds.
Distribution: They can spotted in various places around the Indian Ocean, as they are residents in these regions.
- They breed in places like the Arabian Sea in Pakistan, the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, Somalia, the Andaman Islands, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, and Madagascar.
Habitat: Crab Plovers make their homes in a variety of coastal environments, including sandy coastlines, mudflats, estuaries, lagoons, exposed coral reefs, and rocky shorelines. During the breeding season, they can also be found in sand dunes.
Conservation Status: The Crab-Plover is categorized as 'Least Concern' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Additionally, it falls under the protection of the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA).
CARBON NANOFLORETS (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Carbon nanoflorets made by IIT Bombay researchers can convert incident sunlight to heat with 87% efficiency.
Facts About:
Carbon nanoflorets (NCFs) are a newly discovered type of carbon nanostructure that resembles tiny marigold flowers.
- They are made up of a network of carbon nanotubes arranged in a conical microcavity structure. NCFs have a number of unusual properties, including:
Broadband absorption: NCFs can absorb sunlight at all wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared.
- This is because their conical microcavity structure traps light for a longer period of time, allowing it to be absorbed by the carbon nanotubes.
- They are also extremely black, absorbing more than 95% of sunlight across a broad spectrum of wavelengths.
High light-heat conversion efficiency: NCFs can convert sunlight to heat with an efficiency of up to 87%.
- This is much higher than the efficiency of other solar-thermal materials, such as photovoltaic cells.
Low thermal conductivity: NCFs have a very low thermal conductivity, which means that they can efficiently convert sunlight to heat without losing much of the energy to conduction.
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) reported that NCFs could convert incident sunlight to heat with an efficiency of 87%.
- This is significantly higher than the efficiency of other solar thermal materials, such as black carbon.
- It effectively absorbs over 97 per cent of sunlight's ultraviolet, visible, and infrared components, converting them into thermal energy.
- The resulting heat can be efficiently transferred to either air or water for practical applications.
- Research reveals that NCFs can raise the temperature of the surrounding air from room temperature to 60 degrees Celsius, providing smoke-free space-heating solutions.
AGARTALA-AKHAURA RAIL LINK PROJECT (Indian Express)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Bangladesh counterpart Sheikh Hasina will jointly inaugurate the Agartala-Akhaura cross-border rail link project on Wednesday.
Facts About:
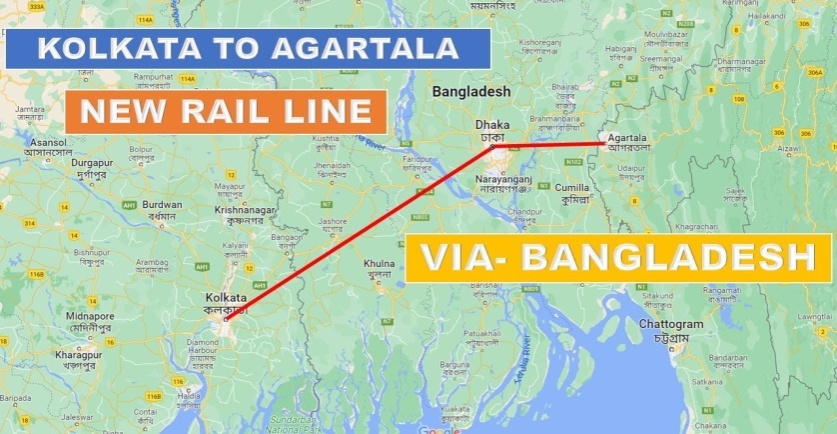
- The rail line between Agartala in Tripura and Akhaura in Bangladesh would pave the way for the first train to run from the northeastern region of India to Bangladesh.
- The project is significant from an international as well as from a domestic point of view.
- At present, the rail route from Agartala to Kolkata is around 1600 kilometres and takes about 38 hours.
- The footfall of passengers from Agartala to Kolkata is significantly very high due to the linguistic similarity between the two states.
Both states also share age-old cultural and business relations and Agartala depends on Kolkata from the medical tourism point of view as well.
- Upon operationalisation of the Agartala-Akhaura Rail link project the distance will be reduced by around 500 kilometres and the travel time will be 16 hours between Agartala and Kolkata.
- In addition, this rail link will also provide direct access between landlocked northeastern India and the Chittagong port of Bangladesh.
- The Ministry for Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) has funded the railway line from Agartala to Nischintpur;
whereas the Ministry of External Affairs has funded the rail line from Nischintpur to Gangasagar which is in Bangladesh.
- The project is part of India's 'Act East Policy', which aims to promote economic cooperation and develop strategic ties with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
