‘Deep tech’ policy to be sent to Cabinet for approval, says scientific adviser (The Hindu)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government will be sending a note, on a new ‘deep tech’ policy for India in the coming weeks to the Union Cabinet for approval, said Prof. Ajay Kumar Sood, Principal Scientific Advisor at a public event on January 5.
Key Details in the Draft NDTSP:
- The Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) stands out through its key highlights, enhancing the existing Startup India policies by fostering an environment conducive to the growth of deep tech startups.
- It addresses the unique challenges these startups face.
- The draft NDTSP introduces new policy instruments and recommends essential policy changes under several themes, including nurturing research, development, and innovation, strengthening the intellectual property regime, facilitating access to funding, enabling shared infrastructure and resource sharing, creating supportive regulations, standards, and certifications, attracting human resources, initiating capacity building, promoting procurement and adoption, ensuring policy and program interlinkages, and sustaining deep tech startups.
India's 'Deep Tech' Startup Ecosystem faces significant challenges as outlined in the draft 'deep tech' policy:
- As of May 2023, the DPIIT recognizes 10,298 startups, but only about 10% fall under the 'deep tech' category, indicating a need for more effort and support.
- A major hurdle is the inadequate funding for 'deep tech' startups. Unlike fintech or retail software startups that require comparatively smaller funds, 'deep tech' startups demand significantly larger financial investments.
- This financial gap poses a notable obstacle to their growth and development.
What is Deep Tech?
- Deep technology, often referred to as "deep tech," encompasses advanced technologies rooted in substantial scientific or engineering innovations.
- These innovations are considered "deep" due to their sophisticated and highly advanced nature, providing solutions to complex challenges or issues.
- Examples of breakthroughs in deep tech include genomics, robotics, nanotechnology, and clean energy initiatives emerging from research labs and academia.
- Deep-tech startups and companies are characterized by their pursuit of solutions to intricate problems through technologies and processes involving lengthy research and development cycles.
- Importantly, businesses and startups that rely on easily replicable ideas do not qualify as deep tech startups.
- Deep tech stands apart from high tech, which denotes a broader scope of technical innovations and advancements.
- Unlike high-tech companies, those in deep tech are primarily focused on profound scientific or engineering breakthroughs.
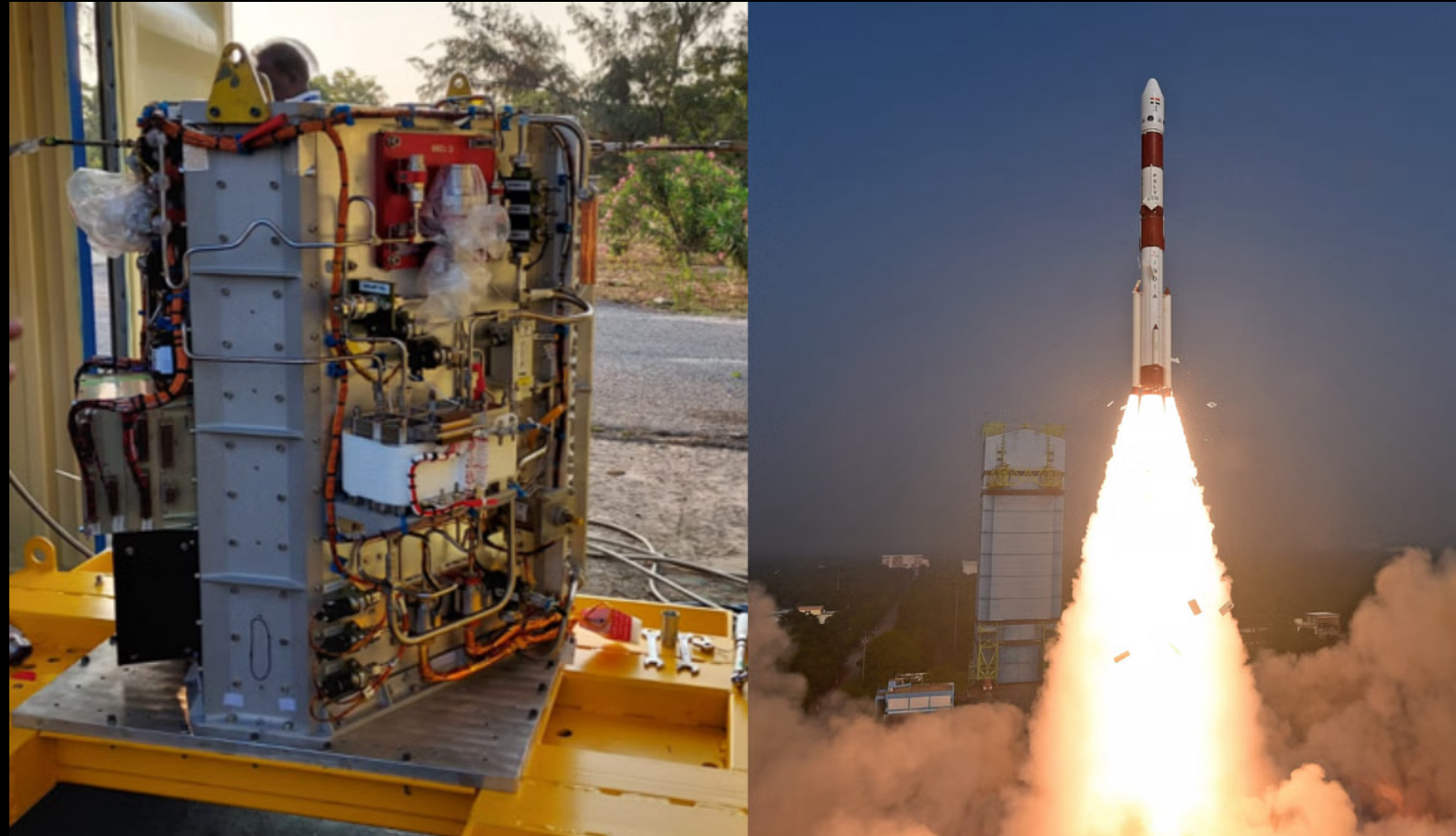
Isro’s futuristic fuel cell system could power space station (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, a futuristic fuel cell-based power system was successfully tested by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to provide a sustainable and reliable power source for space stations.
What is a Fuel Cell?
- Fuel cells, intricate devices powered by chemical reactions, have diverse applications spanning transportation, industrial sectors, commercial and residential buildings, and reversible grid energy storage systems.
- Operationally, fuel cells consist of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte.
- The anode, supplied with hydrogen fuel, undergoes oxidation to produce hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Simultaneously, the cathode, exposed to an oxidizer like oxygen, results in the production of water as hydrogen ions absorb electrons.
- The voltage per unit cell is determined by the energy level disparity at the electrodes. While a single fuel cell generates a modest amount of direct-current electricity, practical use often involves assembling stacks of these cells.
- Advantages: Advantages of fuel cells include lower or zero emissions, particularly with hydrogen fuel cells emitting only water, addressing climate concerns by avoiding carbon dioxide emissions.
- They operate quietly with few moving parts, achieve higher efficiencies compared to combustion engines, and resemble batteries but offer prolonged electrical energy due to continuous external fuel and air/oxygen sources.
- This longevity distinguishes them from batteries that rely on finite fuel material and oxidant, making fuel cells a sustainable and efficient choice for various applications.
About ISRO:
- The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the pioneer space exploration agency of the Government of India, headquartered at Bengaluru.
- ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development, while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research.
- ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, considered amongst the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
BRO Implements Indigenous Technology for Road Construction Near China Border in Arunachal Pradesh (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
In order to improve operational capacity of the defence forces in the high-altitude areas along the Indo-China border in Arunachal Pradesh, the BRO will build bituminous roads using an indigenous technology, “Rejupave” developed by India’s oldest and premier road research organisation, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI).
What is Rejupave Technology?
- CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), India's oldest road research organization, developed the Rejupave Technology.
- It is beneficial for constructing high-altitude bituminous roads in low and sub-zero temperatures.
- The technology actively reduces production and rolling temperatures of bituminous mixes by 30 to 400 degrees Celsius, ensuring minimal heat loss during transit in snowy conditions and long haulage times.
- The bio-oil-based asphalt modifier of this technology significantly lowers the heating requirements of bituminous mixes and preserves mix temperature during transit.
- In cold climatic regions, the 'Rejupave' asphalt modifier enhances long-term durability and resistance to thermal cracking under low-temperature conditions.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the eco-sensitive mountainous environment of Arunachal Pradesh.
About CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI):
- Established in 1952, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) stands as a premier national laboratory under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CRRI's major research and development programs encompass a range of projects, including the design, construction, and maintenance of roads and runways, traffic and transportation planning for large and medium cities, management of roads in diverse terrains, improvement of marginal materials, utilization of industrial waste in road construction, and landslide control.
- The institute extends its expertise by providing technical and consultancy services to various organizations both within India and internationally.
- CRRI actively contributes to capacity building in highway engineering, empowering human resources to undertake and execute road and runway projects.
High-frequency waves detected in the Martian Upper Atmosphere could help understand plasma processes over Mars (PIB)
- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, scientists have detected the existence of high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian Upper Atmosphere with novel narrowband and broadband features that can help to understand plasma processes in the Martian plasma environment.
What are Plasma Waves?
- Plasma waves, commonly observed in Earth's magnetosphere, denote short-time scale fluctuations in electric and magnetic fields.
- These waves play a crucial role in energizing and transporting charged particles within Earth's magnetosphere.
- Specific plasma waves, like electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves, serve as a safeguard, cleansing Earth's radiation belt, known to pose threats to satellites.
- Researchers, intrigued by this phenomenon, seek to understand the presence of diverse plasma waves around planets without intrinsic magnetic fields, such as Mars.
Key Observations:
- Scientists utilized high-resolution electric field data from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) spacecraft to examine high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian environment.
- These waves manifest as either parallel-propagating electron oscillations (Langmuir waves) or perpendicular-propagating electron oscillations (upper-hybrid type waves) in Mars' magneto sheath region.
- Two distinct wave modes, below and above the electron plasma frequency, were observed in the Martian magnetosphere.
- Broadband and narrowband waves exhibited identifiable features in the frequency domain, with broadband waves displaying periodic patchy structures at intervals of 8–14 milliseconds.
Significance:
- The presence of these waves offers a valuable tool to investigate how electrons gain or dissipate energy within the Martian plasma environment.
Cabinet clears PRITHVI initiative for ease of research in earth sciences (Indian Express)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government Friday approved an initiative that will give it the flexibility to pursue research and use funds allocated to five different sub-schemes related to earth sciences over a five-year period.
About the PRITHVI Scheme:
- The PRITHVI Scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) designed to deepen our understanding of the Earth and its essential indicators.
- With a substantial allocation of Rs 4,797 crore spanning 2021-26, this comprehensive initiative aims to significantly advance research, modeling, and service delivery in critical domains like weather, climate, oceans, and polar regions.
- The scheme amalgamates five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Collectively, these programs strive to deepen our comprehension of Earth's vital signs and translate scientific knowledge into practical services for the benefit of society, the environment, and the economy.
Objectives:
- A primary aim of PRITHVI is to enhance and sustain long-term observations across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- This facilitates the recording and monitoring of vital signs and changes within the Earth System.
- The scheme places emphasis on developing predictive models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards while advancing our understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring polar regions and high seas is a significant aspect, targeting the discovery of new phenomena and resources.
- The scheme underscores the development of technology for exploring and sustainably harnessing oceanic resources for societal applications.
Implementation:
- Various components of the PRITHVI scheme are interdependent, executed in an integrated manner through the collective efforts of the institutes under the MoES.
