Chimaeras (The Hindu)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a recent landmark study, scientists reported successfully generating a live chimaera in non-human primates
About Chimaeras:
- A genetic chimaera is a single organism made up of cells from more than one distinct genotype (or genetic makeup).
- Examples of varying degrees of chimerism exist in the animal kingdom.
- For instance, the half-sider budgerigar, a common pet parakeet, displays different colors on each side of its body due to chimerism.
- In anglerfish, the male fuses with the female, eventually being absorbed, creating a single animal with a merged genetic makeup.
- Marine sponges are known to have up to four distinct genotypes in one organism.
- In humans, natural chimaeras occur when the genetic material in one cell changes, leading to a clonal population of cells different from the rest.
- Fusion of two fertilized zygotes early in embryonic development can result in a condition where two genetic makeups coexist in a single individual.
- Chimerism can also arise from twin or multiple pregnancies evolving into a single fetus or a twin fetus being absorbed into a singleton.
Hard Currency (Financial Express)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) said in a statement that Conditions are not ripe to make INR a hard currency.
What is Hard Currency?
- Usually, developed countries issue hard currency, and this currency is easier to trade and receive funds from other countries or investors from other nations.
Key characteristics of hard currencies:
- Hard currency means a stable currency, and its value does not fluctuate much in the international markets.
- It makes hard money currency easily tradable.
- It is issued by a sound economy. Developed countries issue hard currency and it is accepted by all nations across the world.
- It is highly liquid and several countries prefer to accept hard currency instead of local currency as it has lesser fluctuations and can be easily converted to local currency.
- Hard currency is universally accepted and international investors have a sense of faith in hard currency for trading.
- Countries across the globe consider hard currency as a foreign currency reserve, further adding to its value.
- As hard currency is easily convertible and stable, it is widely used in international exchanges.
- The value of the hard currency does not change much in response to global events.
- When domestic currencies struggle, people start holding on to hard currencies to protect their wealth.
Examples of hard currencies:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF) etc.
The E Prime Layer (HT)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
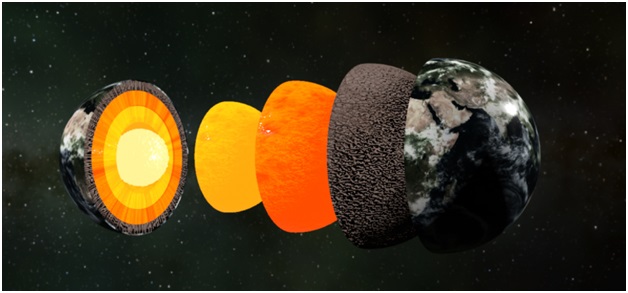
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
What is ROV ‘Daksh’? (HT)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Defence Research Development Organisation's robotics team utilized the Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Daksh to aid in the ongoing rescue operations during the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse.
What is ROV Daksh?
- Daksh is a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), designed by the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) for the recovery of unexploded bombs.
- It can negotiate various hurdles in an urban setting and can also be utilised to survey and monitor nuclear and chemical contamination levels.
- 90% of its components are indigenous.
- It has ladder climbing abilities and can function for three continuous hours, with the capability to operate over distances exceeding 100 to 500 meters.
- It serves the bomb disposal units (BDU) of an army, police, and paramilitary forces, aiding in handling IEDs and other dangerous substances.
- Its manipulator arm can handle hazardous objects weighing up to 20kg from 2.5 meters and 9kg from 4 meters away.
- Daksh demonstrates the ability to climb stairs and maneuver steep slopes, with durable rubber wheels capable of withstanding blast impacts.
- It is equipped with multiple cameras, IED handling tools, nuclear biological chemical (NBC) reconnaissance systems, a master control station (MCS), and a shotgun.
- The equipment is specifically designed for use on a motorized pan-tilt platform, which can help reach the risky terrain.
Atmospheric Waves Experiment (Indian Express)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
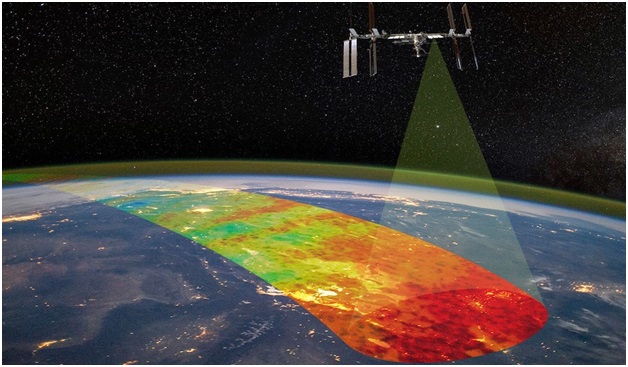
Atmospheric Waves Experiment is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and space weather.
What is the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE)?
- AWE is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and Space weather.
- Planned under NASA’s Heliophysics Explorers Program, the $42 million mission will study the links between how waves in the lower layers of the atmosphere impact the upper atmosphere, and thus, Space weather.
- AWE will be launched and mounted on the exterior of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
- From the vantage point, it will look down at the Earth and record the colourful light bands, commonly known as airglow.
- It will try to understand the combination of forces that drive the Space weather in the upper atmosphere.
- “AWE could open a new window of study, wherein scientists are attempting to understand if Space weather is affected by terrestrial and bottom-up forces.
- It will measure the airglow at mesopause (about 85 to 87 km above the Earth’s surface), where the atmospheric temperatures dip to minus 100 degrees Celsius.
- At this altitude, it is possible to capture the faint airglow in the infrared bandwidth, which appears the brightest enabling easy detection.
- AWE will be able to resolve waves at finer horizontal scales than what satellites can usually see at those altitudes, which is part of what makes the mission unique.
- The health of the ionosphere, whose lower layers sit at the edge of Space, is important for maintaining seamless communication.
- It is still not fully understood if the ionosphere is affected by the transient events or intense perturbations resulting from hurricanes or tornadoes.
- It was expected to launch in the month of August 2022, but the fresh launch is planned for later this month.
